Method for diagnosing pregnancy in ruminant
A ruminant and cell technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, biological testing, etc., can solve the problems of unreliable judgment results, fluctuations in gene expression, etc., to achieve pregnancy rate, The effect of shortening the interval between births
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1. Interference in extrauterine tissues (cervical canal and ectopic os) of pregnant and non-pregnant cattle Expression analysis of hormone-inducible factors
[0067] 1) Collection of mucous membrane
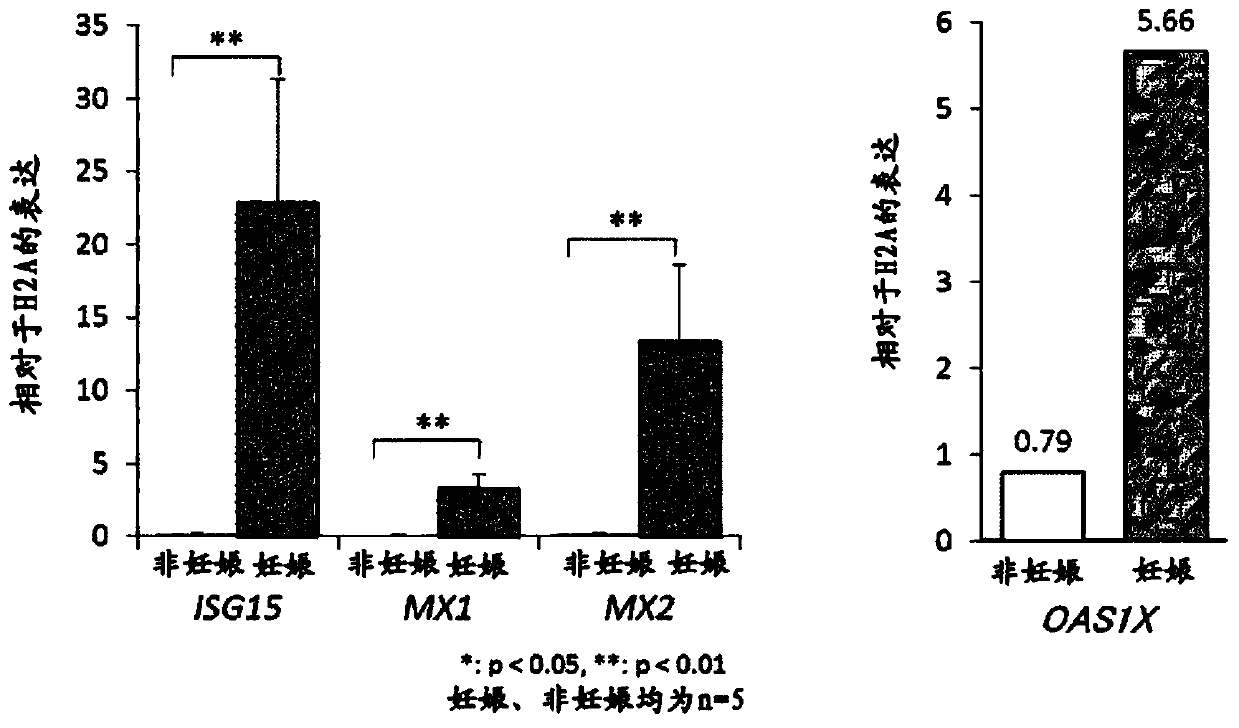
[0068] Among the milking cows of the Holstein breed raised at the Dairy Product Production Research Facility of the Bioproduction Research Farm of the Northern Biosphere Field Science Center, Hokkaido University, 18 days after artificial insemination were selected, the pregnancy was confirmed through the subsequent pregnancy test. For domestic cattle and cattle that have not been artificially inseminated, wipe the vulva with an inverse soap solution. Open the vestibule of the vagina directly or using a colposcope, insert a commercially available measuring spoon, and scrape and collect the mucous membranes from the endocervical canal and the periphery of the ectopic os. It was confirmed by visual observation of the collected sample that blood was mixed, and b...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2. Extrauterine tissues of pregnant and non-pregnant cattle (cervical canal, peripheral portion of the uterine ostium, and prevaginal Expression analysis of interferon-inducible factors in
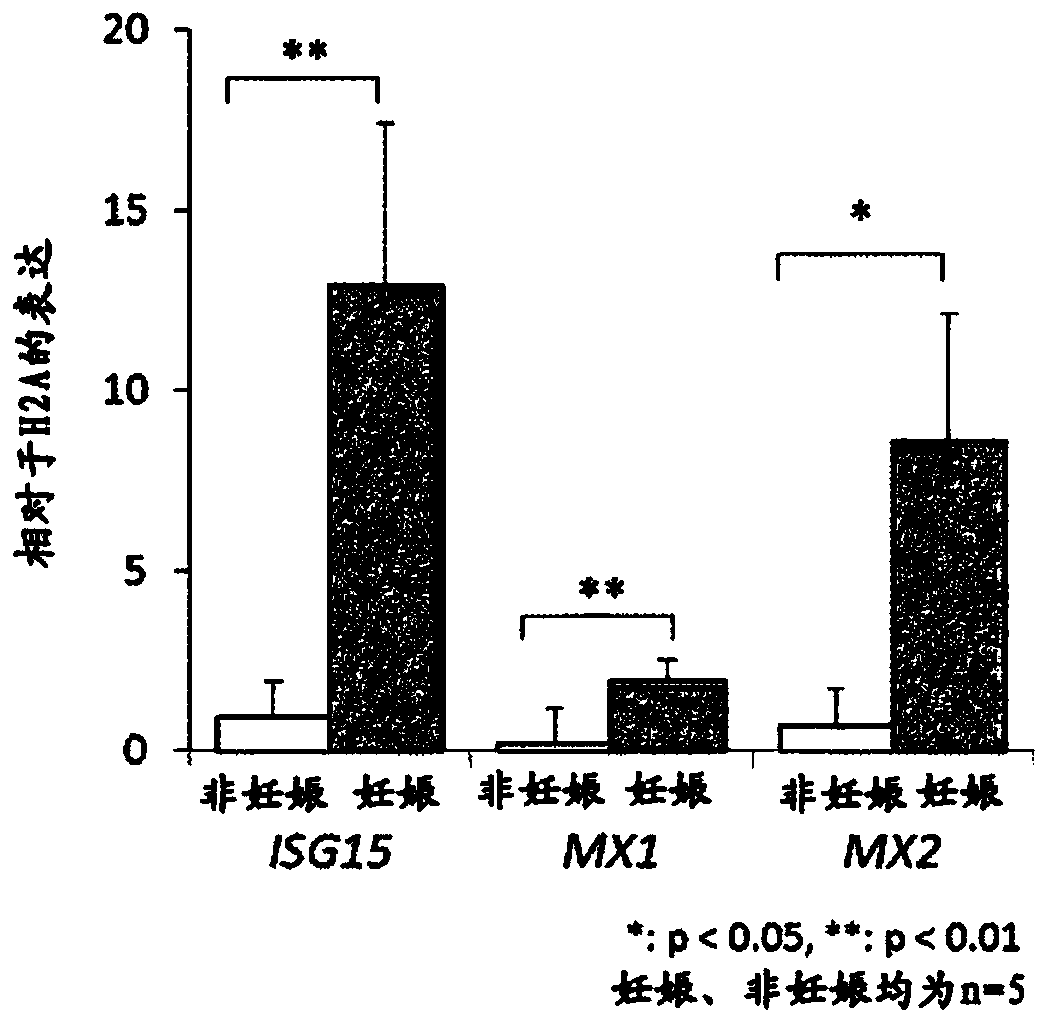
[0080] Except for using a cotton swab instead of a measuring spoon as a collection tool, proceed in the same manner as in Example 1, and collect samples from the endocervical canal, the peripheral part of the uterine ostium, and the vaginal vestibule of pregnant cows, and from the endocervical canal of non-pregnant cows. mucous membranes. The collected cotton swabs were soaked in 500 μL of ISOGEN II (Nippon Gene) and ice-cooled 1.5mL tubes, and the cells in the mucosa were recovered, and the total RNA was extracted in the same manner as in Example 1. cDNA synthesis and real-time PCR by transcription reaction.
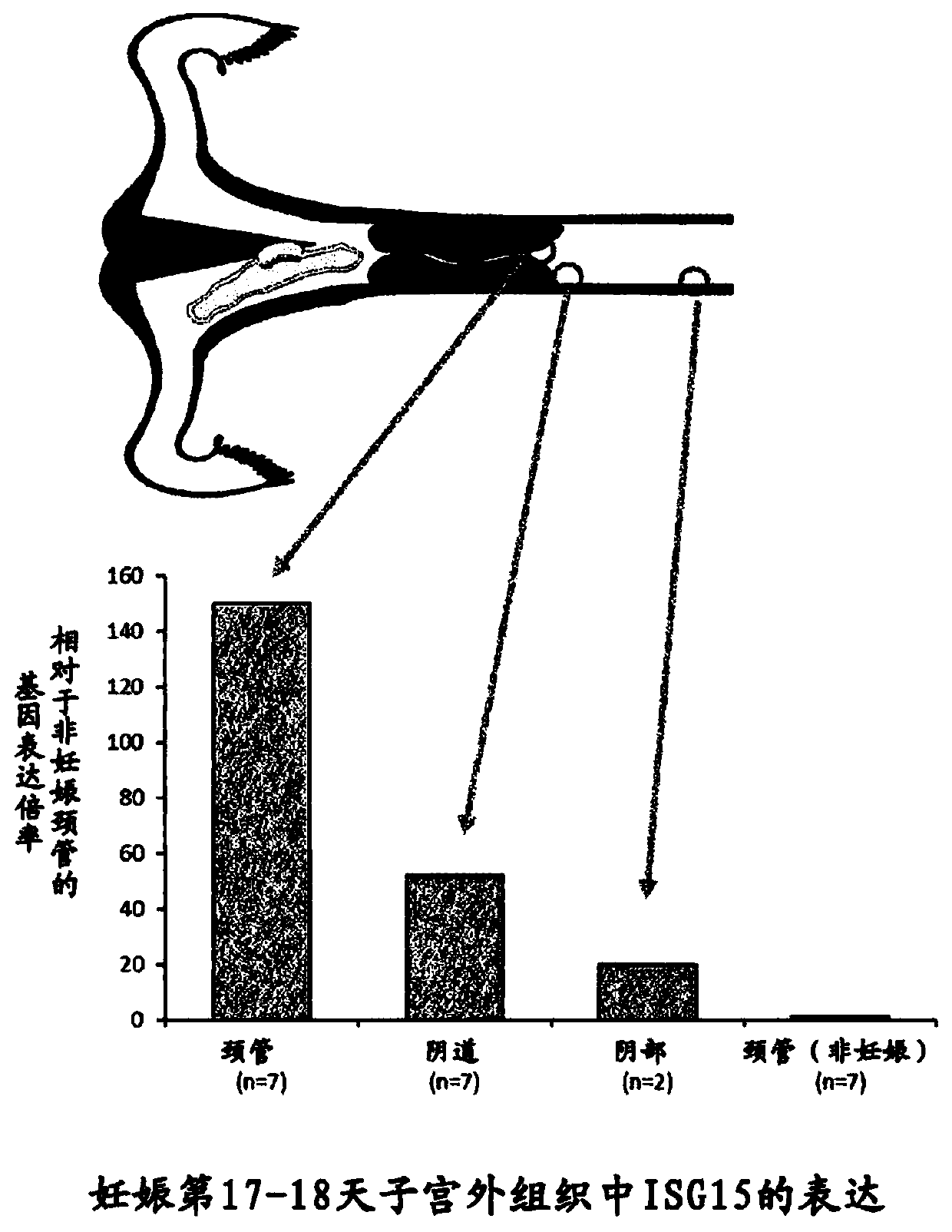
[0081] The results of the relative gene expression level of ISG15 are shown in image 3 . The expression of ISG15 was observed in the mucous membranes of the c...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Example 3. Extrauterine tissue (cervical canal) of pregnant and non-pregnant cows by quantitative RTLAMP method Expression analysis of interferon-inducible factors in
[0083] For the RNA samples from the cervical canal mucosa of pregnant cows and non-pregnant cows collected and prepared by the same method as 1) and 2) of Example 1, the total RNA amount was adjusted to 100ng respectively and then DNase treatment was carried out. DNA digestion. Use 100 ng of RNA samples from pregnant cattle and non-pregnant cattle cervical canal mucosa treated with DNase, 100 ng of RNA samples from pregnant cattle and non-pregnant cattle cervical canal mucosa without DNase treatment, and 100 ng of RNA samples from non-pregnant cattle without DNase treatment. The RNA sample 1000ng of pregnant bovine cervical canal mucosa was directly subjected to RTLAMP reaction.
[0084] The reaction conditions are as follows. Add 2.9 μl of sterilized distilled water, 12.5 μl of reaction solution, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com