Method for carrying out molecular detection on fusobacterium or carrying out classified authentication on culture level of fusobacterium
A molecular detection technology for Fusobacterium, applied in the field of biomedicine, which can solve the problems of non-specific amplification, lack of a method for classification and identification of strains for molecular detection of Fusobacterium, and inability to exclude interference from other strains.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] This embodiment provides the application of the above-mentioned method for molecular detection of Fusobacterium or classification and identification of its species level in the sequenced genome.
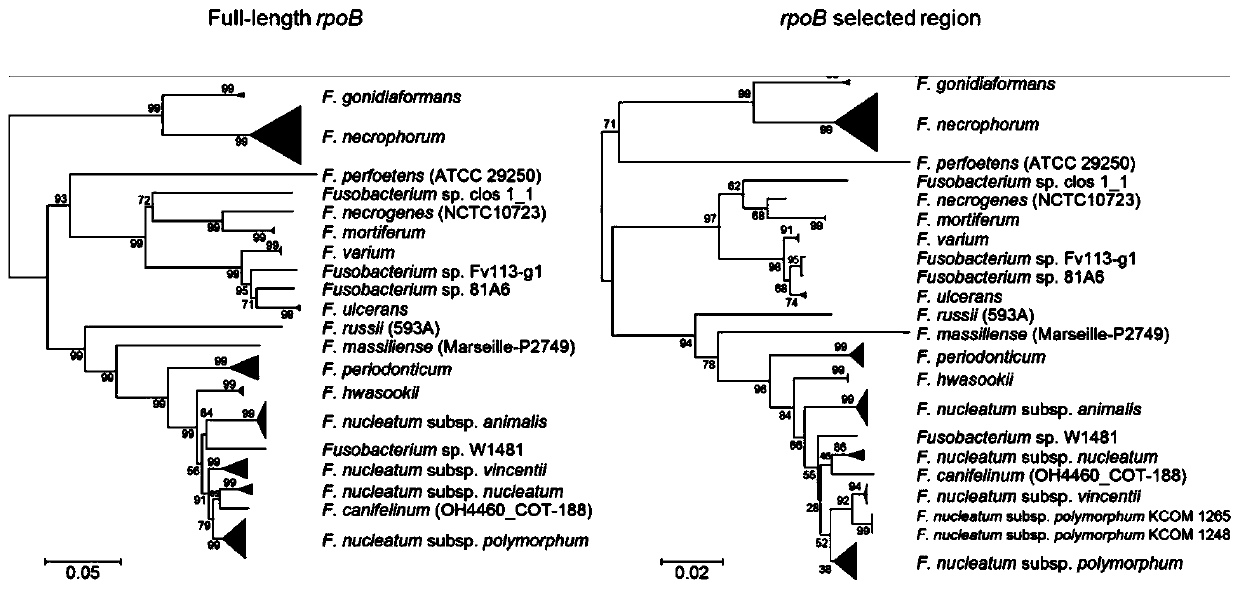
[0046] The whole-genome sequencing data of Fusobacterium strains were downloaded from the NCBI genome database, and the strains with wrong species names in the database were corrected according to the ANIb value between the whole genomes. Among them, Fusobacterium nucleatum was classified at the subspecies level; Fusobacterium naviforme and genomes that did not meet the RefSeq criteria were not included in the analysis. Furthermore, the complete sequence of rpoB gene and the fragment corresponding to rpoB_subregion_3 were extracted from each genome, and the phylogenetic tree was established with MEGA software after multiple sequence alignment by MUSCLE software.
[0047] like figure 1 As shown, it shows that the fragment corresponding to rpoB_subregion_3 can distinguish Fusob...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This embodiment detects the amplification specificity of the primers shown in SEQ ID NO.4 to SEQ ID NO.5 in a single isolate of Fusobacterium and clinical samples.
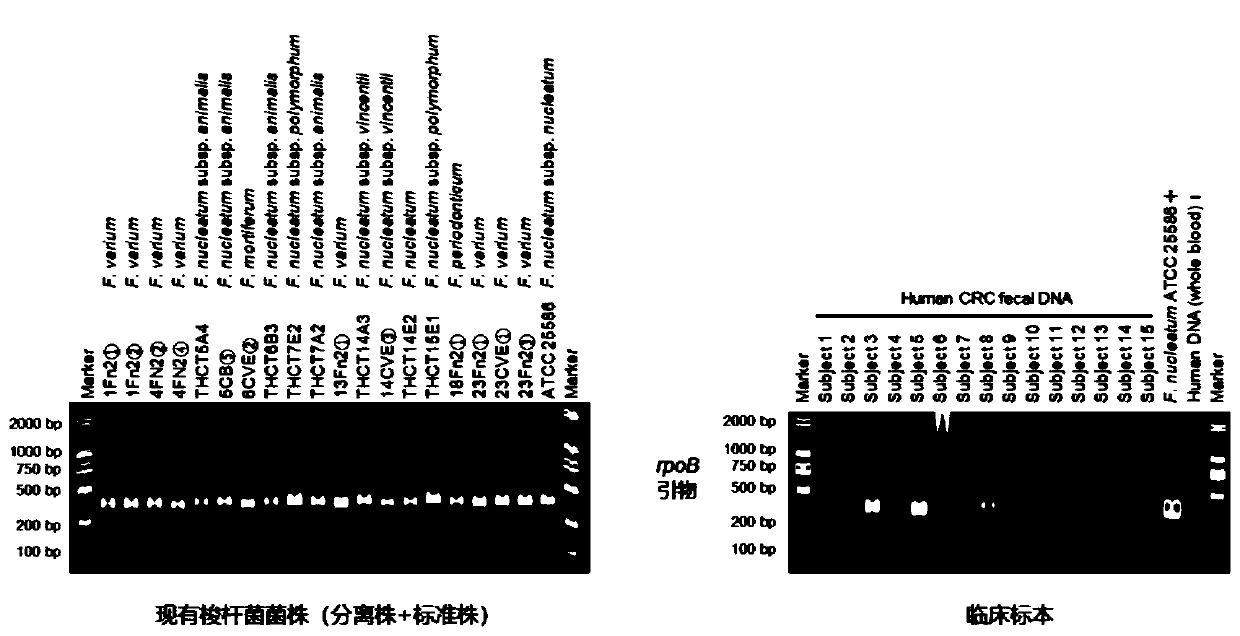
[0050] Since the primer sequence provided by the present invention has degenerate bases, it needs to effectively amplify different Fusobacterium species in the same genus, so different Fusobacterium strains are used to test its versatility. DNA extracted from stool samples of colorectal cancer patients was also tested for positive amplification.
[0051] like figure 2 As shown, the primers provided by the present invention all obtain specific bright bands with uniform fragment lengths in different single isolates of Fusobacterium, which fully verifies the good universality of the primers. In stool samples, specific bands with uniform fragment lengths can also be amplified, and the negative amplification was negative in the negative control using human blood DNA as a template, indicating that the primers h...
Embodiment 3
[0053] This example provides the application of the above method in the feces of 20 patients with colorectal cancer, so as to verify the reliability of the method.
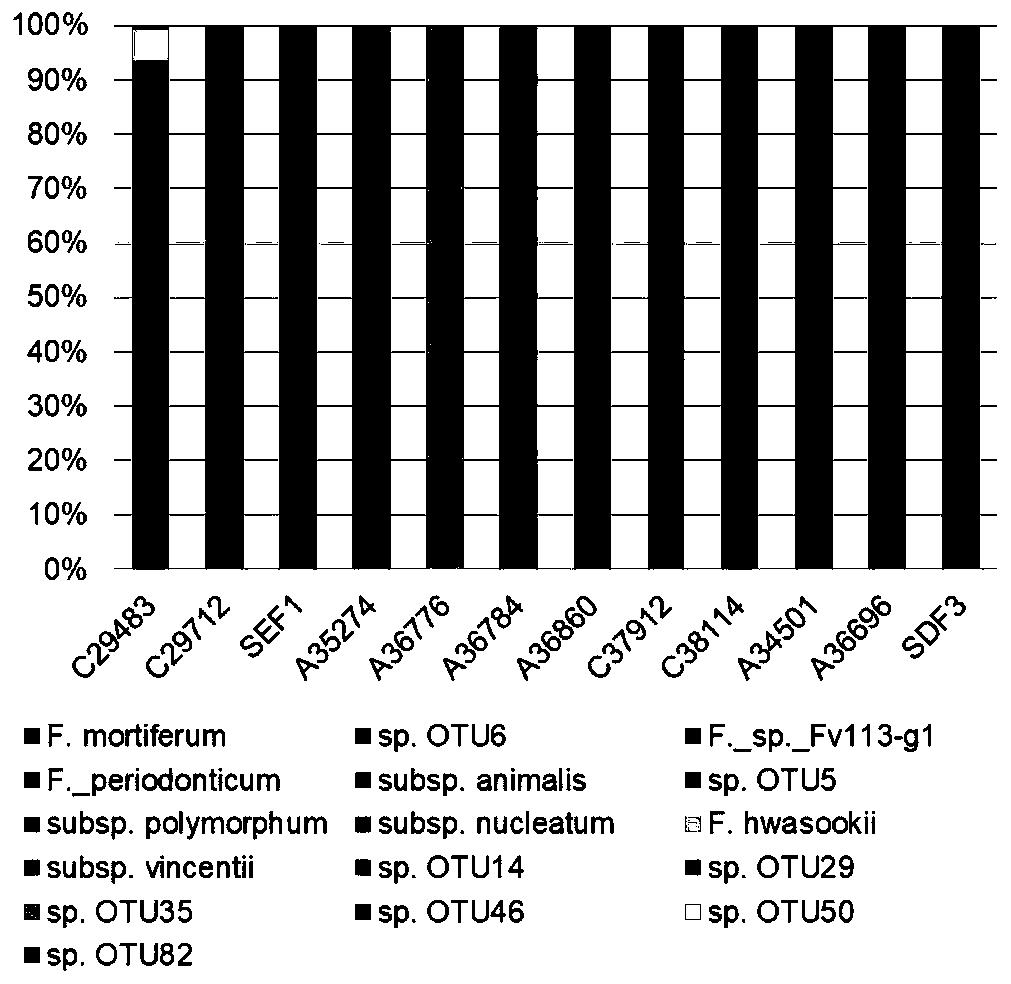
[0054] The preoperative feces of 20 patients with primary colorectal cancer were collected, amplicon sequencing was performed according to the method of the present invention, and the data were analyzed.
[0055] like image 3 As shown, the presence of Fusobacterium was detected in a total of 12 samples. In these samples, 96% of the reads (sequenced fragments) obtained by amplification and sequencing were Fusobacterium-specific target sequences, and only 4% of the reads is a non-specific sequence. The resulting sequences could be combined into 18 OTUs belonging to 16 Fusobacterium species / subspecies, of which 8 were known and 8 were unknown. Analysis of the Fusobacterial composition in each sample revealed that the Fusobacterial population in the feces of these patients was often dominated by a specific species....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com