Method for producing lipopeptide antibiotics by optimizing bacillus subtilis with response surface method
A technology for Bacillus subtilis and lipopeptide antibiotics, which is applied in the field of optimizing the production of lipopeptide antibiotics by Bacillus subtilis by response surface methodology, can solve problems such as unclear optimal fermentation conditions, and achieve the effects of improving production efficiency and preventing and controlling diseases. Improve the ability to control plant fungal diseases, the effect of improving the ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
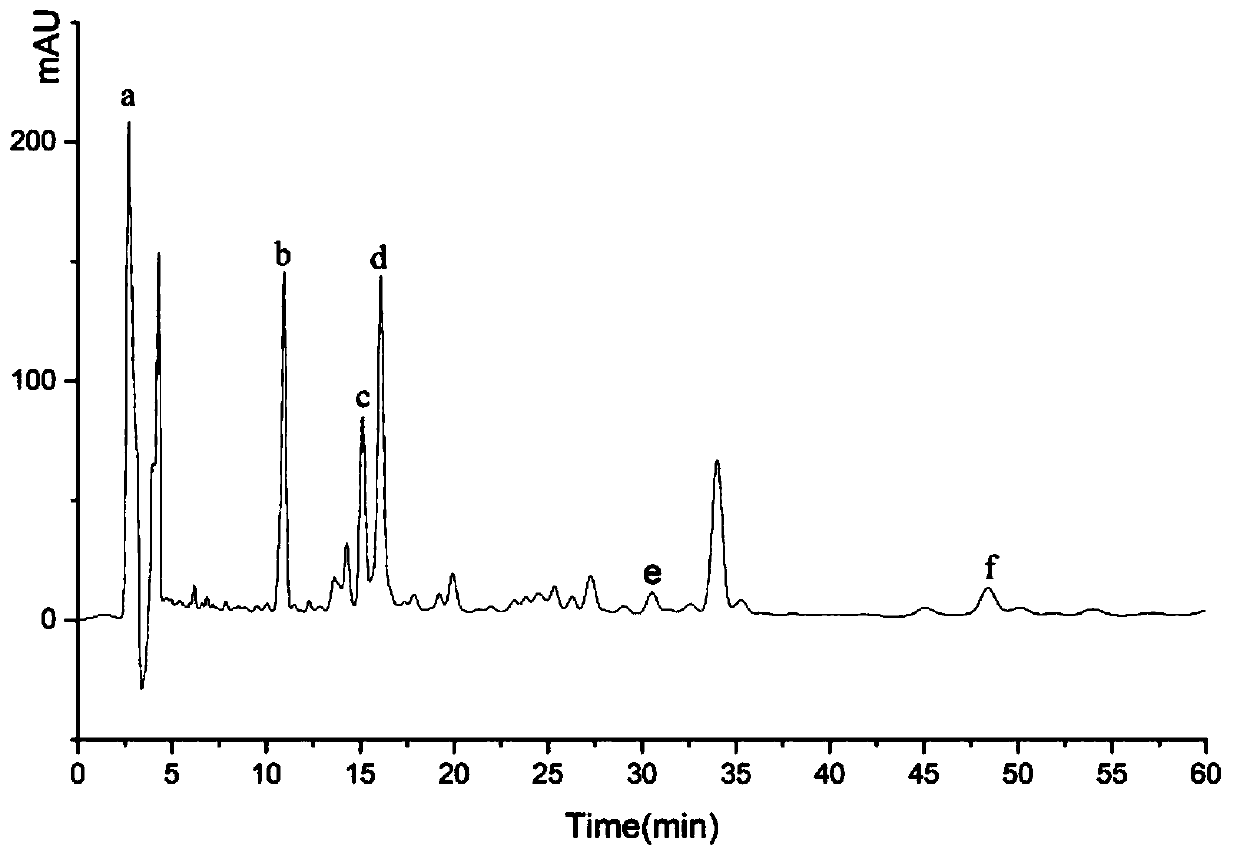
[0044] Isolation and identification of antibacterial substances in the fermentation supernatant of Bacillus subtilis Z-5
[0045] Inoculate the Bacillus subtilis Z-5 strain stored at -80°C into the NA slant medium, and culture at a constant temperature of 37°C overnight. Inoculum size Inoculate the fermentation broth into the basal medium (glucose 20.0g, peptone 20.0g, NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O 2.0g, Na 2 HPO 4 2H 2 O 4.0g, MgSO 4 ·5H 2 O 0.5g, H 2 O 1L, pH 7.2-7.4), shake culture at 37°C for 48h, centrifuge at 8000r / min for 10min to recover the supernatant, filter through a 0.22μm microporous membrane, and recover the filtrate as the sterile supernatant.
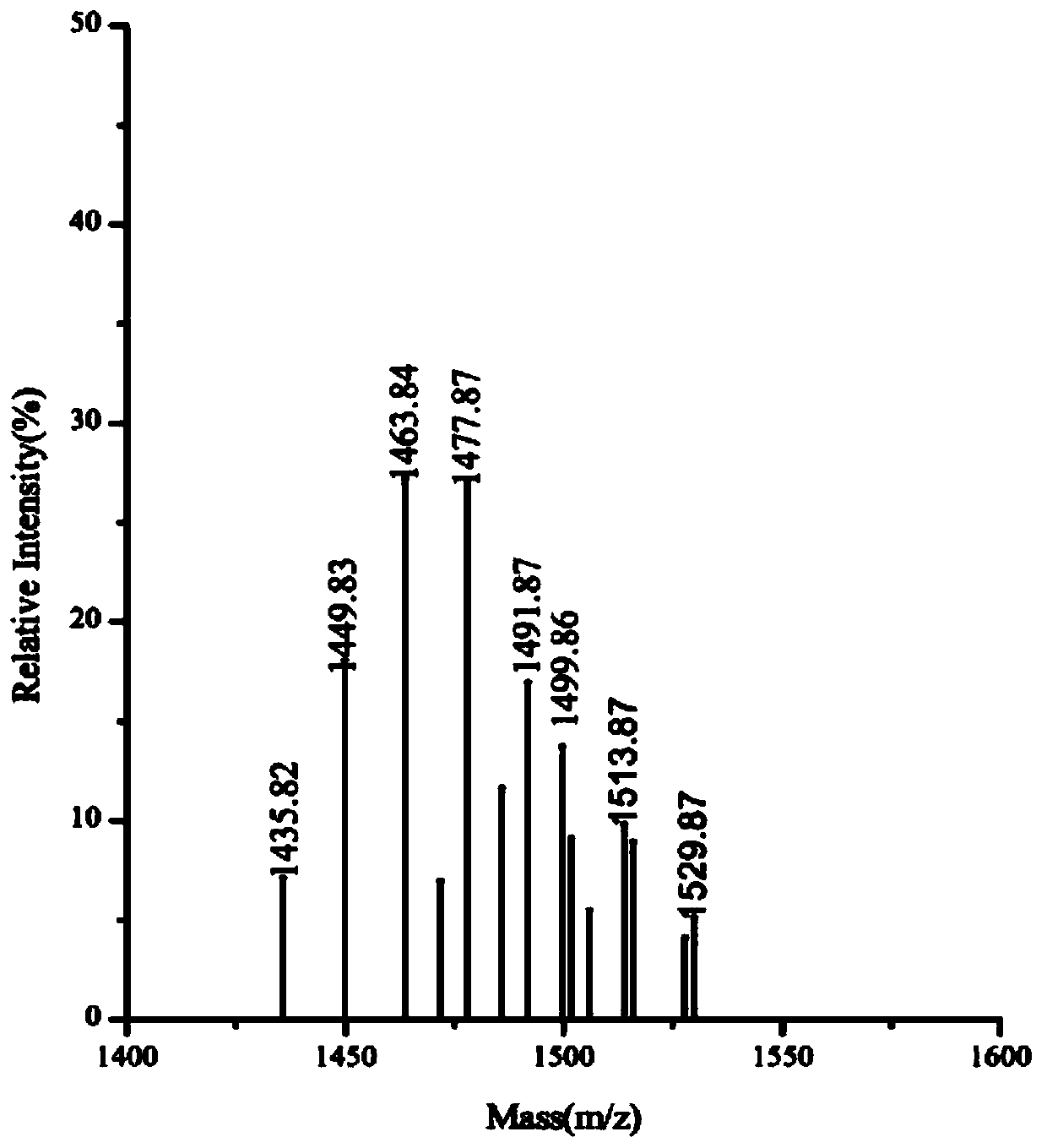
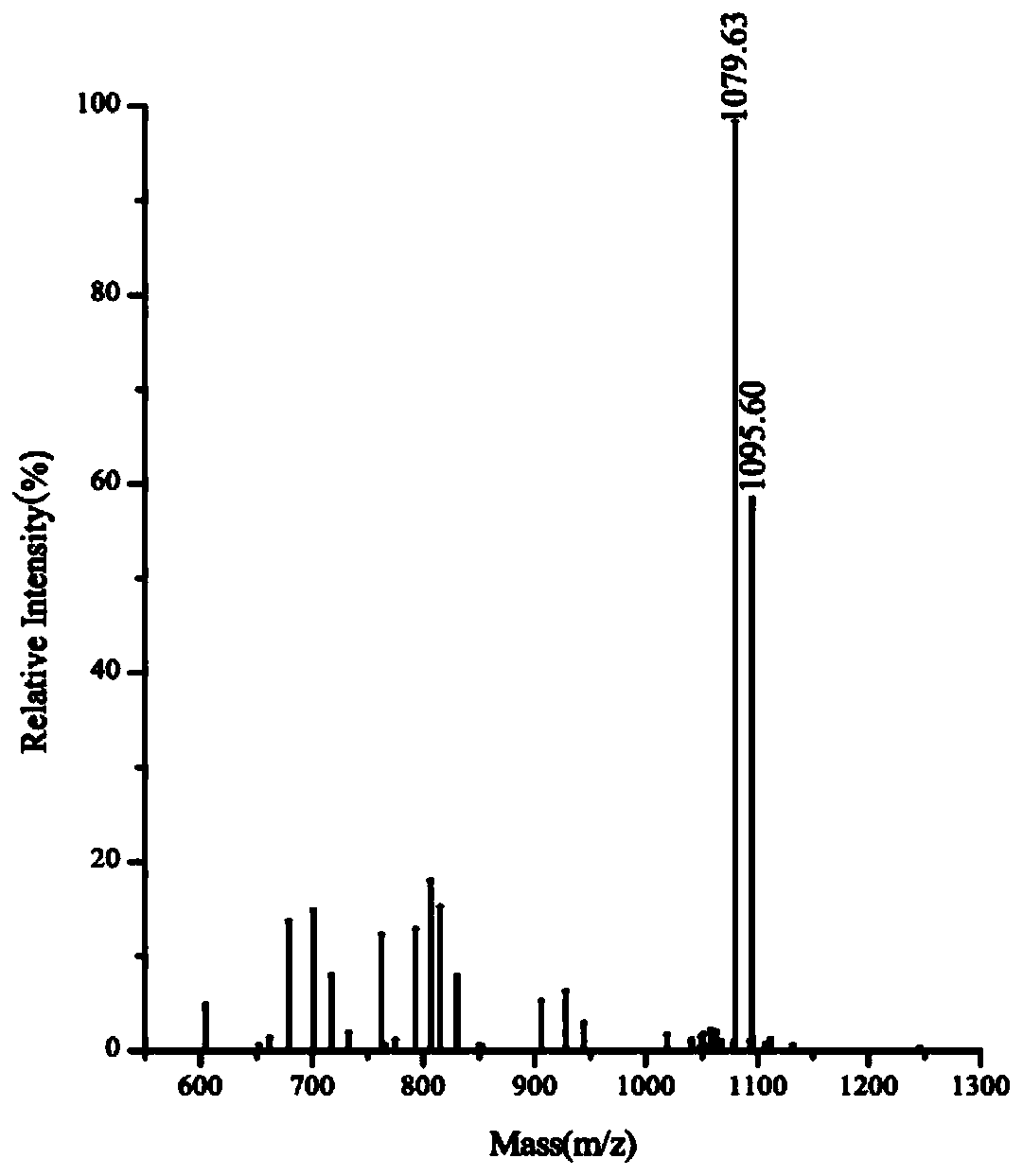
[0046] In order to determine the structure of antibacterial substances synthesized by strain Z-5, it was isolated and identified. Take 50 mL of the fermentation supernatant, adjust the pH to 2.0 with 6 mol / L hydrochloric acid solution, place in a refrigerator at 4°C overnight, centrifuge at 8000 r / min for 20 min, discard t...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Determination of carbon source, nitrogen source and inorganic salt of medium
[0051] Corn flour and mannitol had the best effect on producing lipopeptide antibiotics, and the width of the antibacterial zone was 1.12cm. Considering the economic benefits of later industrial production, corn flour was selected as the best carbon source for follow-up experiments. When soybean cake powder, peptone, tryptone and yeast extract were used as nitrogen source for culture, there was no significant difference in the width of the inhibition zone of the fermentation supernatant. Considering economy and source of raw materials, soybean meal was finally selected as the best nitrogen source. The best inorganic salt is FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O. The best carbon source, nitrogen source, and inorganic salt for cultivating the Z-5 strain were corn flour, soybean cake flour, and FeSO by single factor experiments. 4 ·7H 2 O.
[0052] For corn flour, soybean meal and FeSO 4 Carry out the steepest...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Optimizing Box-Behnken Test of Medium Components
[0057] Design-Expert 8.0.6 software was used to design the Box-Behnken experiment. According to the design, there were 17 groups of experiments, of which 5 groups were center-point repeated experiments (Table 2). According to the design results, the medium was prepared and fermented, and the width of the inhibition zone of the fermentation supernatant against the pathogen of wheat take-all was detected. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0058] Table 2 Media composition Box-Behnken test design and results
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] The regression equation obtained by software analysis of the width of the antibacterial zone is:
[0062] Y=–0.29741+0.40575A+0.14825B+49.3C+0.07875AB–1.75AC–1.75BC–0.058375A 2 –0.12338B 2 –521.25C 2 (R 2 = 0.9946; R 2 -adj=0.9878)
[0063] Where Y is the predicted value of the width of the inhibition zone (cm), A, B and C are corn flour, soybean cake flour and FeSO4·7H 2 O.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com