Glass heating container and manufacturing method thereof
A glass heating and container technology, which is applied to cooking utensils, water boiling utensils, and special materials for cooking utensils, etc., can solve the problems of wide use and sales constraints, low thermal efficiency, physical injury, etc., and achieve easy sales, promotion and use, and heat conduction Uniform area and improved heating efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
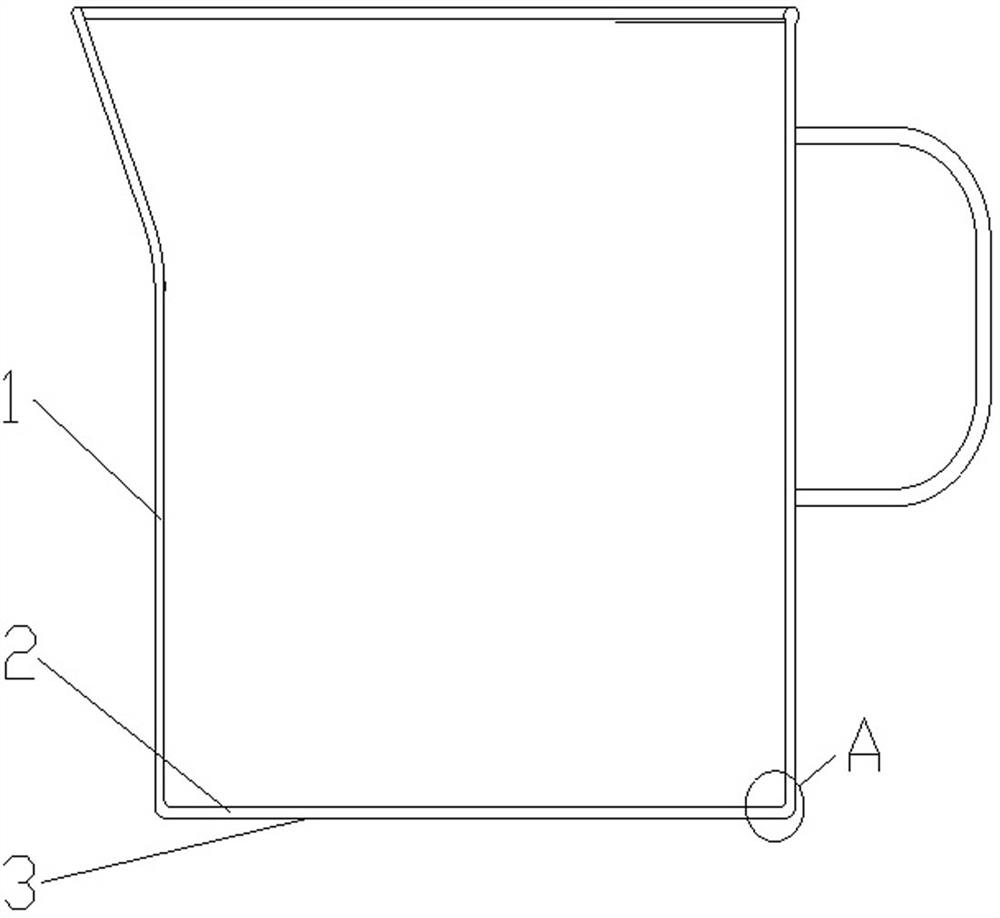
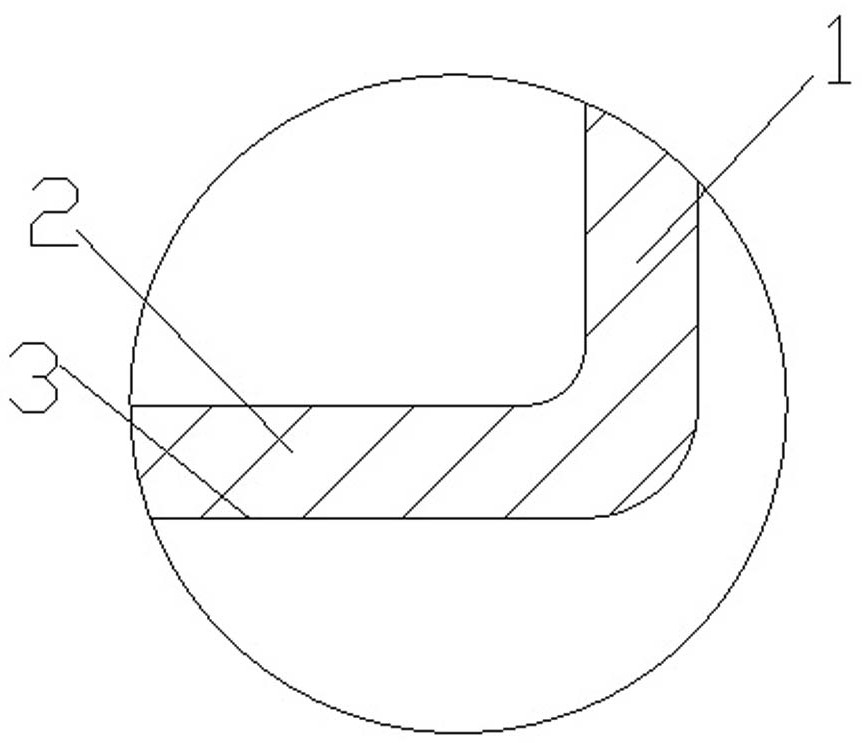
[0036] Embodiment 1, the glass heating container of the present invention includes a glass body 1 and a glass bottom 2 integrally formed with the glass body, the flatness tolerance of the bottom surface 3 of the glass bottom 2 is 0.02-0.30mm, and the bottom surface of the glass bottom 2 3. The preferred flatness tolerance is 0.03mm-0.05 mm, or 0.03-0.08 mm. The thickness of the glass bottom 2 in this embodiment is between 1.0-2.2 mm, preferably 1.3-1.5 mm. The above-mentioned glass bottom The flatness tolerance of the bottom surface and the thickness of the bottom of the glass are the best solutions obtained through infinite tests. No matter how large the flatness tolerance value of the bottom surface of the glass cup is, the heating efficiency will deteriorate, and no matter how small the flatness tolerance value is , the processing is very difficult, and a large number of defective products will be produced, thereby increasing the production cost.
[0037] The main reason wh...
Embodiment 1-1
[0042] Embodiment 1-1, the difference between this embodiment 1-1 and embodiment 1 is that the bottom surface 3 of the glass cup bottom 2 is polished by water and then sandblasted to obtain the most economical appearance surface. The particle size of the sandblasting on the bottom surface is between 0.01 and 0.1mm. This sandblasting treatment is to obtain the most economical appearance and stability requirements without causing excessive damage to the thermal conductivity.
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2, the difference between this embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that, after the bottom surface 3 of the above-mentioned glass cup is ground and cleaned (using water and alcohol to clean), the bottom surface of the glass cup is brushed with heat-conducting metal powder Coating 4, coating 4 with heat-conducting metal powder can be screen printed, the heat-conducting metal powder can be metal aluminum powder or metal copper powder, etc., the coating 4 is specifically a heat-resistant metal powder containing heat-conducting High-temperature paint, high-temperature-resistant paint can be purchased on the market, and heat-conducting metal powder is mixed into it. The thickness of the coating 4 is 0.005-0.05mm; The coating 4 can further improve the heating efficiency. Through the same test as in Example 1, it only takes about 12 minutes to heat 1200 ml of water in the glass heating container of this application from 25 ° C to 100 ° C, and the heating efficiency is hi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com