A Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Based on Black Phosphorus-Planar Waveguide
A surface plasmon and resonant sensor technology, applied to instruments, scientific instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of low Q factor and sensitivity, high energy loss of SPR sensors, etc., to achieve improved imaging sensitivity, fast detection speed, and imaging The effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
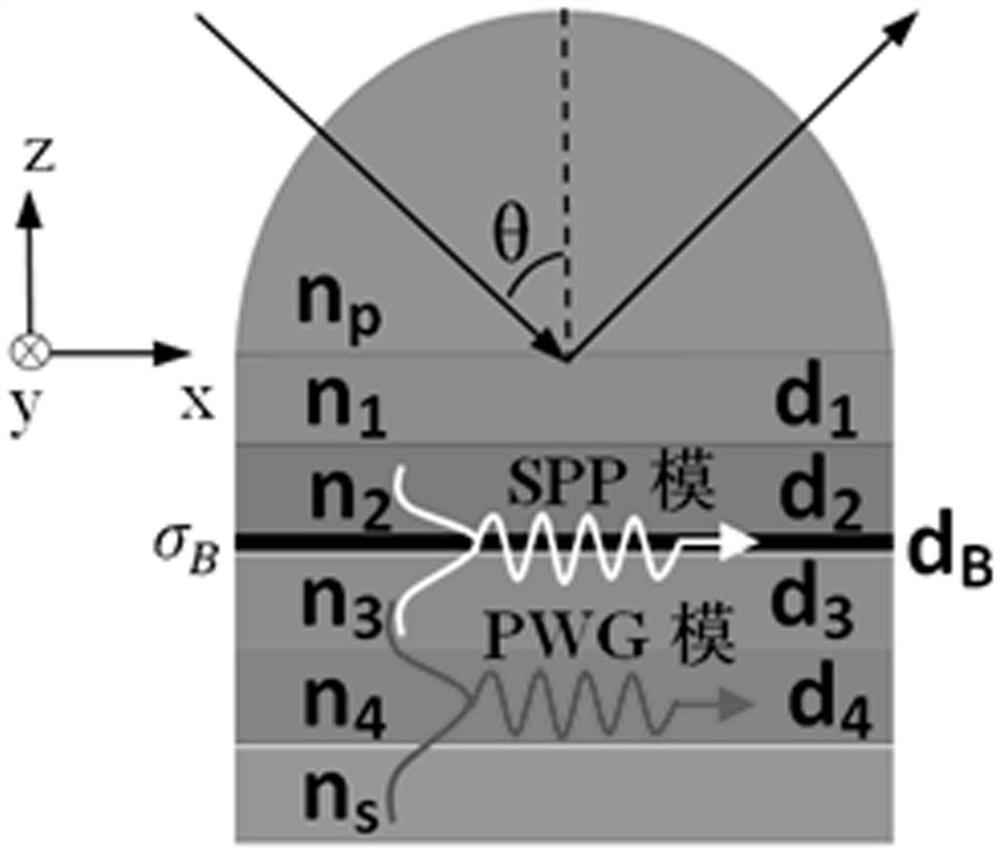
[0022] like figure 1 As shown, a SPR resonance sensor based on BP / planar waveguide, from top to bottom are germanium prism, CaF 2 , quartz crystal, BP, CaF 2 , quartz crystal layer and sensing layer, the thicknesses of the second to sixth layers are respectively set to 10.1, 8.4, 2.62×10 -3 , 28, 9.2 μm. . CaF 2 , lower CaF 2 1. The quartz crystal and the sensing layer constitute a planar dielectric waveguide (referred to as PWG). In order to illustrate the performance of this structure, the advantages of the present invention will be further described in conjunction with specific examples below.
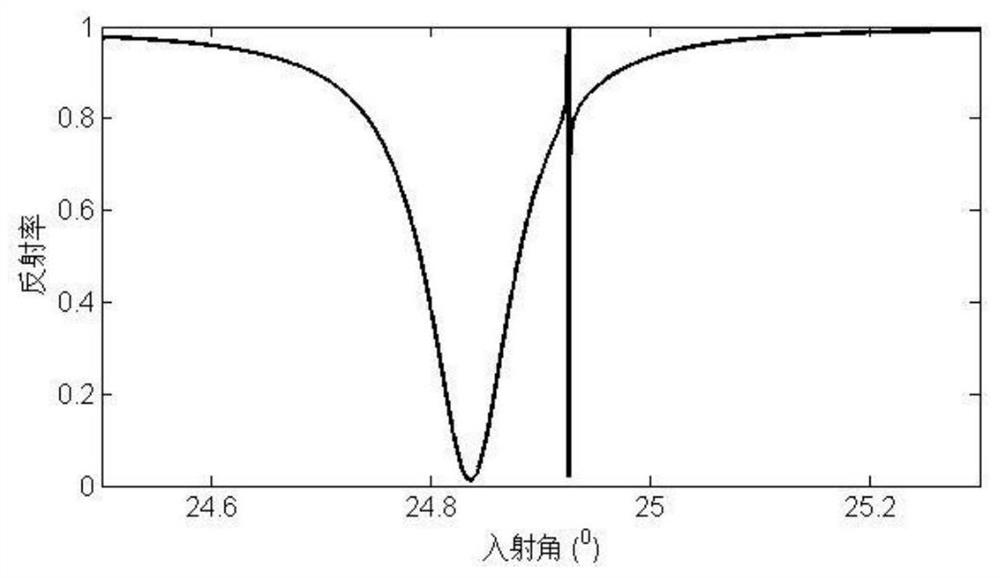
[0023] A beam of TM polarized light with a wavelength of 30 μm enters the prism, the sawtooth direction of BP is located in the incident plane, and the light passes through the CaF 2 , quartz crystal and BP, enter the next layer of CaF 2 , the SPP mode is generated at the upper and lower interface of BP, and its effective refractive index is 1.679. In order to generate a str...
Embodiment 2
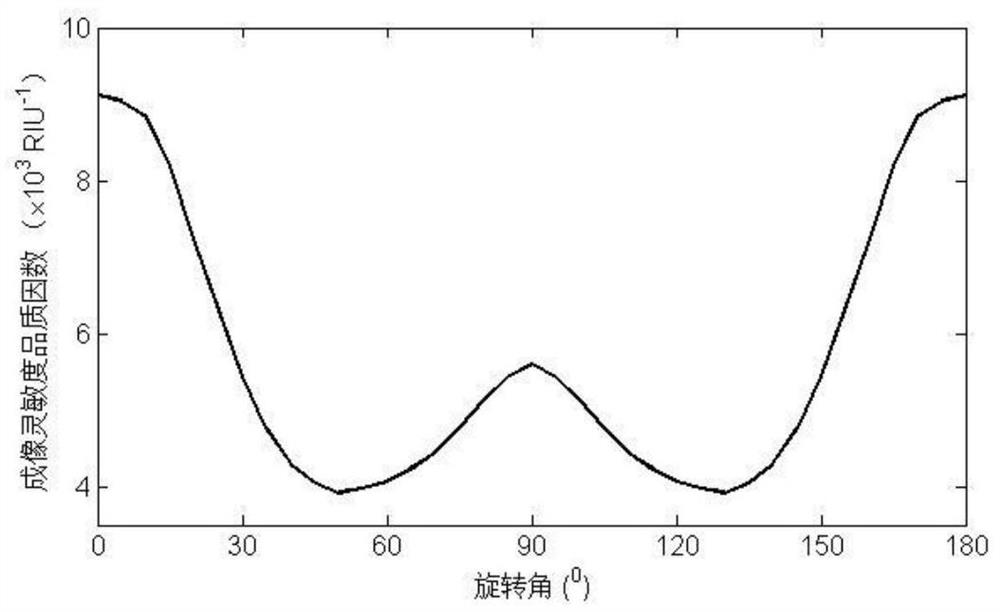
[0025] Embodiment 2: When the sensor rotates around the z-axis in the xoy plane, since the in-plane conductivity of BP is anisotropic, the sensitivity quality factor will change with the rotation angle. image 3 is the relationship between the sensitivity figure of merit of the device of the present invention and the rotation angle. The sensitivity extremum takes on a "W" shape as the rotation angle changes (the rotation angle is the angle between the BP sawtooth direction and the incident plane). When the rotation angle is 0, the quality factor of the imaging sensitivity of the sensor is the highest (9.12×103 RIU -1 ), when the rotation angle increases to 50 0 When , the figure of merit reaches the lowest value (3.92×103 RIU -1 ). As the rotation angle continues to increase, the quality factor increases, and at a rotation angle of 90 0 When , the quality factor of imaging sensitivity reaches the second extreme value (5.60×10 3 RIU -1 ). Due to the rotational symmetry o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com