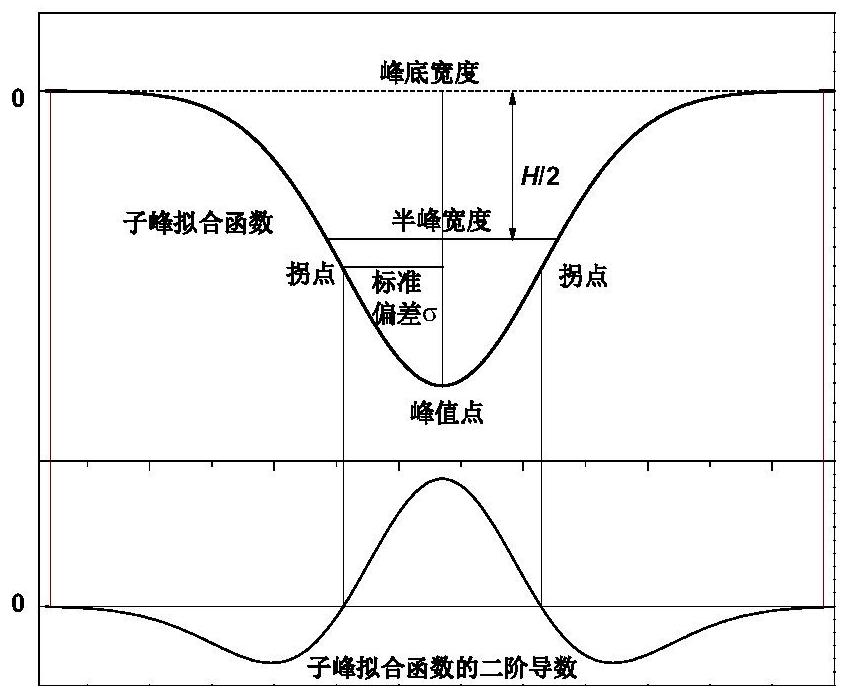
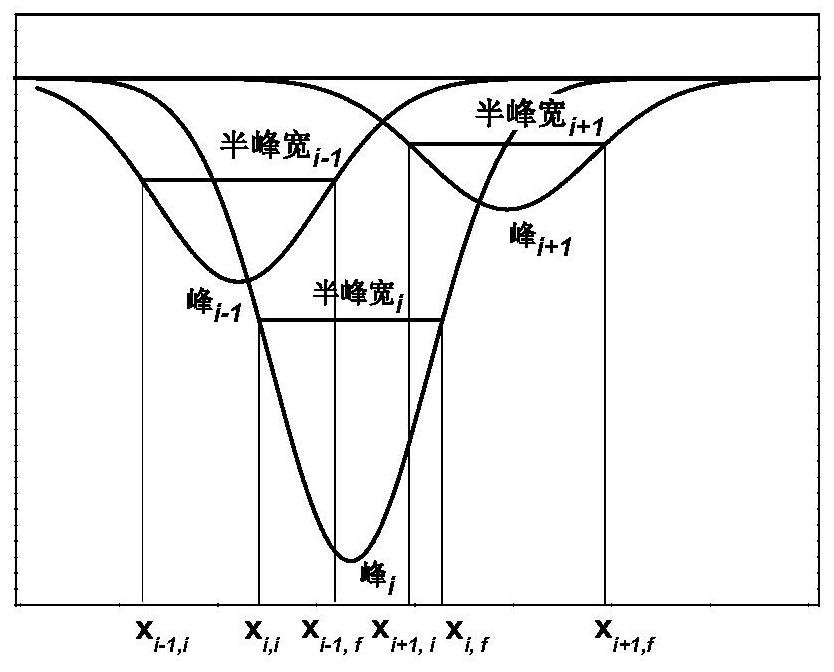
Method for peak-splitting decoupling of chemical reaction process or chemical structure of substance
A technology of chemical reaction and material structure, applied in the field of peak fitting, can solve the problems of inability to obtain peak decoupling, large error, small degree of overlap, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
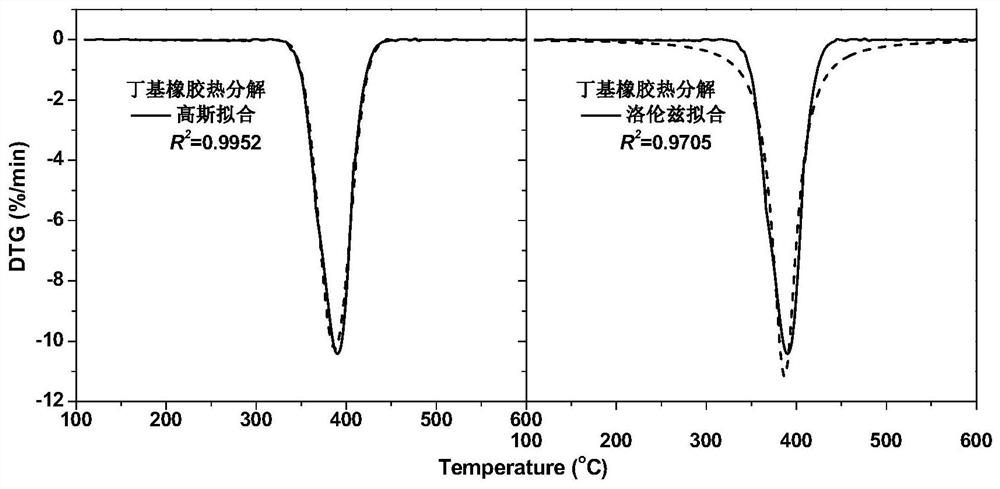
[0032] The thermal decomposition process of organic and inorganic substances was investigated by thermogravimetry. Choose butyl rubber for organic matter and calcium carbonate for inorganic matter. The mass loss rate curves (DTG curves) of the two thermal decomposition processes are shown in the accompanying drawings image 3 with Figure 4 shown. The DTG curve of butyl rubber conforms to the characteristics of normal distribution function, and the DTG curve of calcium carbonate conforms to the characteristics of non-normal distribution function. The decomposition process of butyl rubber involves the interaction between protons, which conforms to the Gaussian distribution curve.
Embodiment 2
[0034] The structural characteristics of oil shale can be obtained by 13 The C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum is analyzed, and various structures of carbon have been classified and summarized in the literature. The accompanying drawings Figure 5 The organic matter of Huadian oil shale was analyzed according to the following references 13 The C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum has carried out the peak fitting:
[0035] Zhao X, Liu Z, Lu Z, Shi L, Liu Q. A study on average molecular structure of eight oil shale organic matters and radical information during pyrolysis. Fuel, 2018, 219: 399-405.
[0036] Since NMR involves the interaction between protons, a Gaussian distribution function is used for fitting, and the fitting constraints are as follows:
[0037] (1) The peak position of each fitting sub-peak is limited according to the chemical shift range of various carbon structures in the above literature;
[0038] (2) The half-peak width of each fitted sub-peak is no...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Catalyst carbon deposition is one of the important reasons leading to catalyst deactivation. The type of carbon deposition on the catalyst can be determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Image 6 The XPS patterns of carbon-deposited catalysts with different degrees of deactivation are shown. Since the XPS measurement involves the interaction between electrons, the Lorentz distribution function is used for peak fitting, and the fitting constraints are as follows:
[0042] (1) The peak position of each fitting sub-peak is limited according to the binding energy range in the above-mentioned standard spectral library;
[0043] (2) The half-width of each fitted sub-peak does not exceed 2.8eV (binding energy);
[0044] (3) The distance between the peaks of adjacent sub-peaks is not less than 1eV (binding energy).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com