Cross-linking modification method of antibacterial gelatin
A technology of cross-linking modification and gelatin, which is applied in medical science, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of no antibacterial properties, and achieve the effects of improving safety, good biocompatibility, and superior mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
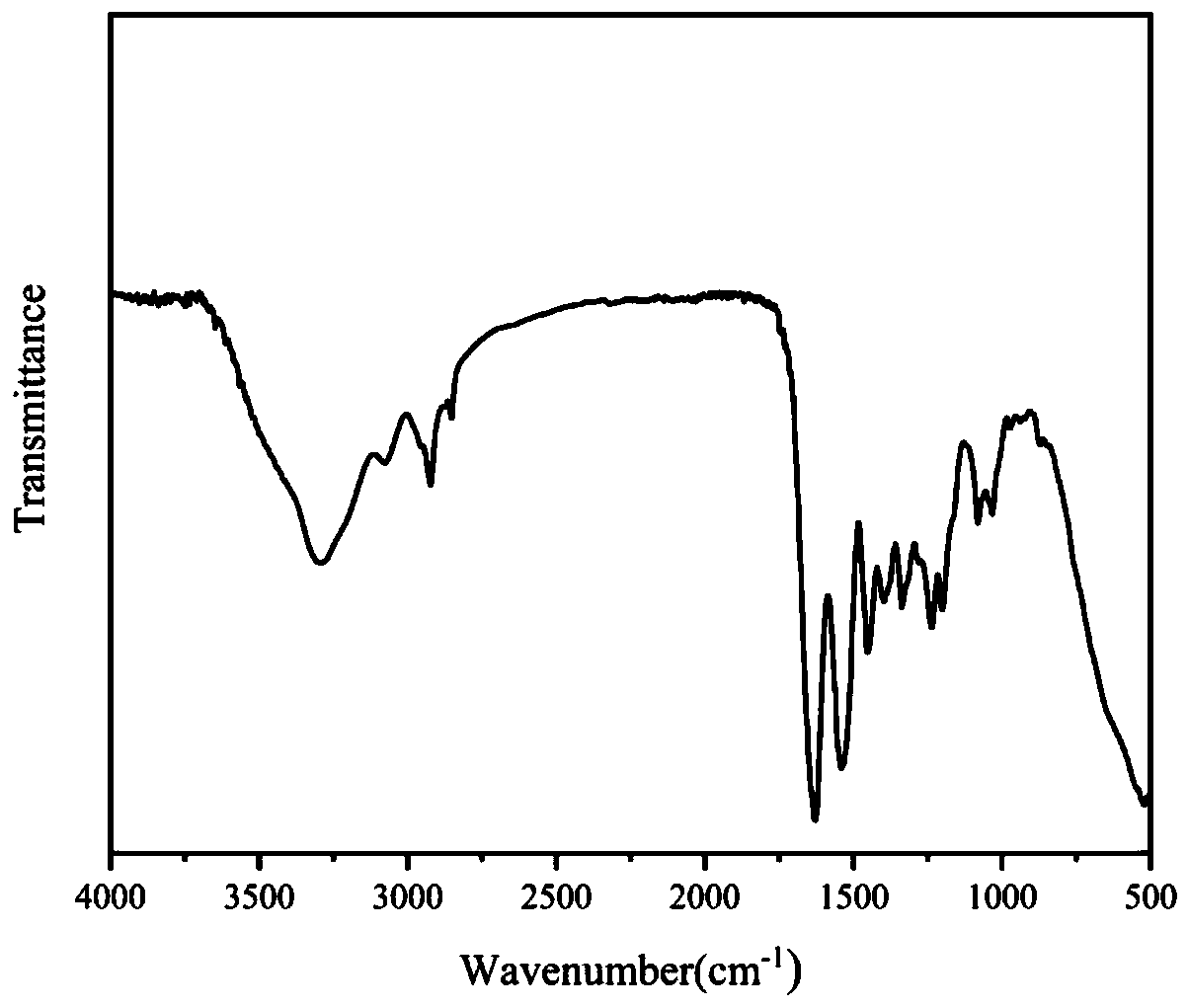
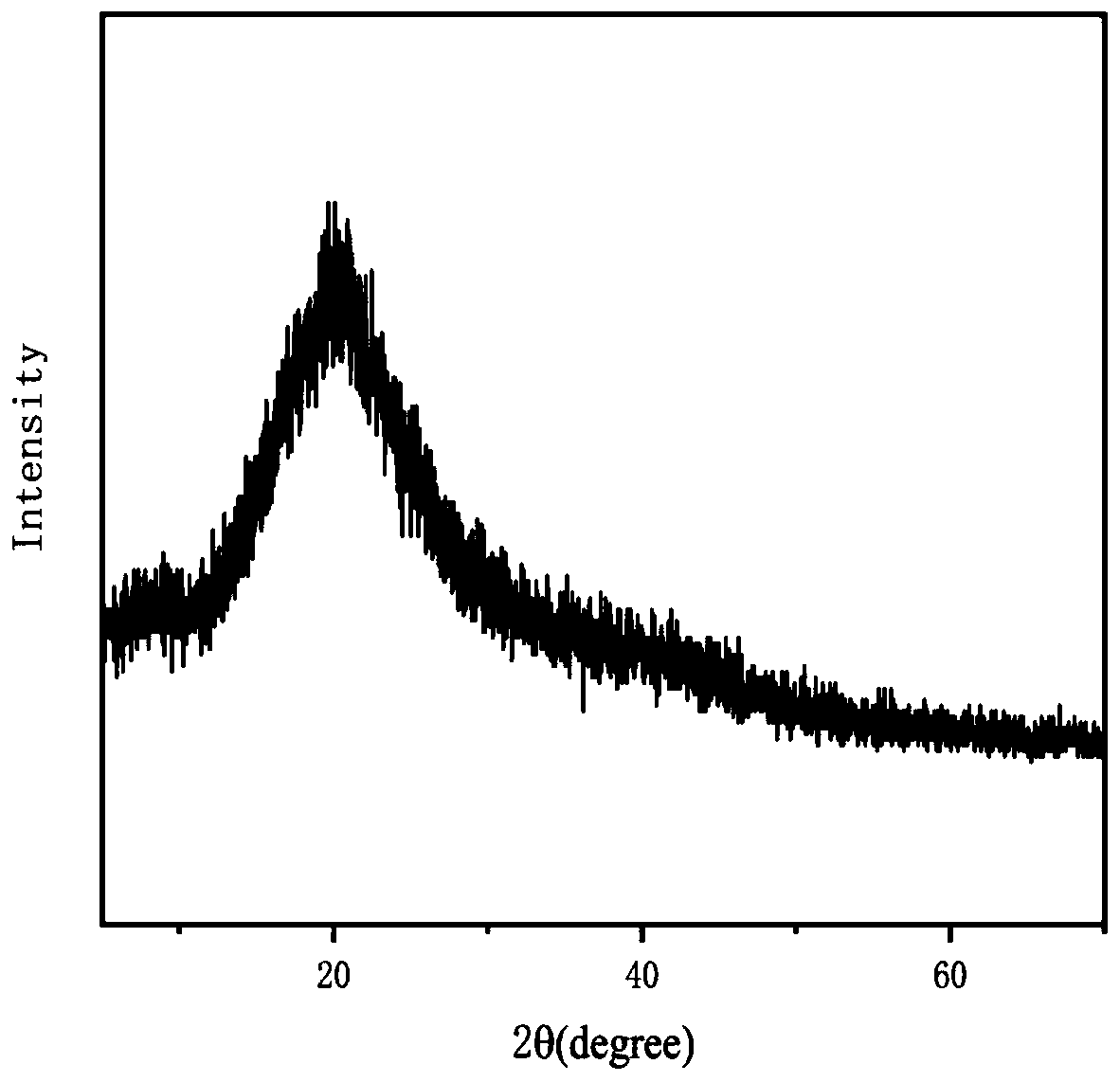
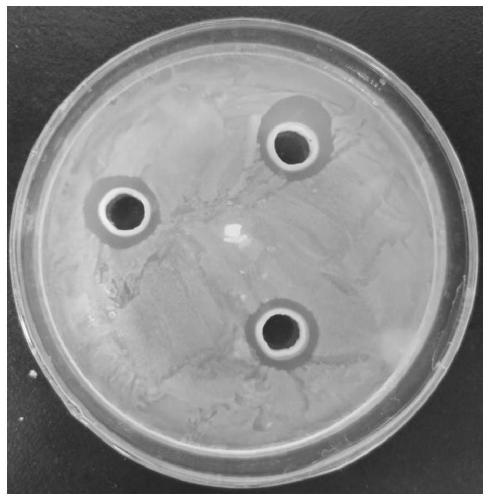
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] A cross-linking modification method of antibacterial gelatin, comprising steps as follows:
[0058] (1) Dissolve 2.5g of gelatin in 22.5g of phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 10 to prepare a gelatin solution with a mass fraction of 10wt%. After swelling at room temperature for one hour, heat and magnetically stir in a water bath at 50°C for 1 hour to dissolve.
[0059] (2) add 0.486g N in the 10wt% gelatin solution that prepares, N dimethyl glycidyl octadecyl ammonium chloride, make the mol ratio of epoxy group in gelatin primary amino group and quaternary ammonium salt be 1 : 0.5, keep the temperature at 50°C for 5h under magnetic stirring.
[0060] (3) After the quaternization reaction is completed, add 1 mL of a cross-linking agent tannic acid aqueous solution of 200 mg / mL configured in the reaction system, so that the mass ratio of the cross-linking agent to antibacterial gelatin is 0.07:1, and the concentration of the cross-linking agent to 0.76%, continue to...
Embodiment 2
[0066] A cross-linking modification method of antibacterial gelatin, comprising steps as follows:
[0067] (1) Dissolve 2.5g of gelatin in 22.5g of buffer solution with a pH of 9 to prepare a gelatin solution with a mass fraction of 10wt%. After swelling at room temperature for one hour, heat in a water bath at 50°C with magnetic stirring to dissolve for 1 hour.
[0068] (2) add 0.972gN in the 10wt% gelatin solution that prepares, N dimethylglycidyl octadecyl ammonium chloride, make the mol ratio of epoxy group in gelatin primary amino group and quaternary ammonium salt be 1: 1. Keep the temperature at 45°C for 5 hours under magnetic stirring.
[0069] (3) After the quaternization reaction is completed, add 1 mL of a cross-linking agent tannic acid aqueous solution of 200 mg / mL to the reaction system, so that the mass ratio of the cross-linking agent to antibacterial gelatin is 0.06:1, so that the cross-linking agent The concentration was 0.74%, and the temperature was kept a...
Embodiment 3
[0073] A cross-linking modification method of antibacterial gelatin, comprising steps as follows:
[0074] (1) Dissolve 2.5g of gelatin in 22.5g of phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 11 to prepare a gelatin solution with a mass fraction of 10wt%. After swelling at room temperature for one hour, heat and magnetically stir in a water bath at 50°C for 1 hour to dissolve.
[0075] (2) add 1.458gN in the 10wt% gelatin solution that prepares, N dimethylglycidyl octadecyl ammonium chloride, make the mol ratio of epoxy group in gelatin primary amino group and quaternary ammonium salt be 1: 1.5, keep the temperature at 55°C for 5h under magnetic stirring.
[0076] (3) After the quaternization reaction is completed, add 1 mL of a cross-linking agent tannic acid aqueous solution of 200 mg / mL to the reaction system, so that the mass ratio of the cross-linking agent to antibacterial gelatin is 0.05:1, so that the cross-linking agent The concentration was 0.73%, and the temperature was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com