N-type fragmented solar cell structure and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of a solar cell and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems such as the reduction of the efficiency of the sliced cell, and achieve the effects of edge recombination suppression and FF improvement.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0054] Specifically, see Figure 5a , Figure 5b A method for preparing an N-type sliced solar cell structure provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
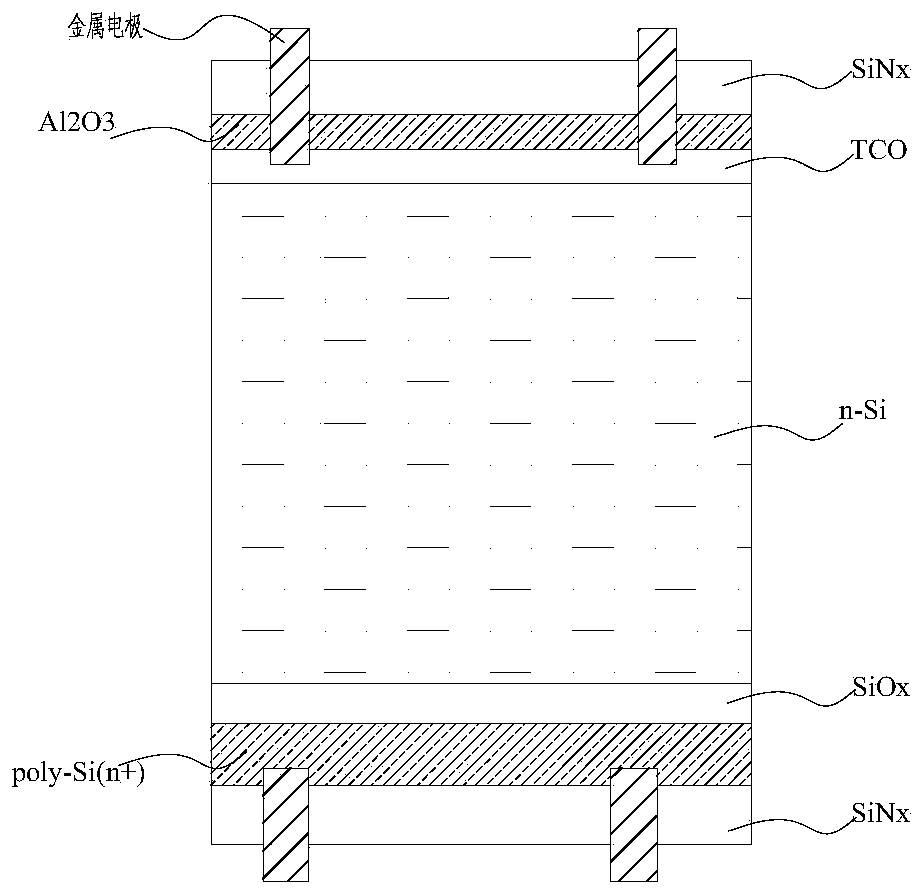
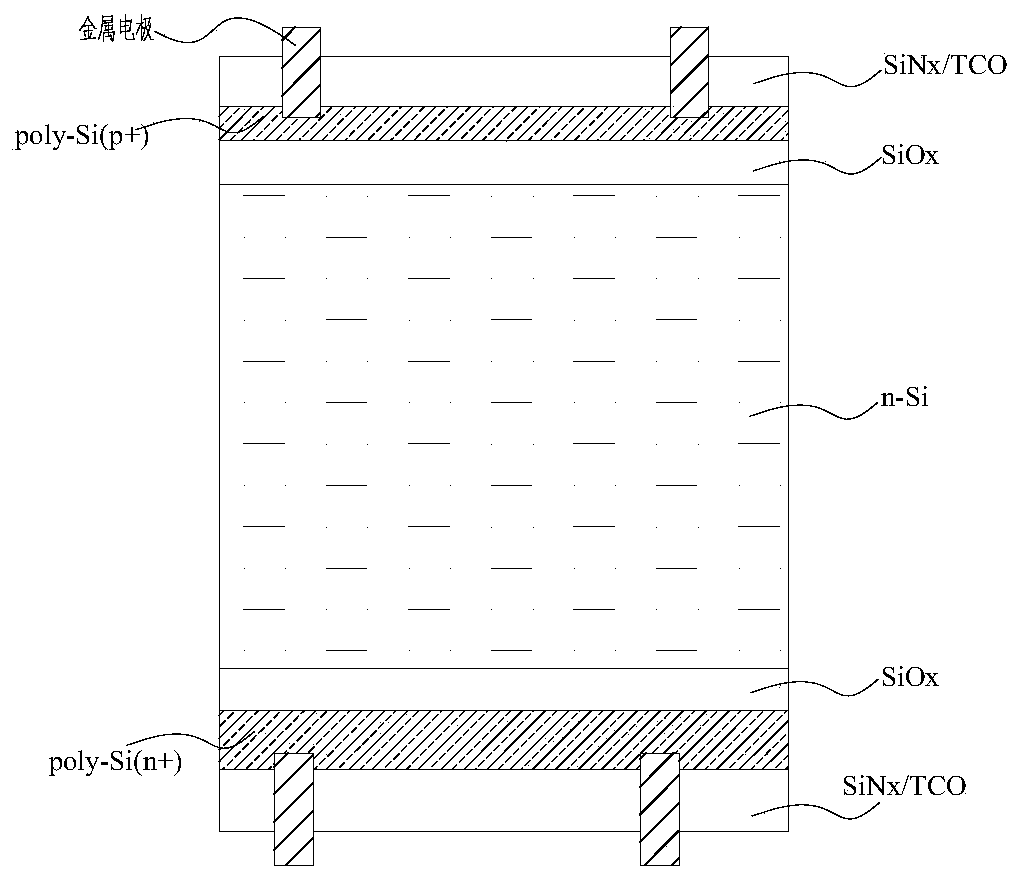
[0055] 1) Provide an N-type silicon wafer with a resistivity of 0.1-3Ω·cm, and process the N-type silicon wafer by laser cutting at the position corresponding to the slice on the first surface of the N-type silicon wafer to form a groove for the split, The width of the groove is 0.2-10um, preferably 0.2-1um; the depth of the groove is 0.5-50um, preferably 0.5-15um, and then a laminated passivation layer is deposited on the first surface, and the laminated passivation layer and N Type silicon wafers form heterogeneous p-n junctions;
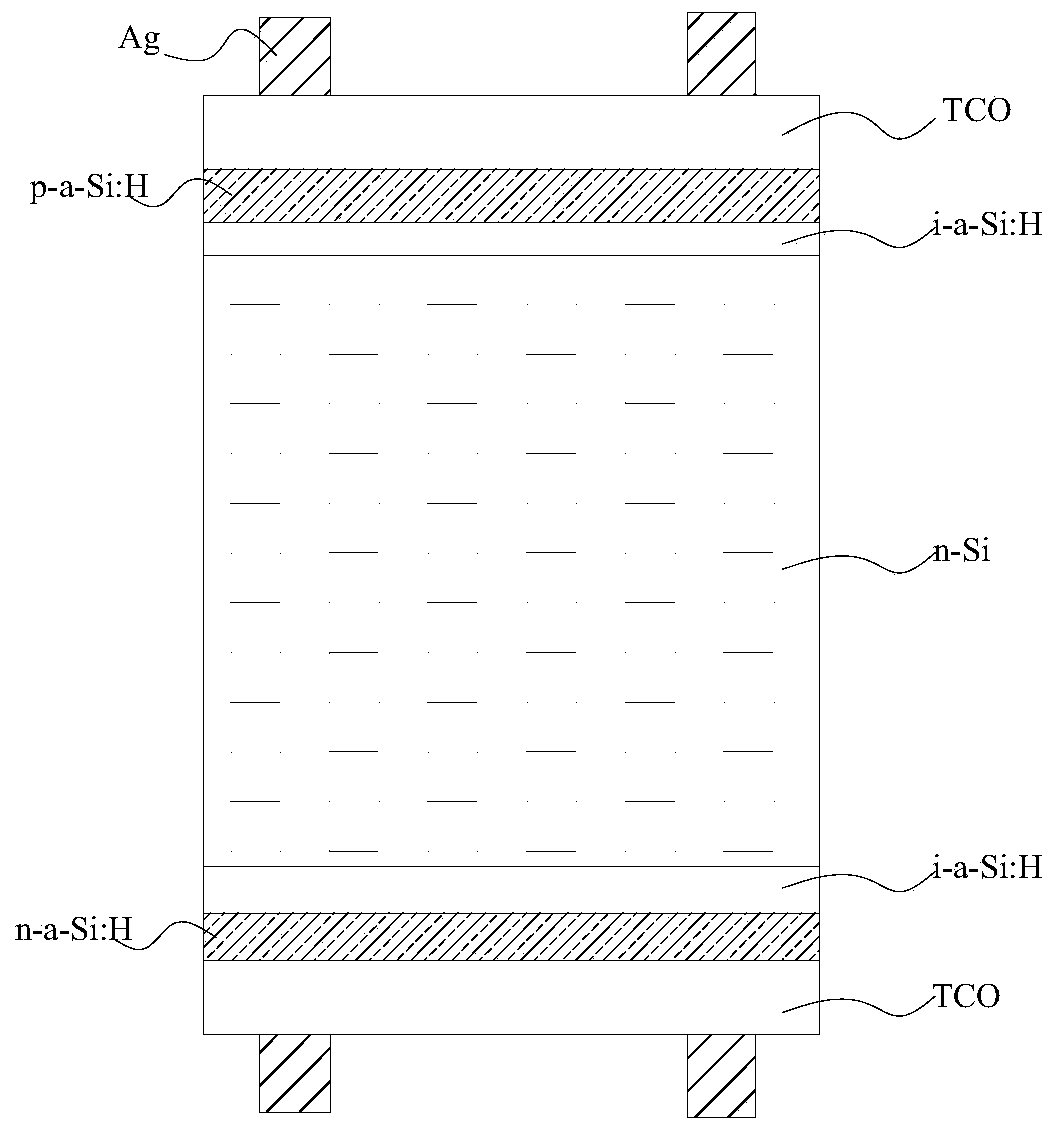
[0056] If the battery is an N-type heterojunction battery, the stack passivation layer is i-a-Si:H / p-a-Si:H / TCO stack, where i-a-Si:H is 1-10nm thick, which is chemical passivation layer, p-a-Si:H thick 1-15nm is the field passivation layer, TCO is the ...
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1 Process of bisecting N-type heterojunction cells
[0064] 1) Provide N-type silicon wafers with a resistivity of 0.1-3Ω·cm;
[0065] 2) On the first surface of the N-type silicon wafer and located at 1 / 2 of the side length, a kerf is formed by laser irradiation, the width of the kerf is 0.2-10um, preferably 0.2-1um; the kerf The depth is 0.5-50um, preferably 0.5-15um;
[0066] 3) Surface treatment of the N-type silicon wafer with an alkaline solution to remove the damaged layer, and then the N-type silicon wafer is cleaned and textured. After cleaning, the silicon wafer is required to be free of spots, scratches, water marks, etc.;
[0067]4) Deposit the laminated intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (i-a-Si:H) and N-type hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (n-a-Si:H) on the second surface of the N-type silicon wafer by PECVD or hot wire CVD -Si:H);
[0068] 5) Using PECVD or hot wire CVD to deposit a laminated intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous sili...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Example 2 Six equal slices of N-type heterojunction cells
[0085] 1) Provide N-type silicon wafers with a resistivity of 0.1-3Ω·cm;
[0086] 2) The first surface of the N-type silicon wafer is located at 1 / 6 of the side length, and 5 grooves are formed by laser irradiation. The width of the groove is 0.2-10um, preferably 0.2-1um; the depth of the groove is 0.5-50um, preferably 0.5-15um.
[0087] 3) Surface treatment of the N-type silicon wafer with an alkaline solution to remove the damaged layer, and then the N-type silicon wafer is cleaned and textured. After cleaning, the silicon wafer is required to be free of spots, scratches, water marks, etc.;
[0088] 4) Using PECVD or hot wire CVD to deposit stacked intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon films (i-a-Si:H) and N-type hydrogenated amorphous silicon films (n-a- Si:H);
[0089] 5) Deposit a laminated intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (i-a-Si:H) and a P-type hydrogenated amorphous silicon film (p-a-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com