Fabrication method of arrayed optical waveguide flexible tactile sensor
A tactile sensor and optical waveguide technology, applied in the direction of optical waveguide light guide, measurement of the change force of the optical properties of the material when it is stressed, instruments, etc., can solve the large-scale array resistance of tactile sensors, fewer application scenarios, Difficulty in packaging and other issues, to achieve the effect of automatic detection, simple process, and convenient integration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
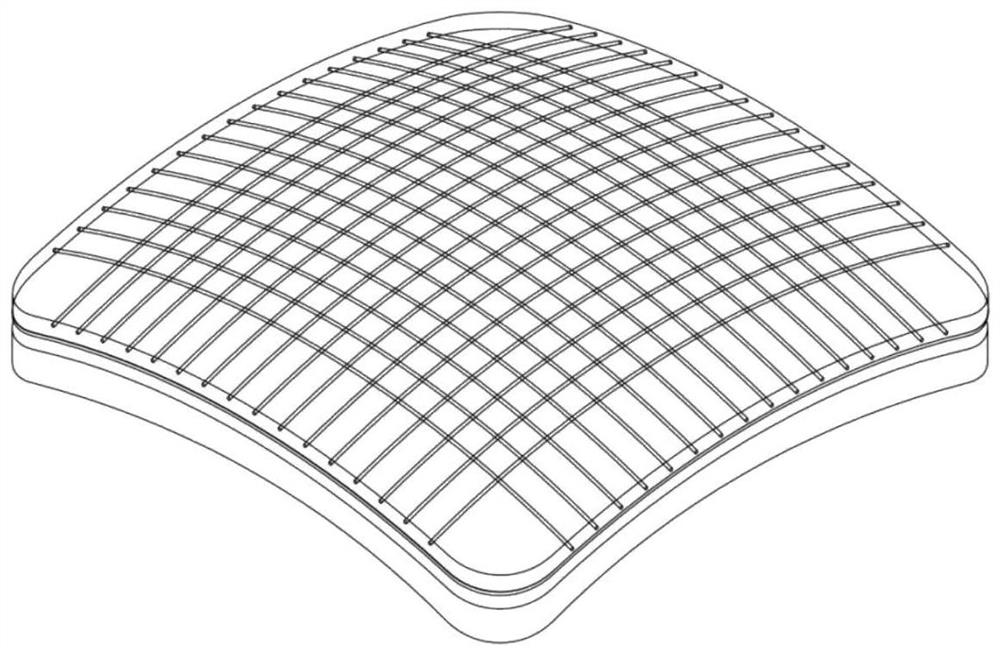
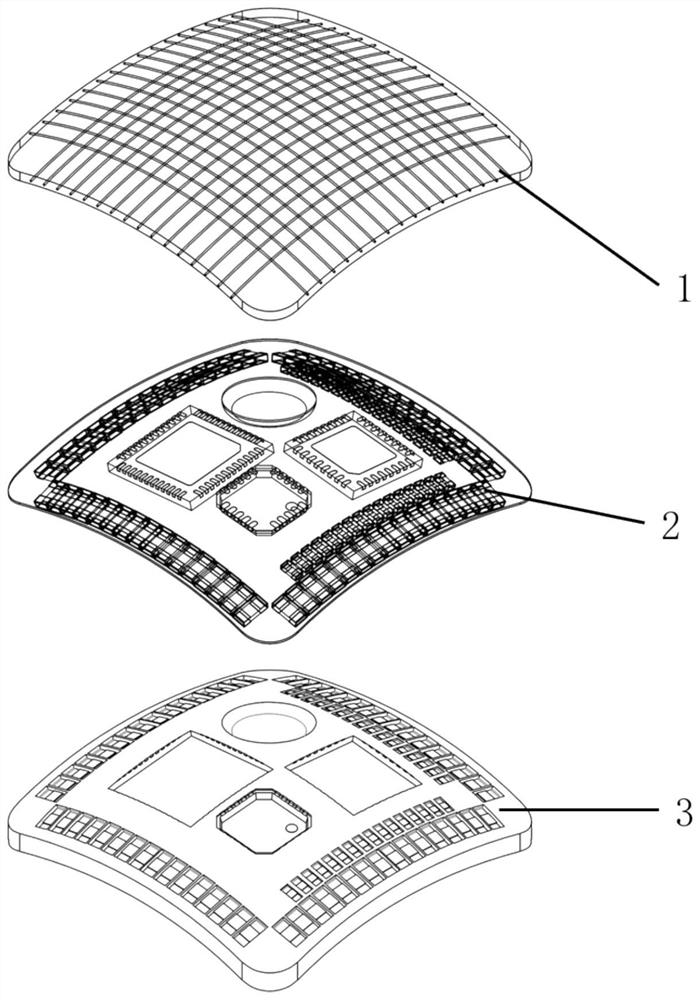
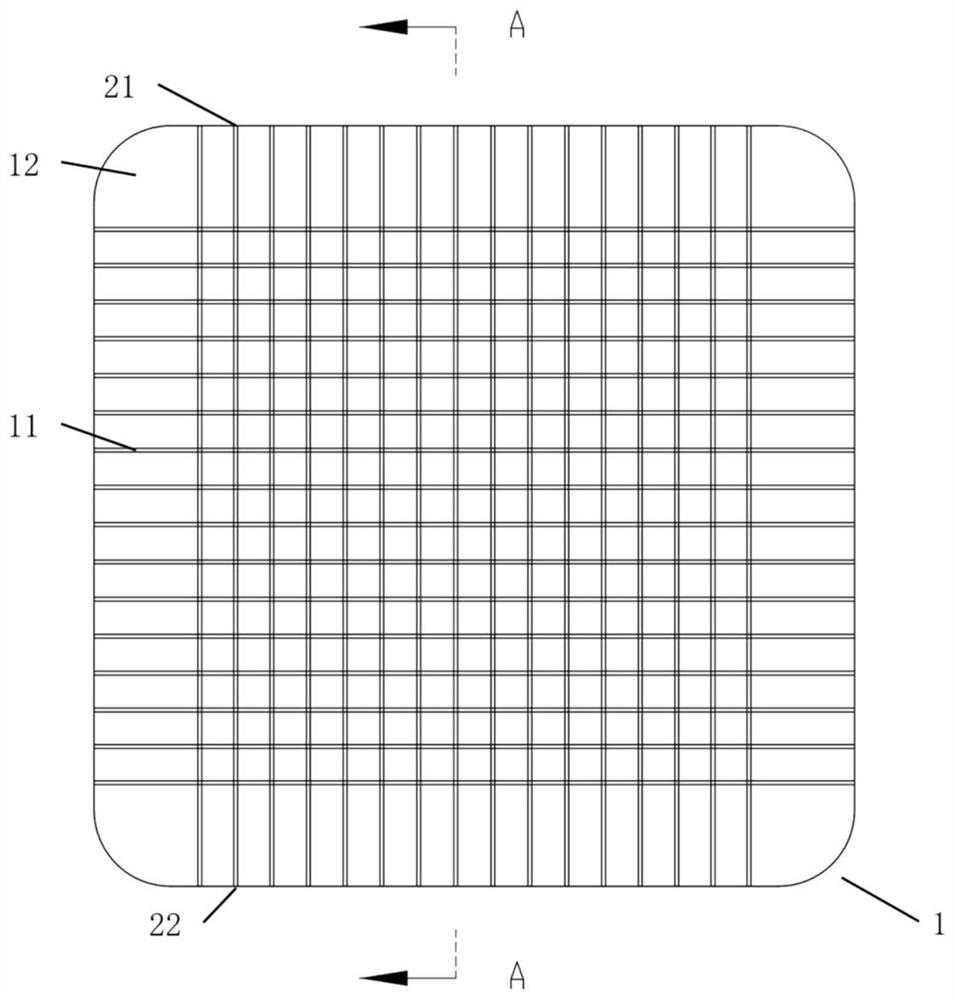
[0047] like figure 1 , figure 2 As shown, the arrayed optical waveguide flexible tactile sensor includes a flexible optical waveguide tactile sensitive layer 1 , a flexible circuit layer 2 , and a flexible substrate layer 3 distributed in layers from top to bottom. The flexible optical waveguide tactile sensitive layer 1 includes several optical waveguide inner cores 11 and an optical waveguide cladding 12 integrally covering the optical waveguide inner cores 11 . Wherein the optical waveguide inner cores 11 are distributed in an array. The flexible circuit layer 2 includes a light-emitting power supply terminal and an optical signal receiving and processing terminal. The flexible substrate layer 3 is made of a flexible material with an adaptable shape, which plays the role of protection and auxiliary fixation. The flexible optical waveguide tactile sensitive layer 1, the flexible circuit layer 2 and the flexible substrate layer 3 are bonded and packaged by silicone rubber...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Such as Figure 7 to Figure 9(b) As shown, one of the differences between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the surface curvatures of the flexible optical waveguide tactile sensitive layer 1, the flexible circuit layer 2, and the flexible substrate 3 are different, and the three-layer structures are all planes; the second difference lies in the flexible The number of optical waveguide inner cores in the optical waveguide tactile sensitive layer is different and is eight. The difference between the technical effect produced by this embodiment and the first embodiment is that it is more suitable for the working environment where the sensitive area is a plane.
[0079] In addition, other contents of this embodiment, including the internal structure and function of the flexible optical waveguide tactile sensitive layer 1, the flexible circuit layer 2, and the flexible substrate 3, and the working principle and preparation method of the tactile sensor, are all consist...
Embodiment 3
[0081] As shown in FIG. 10( a ) and FIG. 10( b ), the difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the optical waveguide inner core 11 in the flexible optical waveguide tactile sensitive layer 1 is distributed in a single layer. The difference between the technical effect produced by this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the number of inner cores of the optical waveguide in the tactile sensitive layer of the flexible optical waveguide is reduced, the difficulty of preparation is reduced, and it is more suitable for detecting whether a collision has occurred on the sensitive surface, rather than extracting Richer tactile information.
[0082] In addition, other contents of this embodiment, including the internal structure and function of the flexible optical waveguide tactile sensitive layer 1, the flexible circuit layer 2, and the flexible substrate 3, and the working principle and preparation method of the tactile sensor, are all consistent wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com