Film bulk acoustic resonator and preparation method thereof
A thin-film bulk acoustic wave and resonator technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, impedance networks, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in consistent etching rates and bulges, and achieve the effect of solving differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
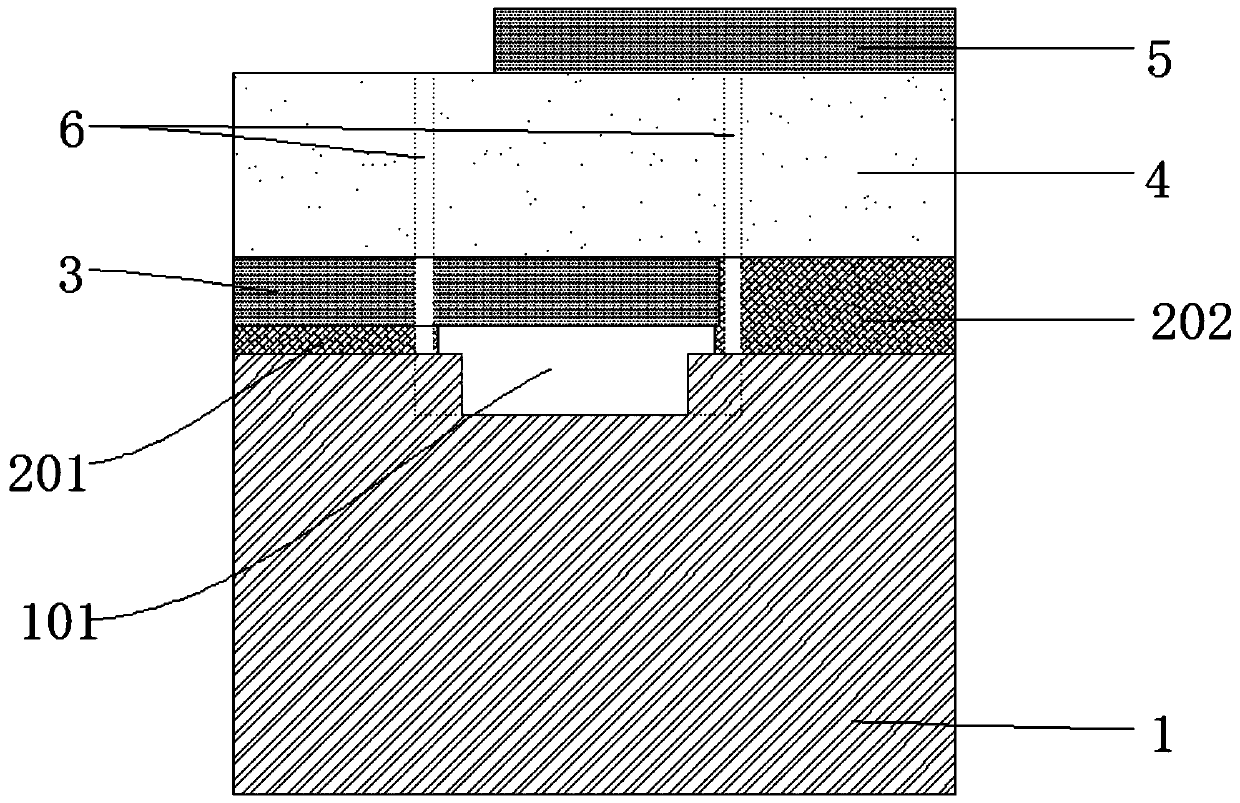
[0056] Such as Figure 1~3 As shown, a thin film bulk acoustic resonator includes a substrate, and the substrate is set as a silicon substrate, that is, a silicon wafer 1, wherein the silicon adopts high-resistance silicon with a resistivity greater than 10000Ω to avoid substrate coupling Part of the energy affects the insertion loss and signal.
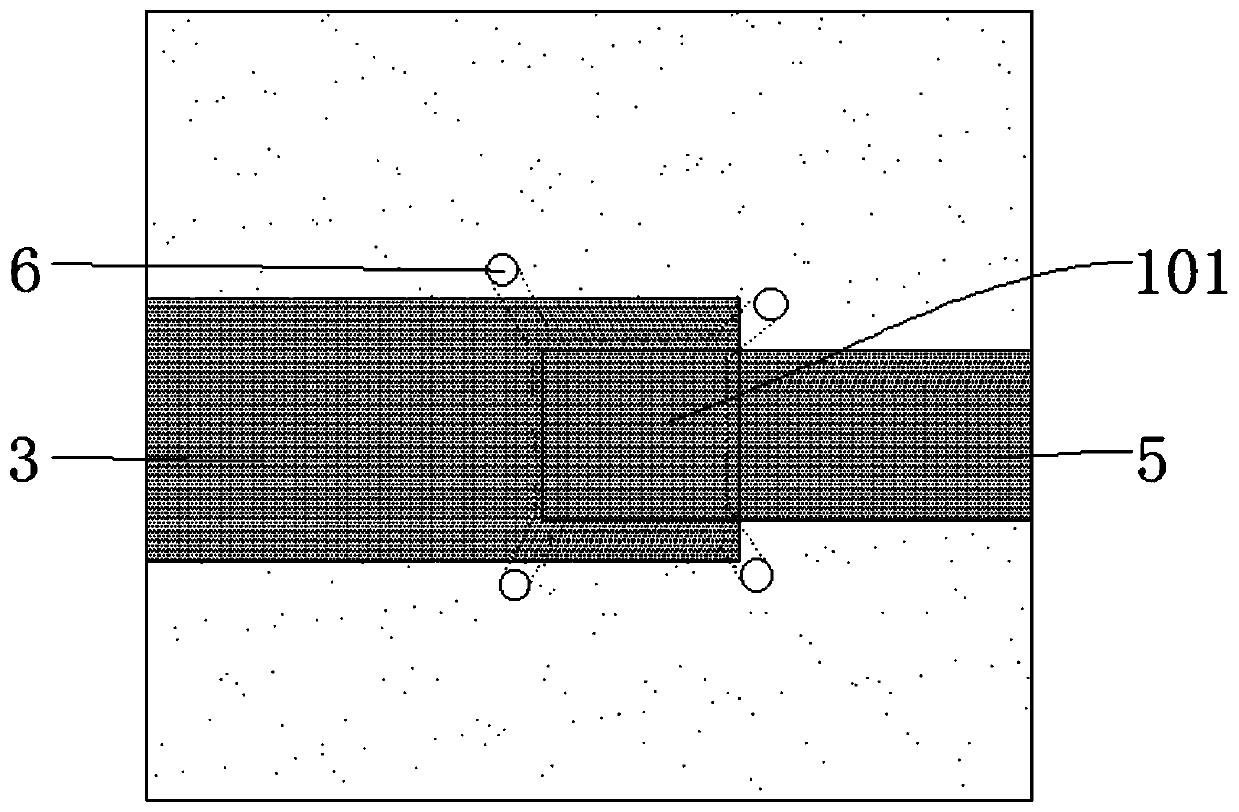
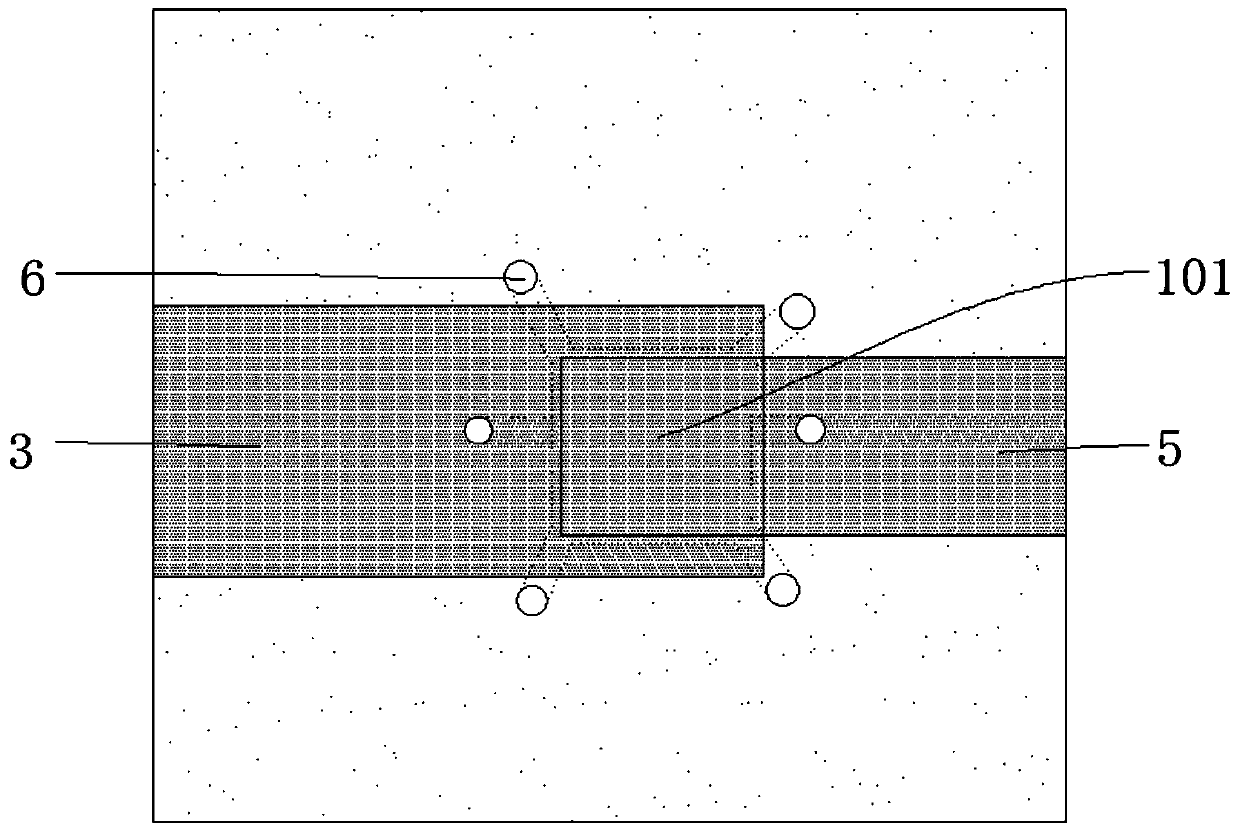
[0057]And a cavity 101 is opened on the substrate, the depth of the cavity 101 is between 2um~4um, and in this embodiment, the cavity depth of the cavity 101 is about 3um, because it does not involve filling , so the inner wall of the cavity 101 and the bottom surface of the cavity 101 can be made into a vertical angle; and the communication channel of the cavity 101, considering the structural stability and process requirements, preferably, can be 10-20um between. In addition, the number of the through-holes 6 communicating with the cavity 101 is set at least two, which can prevent the air in the cavity 101 from being blocked by o...
Embodiment 2
[0066] A method for preparing a thin film bulk acoustic resonator, used to prepare the thin film bulk acoustic resonator as in Example 1, such as Figure 4a~Figure 4m shown, including the following steps:
[0067] Step S1: Select a silicon wafer 1, and engrave a cavity 101 on the silicon wafer 1, such as Figure 4a .
[0068] First select a silicon wafer 1, mark the silicon wafer 1 to facilitate subsequent identification and registration; and pickle and organically wash it to remove impurities such as oxides and organic substances on the silicon wafer 1 . Thereafter, the silicon wafer 1 is uniformly coated, exposed, and developed, and then placed in an ICP device for cavity carving, and a patterned substrate with a cavity 101 is formed after the glue is removed.
[0069] Step S2: growing a bonding layer 2 on the silicon wafer 1 outside the cavity 101, such as Figure 4b .
[0070] The bonding layer 2 also needs to be patterned using an exposure machine. If the bonding lay...
Embodiment 3
[0087] This embodiment is improved on the basis of Embodiment 2. In this embodiment, the bonding layer 2 is metal bonding, and the steps S1 to S4 are the same as those described in Embodiment 2. After the step S4, a step S41 is also included: a support layer 9 is grown on the upper surfaces of the bottom electrode layer 3 and the bonding layer 2, and the support layer 9 can completely cover the bottom electrode layer 3 and the The upper surface of bonding layer 2, such as Figure 6 shown; it can also grow behind the bottom electrode layer 3 and the upper surface of the bonding layer 2, and leave a gap at the position corresponding to the cavity 101, as Figure 5 shown. The thickness of the support layer 9 is preferably above 1um. The material of the supporting layer 9 can be a traditional supporting material, such as silicon nitride.
[0088] Thereafter, the bonding layer 2 in step S5 can be directly grown on the upper surface of the support layer 9 , and the subsequent ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com