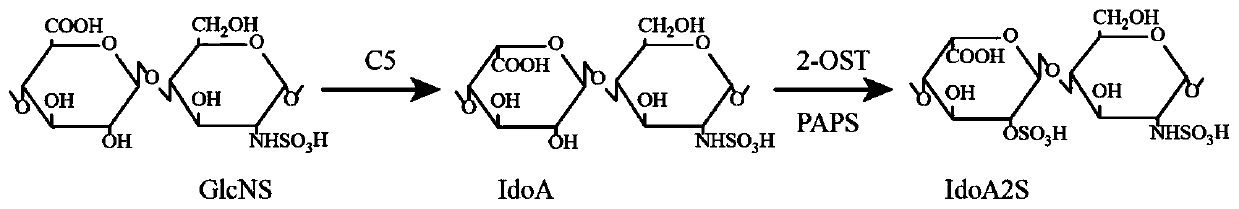
Construction method of heparin C5 isomerase high-catalytic-activity strain
An isomerase and heparin technology is applied in the field of construction of strains with high catalytic activity of heparin C5 isomerase, and can solve the problems of unfavorable industrial production, low catalytic activity, low expression and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1: Preparation of C5, 2-OST and AST IV
[0054] 1. Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli expressing AST IV, 2-OST or C5
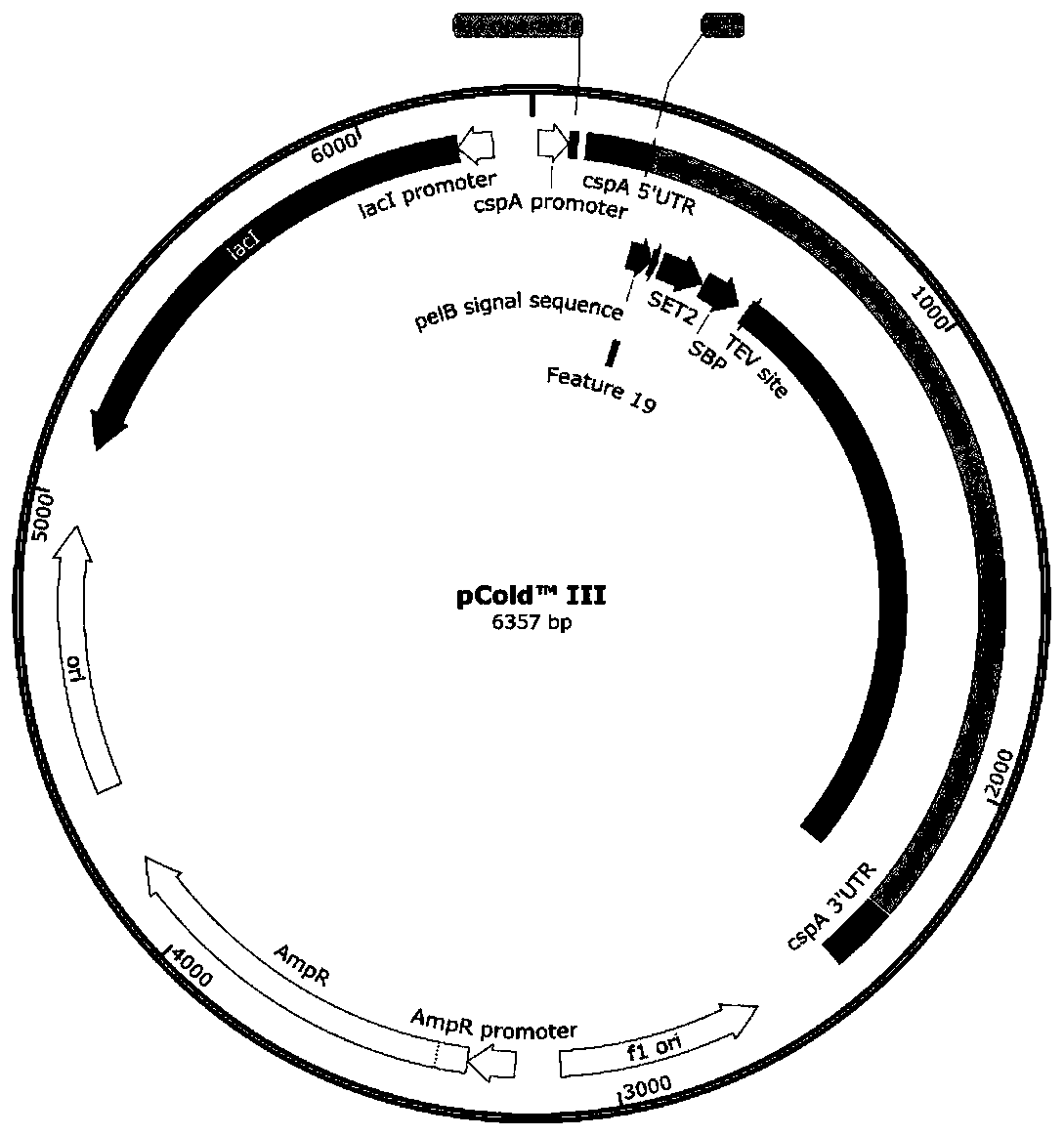
[0055] The gene encoding AST IV was connected to the pCold III vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pCold III-AST IV; the recombinant plasmid pCold III-AST IV was transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3), and the recombinant E. coli E. coli expressing AST IV was obtained. coliBL21(DE3)-pCold III-AST IV.
[0056] The gene encoding 2-OST was connected with the pET28a vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET28a-2OST; the recombinant plasmid pET28a-2OST was transformed into E.coli BL21(DE3) to obtain recombinant E. coli BL21 expressing 2-OST ( DE3)-pET28a-2OST.
[0057] Ligate the gene encoding C5 with the pCold III vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid pCold III-C5; transform the recombinant plasmid pColdIII-C5 into E.coli BL21(DE3) to obtain the recombinant E.coli BL21(DE3) expressing C5 -pColdIII-C5.
[0058] 2. Induced exp...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2: The N-terminus of C5 is fused with the solubilizing tag SET2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0066] The N-terminus of C5 was fused with MBP, SET2 or SUMO, and the fused genes were respectively connected to the pCold III vector to obtain recombinant plasmids pCold III-MBP-C5, pCold III-SET2-C5, and pCold III-SUMO-C5 (see figure 2 ); Transform the recombinant plasmids pCold III-MBP-C5, pCold III-SET2-C5, pCold III-SUMO-C5 into E. coli respectively to obtain recombinant E. coli BL21 expressing C5 and MBP, SET2 or SUMO fusion (DE3)-pColdIII-MBP-C5, E.coli BL21(DE3)-pColdIII-SET2-C5 or E.coli BL21(DE3)-pColdIII-SUMO-C5.
[0067] The induced expression and purification process were the same as in Example 1.
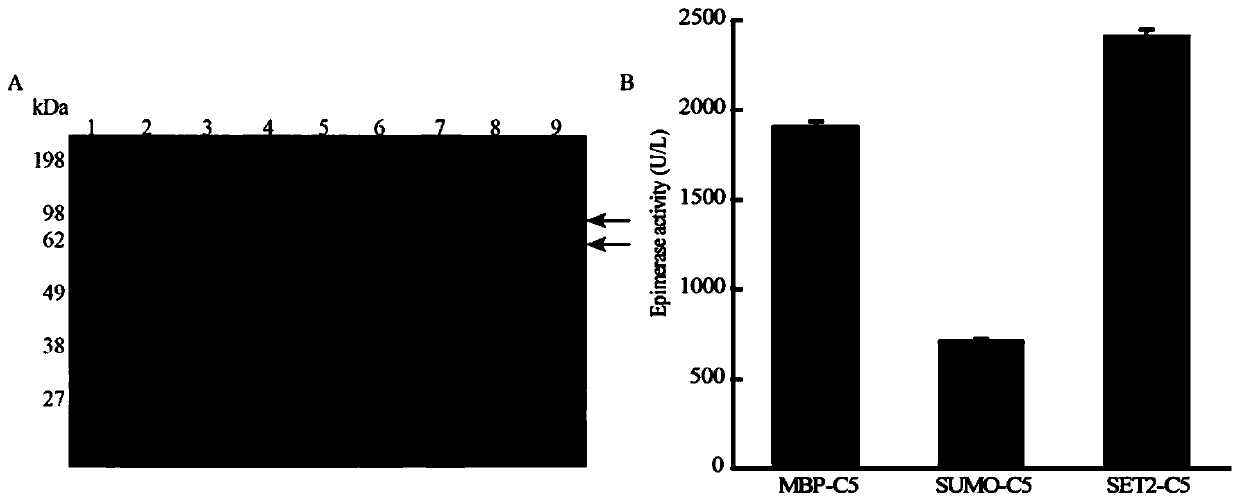
[0068] The result is as image 3 As shown, the measured enzymatic activity after the N-terminal of C5 was fused with MBP, SET2, and SUMO was 1.91U / mL, 2.41U / mL, and 2.41U / mL, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3: Molecular modification of C5
[0070] According to the reported enzyme structure analysis, through Discovery Studio molecular docking, the amino acid sites VAL06ASP498, GLY352, and LYS350 within 5 angstroms of the substrate binding pocket were selected, and based on pCold III-SET2-C5, site-directed saturation mutation was performed (mutation primer See Table 1).
[0071] Table 1 Mutation Primers
[0072] Primer name Primer VAL106-F TTGAGGGTTACAACGTGGAANNNCGTGACCGTGTGAAGTGCAT VAL106-R TTCCACGTTGTAACCCTCAAAGCT LYS350-F GATCATGGTGACCCGTNNNCTGGGTGAAGGTTTTCGTGCG LYS350-R ACGGGTCACCATGATCGGC GLY352-F TCATGGTGACCCGTAAACTGNNNGAAGGTTTTCGTGCGCTGGAG GLY352-R CAGTTTACGGGTCACCATGATCGG ASP498-F AACCTGGCGCGTTGGNNNTATCACACCCACCCACATCAACC ASP498-R CCAACGCGCCAGGTTC
[0073] The result is as Figure 4 As shown, using Escherichia coli to express C5-V106R after the 106th amino acid was mutated from valine t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com