Methods for high-resolution microbiome analysis
A microbial and biological technology, applied in the fields of genomics and metagenomics, which can solve problems such as insufficient discrimination ability and inability to distinguish closely related species and strains with high sequence similarity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
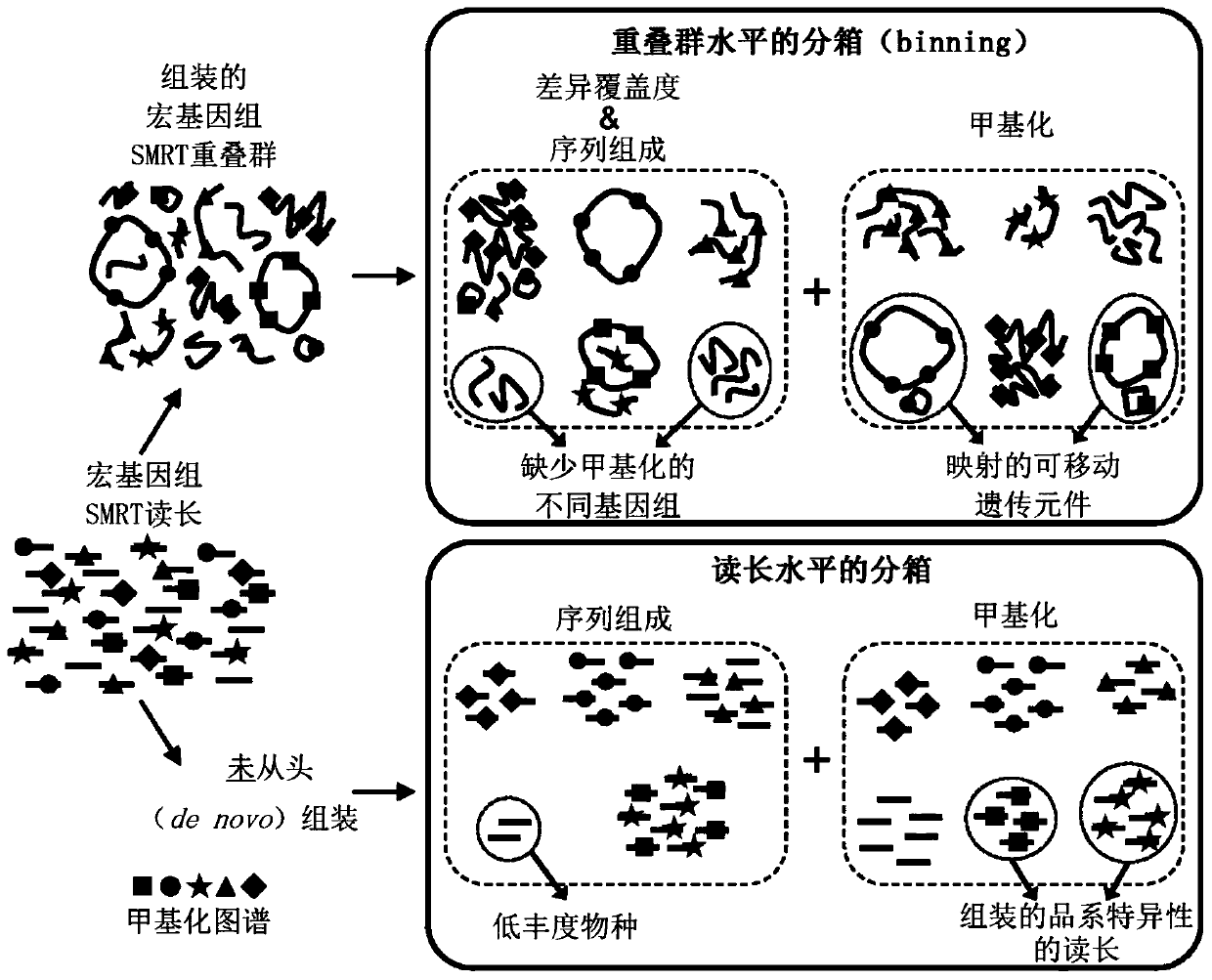
[0248] Example 1: Integrating methylation and composition to bin contigs by lineage
[0249] Epigenetic information was used to isolate contigs assembled from highly similar lines that were indistinguishable using k-mer frequency-based methods. examined the gut microbiota of two groups of children obtained from stool samples from children selected for sequencing based on their high genetic risk of developing T1D.
[0250] Interestingly, it has been observed that the relative abundance of a specific species of Bacteroides that typically dominates the composition of the two samples (i.e., Bacteroides dorsii) is often elevated prior to the onset of T1D in children, making it an Important species for understanding and monitoring. 16S sequencing showed that both samples contained two different strains of Bacteroides multellii: sample A consisted of 63.7% B. dorei) strain 439 (CP008741). Despite the high sequence similarity between the two Bacteroidetes strains (Table 18), each s...
Embodiment 2
[0258] Example 2: Methylome analysis of highly pathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae strains
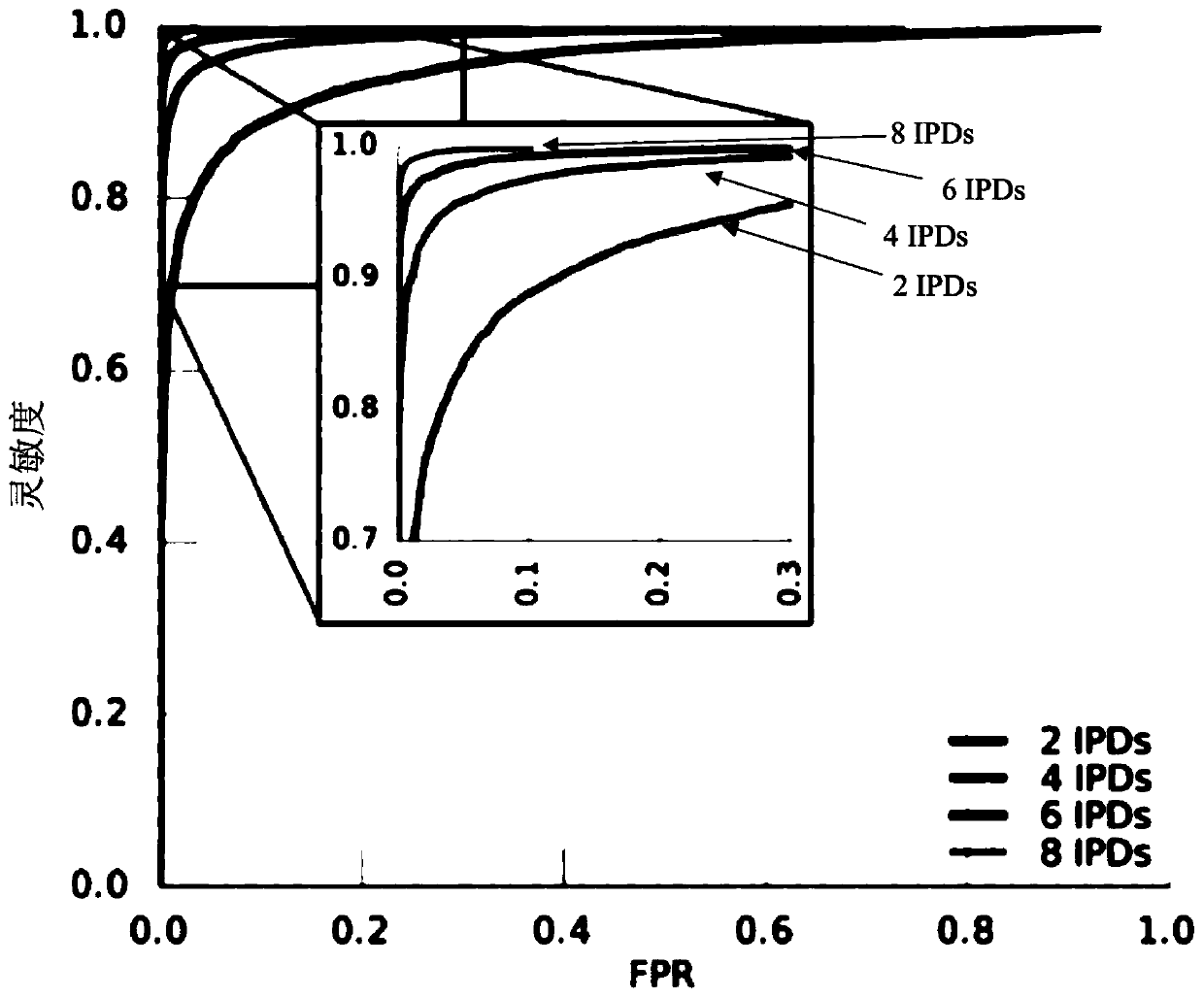
[0259] To assess methylome diversity among strains of clinically relevant bacterial species, 878 bacterial lines in the BASET database with methylation motifs identified by SMRT sequencing were analyzed. These included a highly pathogenic and antibiotic-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strain (strain 234-12) isolated from patients during the 2011 outbreak in Germany. A single 362 kb plasmid (pKpn23412-362) carried by this line contains 13 genes for antibiotic resistance, including the blaCTX-M-15 (Kpn23412_5431) gene responsible for conferring the extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) phenotype on bacteria. Plasmids also contain multiple replicons, which help to expand the range of organisms in which plasmids can successfully replicate.
[0260] The sequence composition profiles of this plasmid and the K. pneumoniae chromosome differ to an extent (Euclidean distance, d = 10.6), which wo...
Embodiment 3
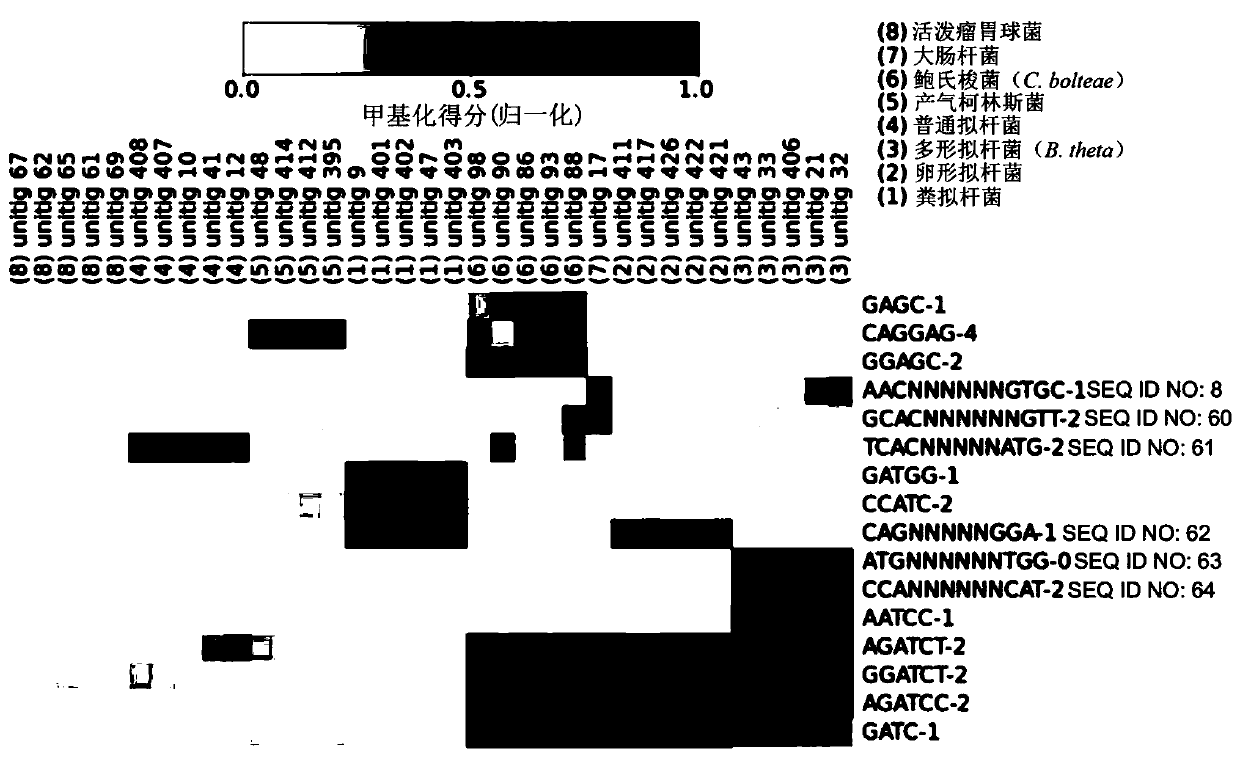
[0261] Example 3: Culture conditions and purification of bacteria from a mixture of eight species
[0262] Bacteroides caccae ATCC 43185, Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482, Bacteroides vulgatus ATCC 8492, Collinsella aerofaciens ) ATCC25986, Clostridium boltae ATCC BAA-613 and Ruminococcus gnavus ATCC 29149 were each cultured in 10 ml of supplemented brain heart infusion in an anaerobic chamber from Coy Laboratory Products. Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) MG1655 was cultured aerobically in 5ml LB broth. A 10 kb DNA library for SMRT sequencing was constructed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com