A rapid test method and system for potential induction decay of solar cells
A solar cell and potential sensing technology, which is applied in the monitoring of photovoltaic systems, electrical components, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve the problem of inability to accurately obtain the potential induction attenuation performance of solar cells, difficult to meet rapid evaluation, and cannot be used to evaluate component packaging materials. performance issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] The potential induction decay rapid test method of the solar cell and packaging material of the present embodiment includes:
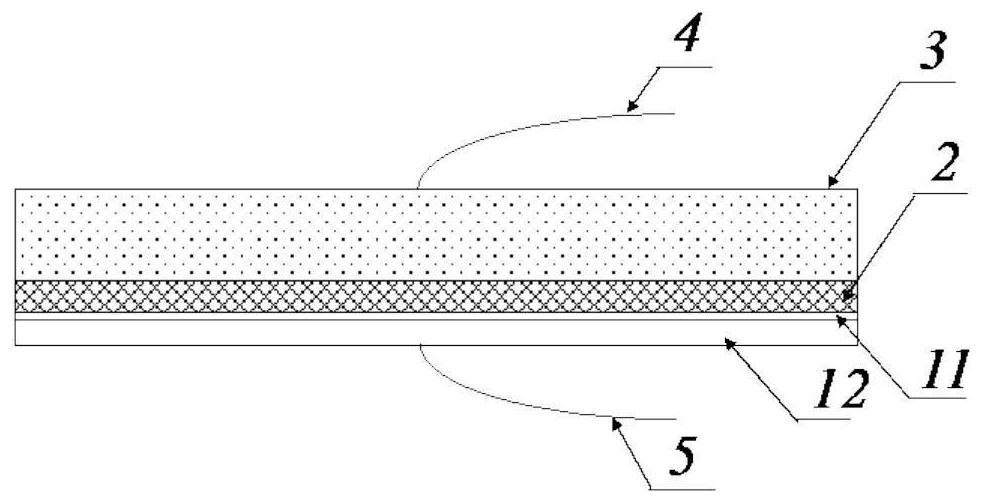
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, the solar cell, the encapsulating polymer material 2, such as ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) film, polyolefin elastomer film (POE), etc., and the encapsulating glass layer 3 are stacked sequentially from bottom to top to form a stack .
[0043]The two planar electrodes are closely combined with the upper and lower surfaces of the stack, the upper electrode 4 is connected to the positive pole of the DC high voltage power supply, and the lower electrode 5 is connected to the negative pole of the DC high voltage power supply. Wherein, the planar electrode is a planar metal electrode, preferably made of aluminum.
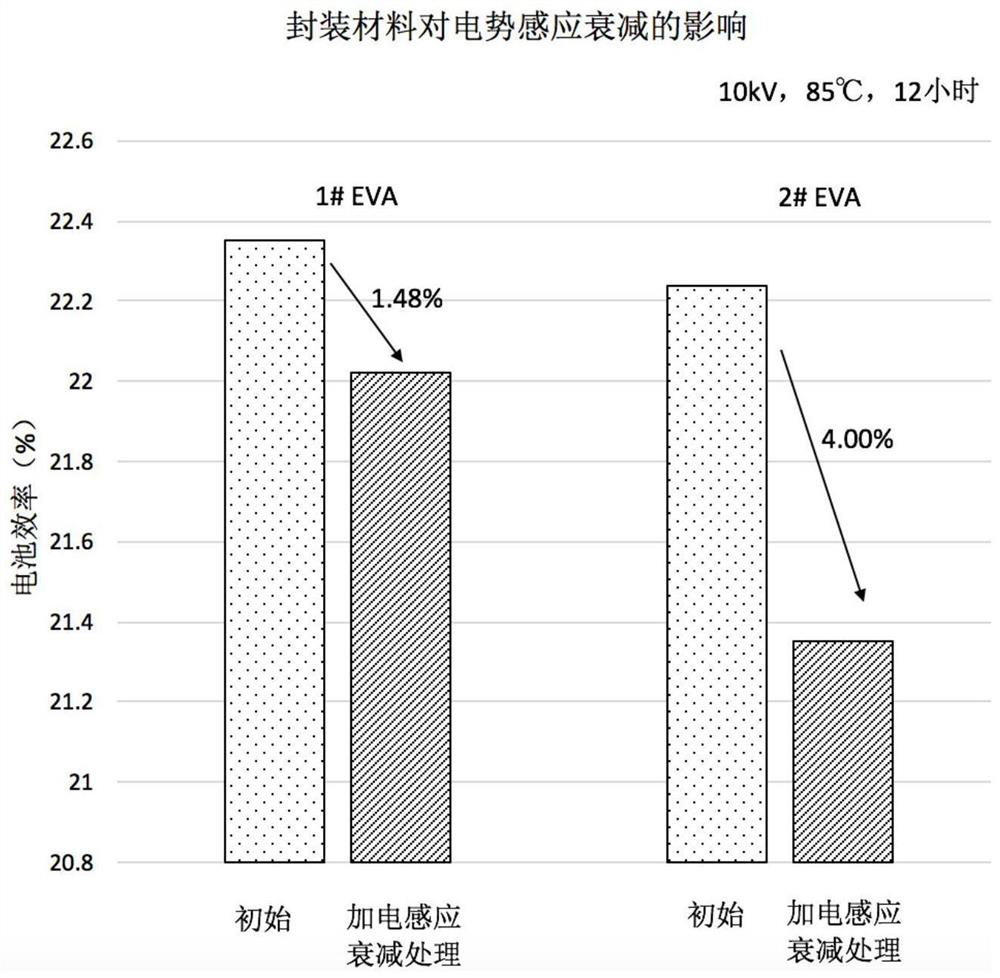
[0044] A voltage of 10 kV was applied between the two electrodes, the direction of the electric field was directed from the glass to the front surface of the solar cell, and the above stack was ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The potential induction decay rapid test method of the solar cell and packaging material of the present embodiment includes:
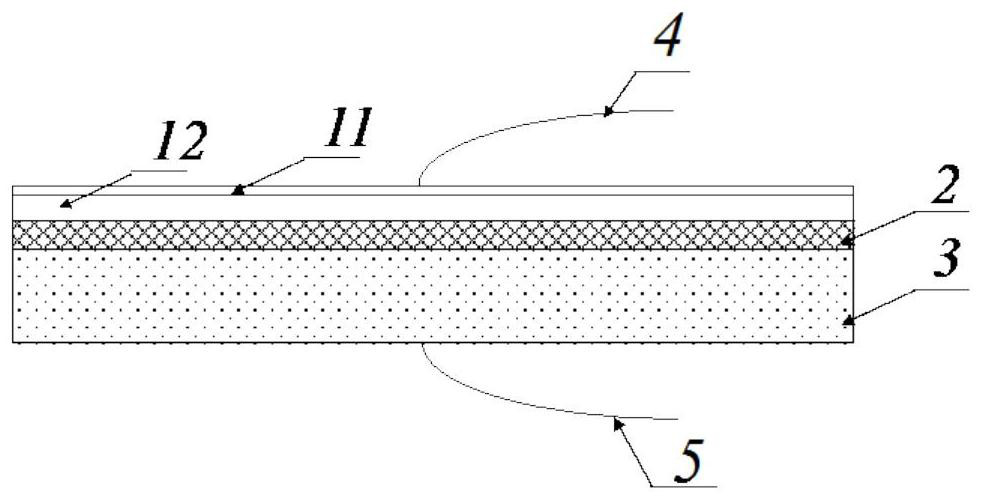
[0048] Such as image 3 As shown, the solar cell, the encapsulating polymer material 2 , the encapsulating glass or the back plate 3 are stacked sequentially from top to bottom to form a stack.
[0049] The two planar electrodes are closely combined with the upper and lower surfaces of the stack, the upper electrode 4 is connected to the negative pole of the DC high voltage power supply, and the lower electrode 5 is connected to the positive pole of the DC high voltage power supply. Wherein, the planar electrode is a planar metal electrode, preferably made of aluminum.
[0050] A voltage of 5 kV was applied between the two electrodes, and the above stack was kept at 60°C for 24 hours. After the process is over, the direct current high voltage is removed, the stack is cooled, and the solar cells are taken out and tested for electrical performan...
Embodiment 3
[0054] The potential induction decay rapid test method of the solar cell module of the present embodiment includes:
[0055] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the two planar electrodes are closely combined with the upper and lower surfaces of the solar cell module, the upper electrode 4 is connected to the positive pole of the DC high-voltage power supply, and the lower electrode 5 is connected to the output terminal of the module with a wire, and the above output terminal is connected to the lower half of the solar cell. For example, for a conventional p-type solar cell, the output end of which is the positive pole of the component, and the lower electrode 5 is then connected to the negative pole of the DC high-voltage power supply. Wherein, the planar electrode is a planar metal electrode, preferably made of aluminum.
[0056] A voltage of 15kV was applied between the two electrodes, and the direction of the electric field was directed from the upper surface glass layer to the so...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com