Multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR primer, probe and kit for detecting clostridium difficile producing toxins
A multiple fluorescence quantitative and Clostridium difficile technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of limited popularization and application, inability to detect binary toxins, etc., to avoid mutual interference and shorten detection time , the effect of high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1 Design of Multiplex Fluorescent Quantitative PCR Primers and Probes for Detecting Toxigenic Clostridium difficile
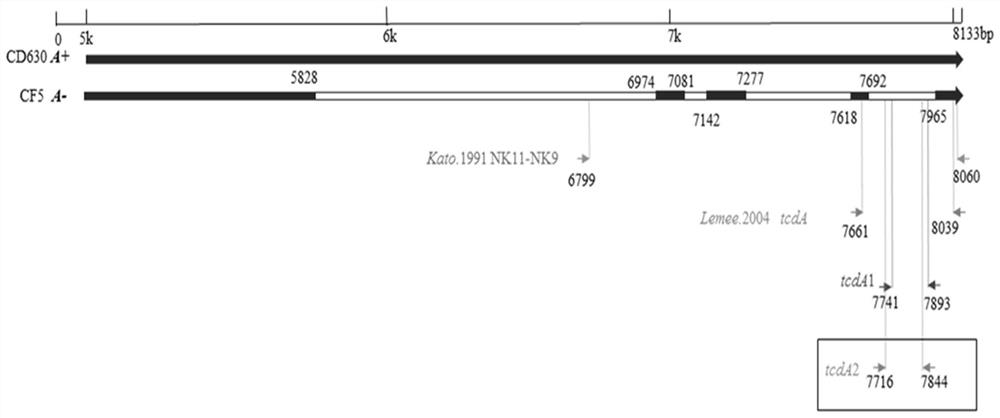
[0051] The present invention takes the tcdA, tcdB and cdtB genes of toxigenic Clostridium difficile as detection targets, and through the tcdA, tcdB and cdtB gene sequences of different molecular types of toxigenic Clostridium difficile reported in the NCBI database, as well as the complete clinical isolates The genome sequencing sequence was analyzed and compared to clarify the genetic characteristics and sequence mutations of the genes. The primer probe design regions of the tcdA, tcdB and cdtB genes were respectively determined, and several pairs of specific primers and probes were designed for the design regions. BLAST was performed online by NCBI to exclude its non-specific binding to other species, and it was further verified and screened through experiments. Among them, the tcdA gene sequence needs special emphasis. At present, the common ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2 Multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR detection method for toxigenic Clostridium difficile
[0068] The optimal primers and probes determined in Example 1 optimize the reaction conditions of multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR, wherein, in order to simultaneously and efficiently amplify the toxin coding genes tcdA, tcdB and cdtB, the optimization of the annealing temperature of the PCR reaction conditions The process is as follows:
[0069] The reaction conditions of multiplex fluorescent quantitative PCR are as follows: the first step, pre-denaturation, 95°C, 20s, one cycle; the second step, PCR reaction, 95°C, 3s, 58°C, 30s, 40 cycles.
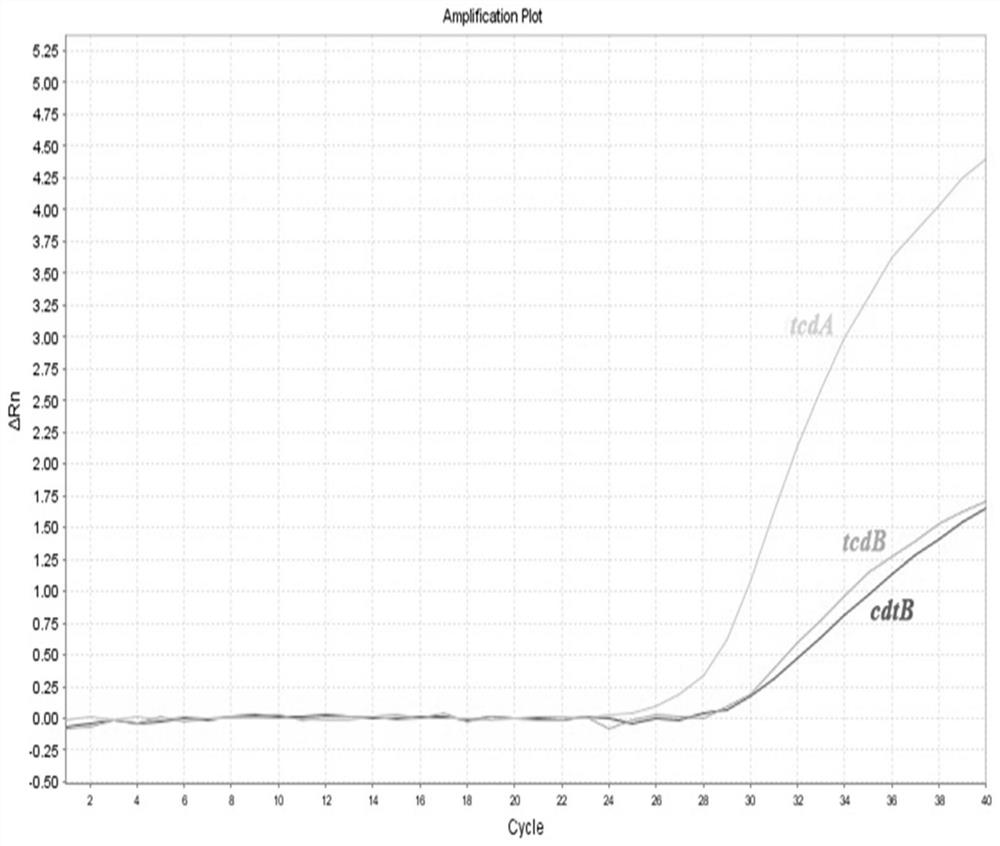
[0070] The annealing temperatures were set at 56°C, 58°C and 60°C, respectively, and the results showed that the amplification efficiencies at each annealing temperature were shown in Table 1. The results showed that the three genes had better amplification efficiencies at 58°C ( figure 2 ), therefore, 58°C was chosen...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3 Sensitivity of fluorescent quantitative PCR to the detection of three Clostridium difficile toxin genes
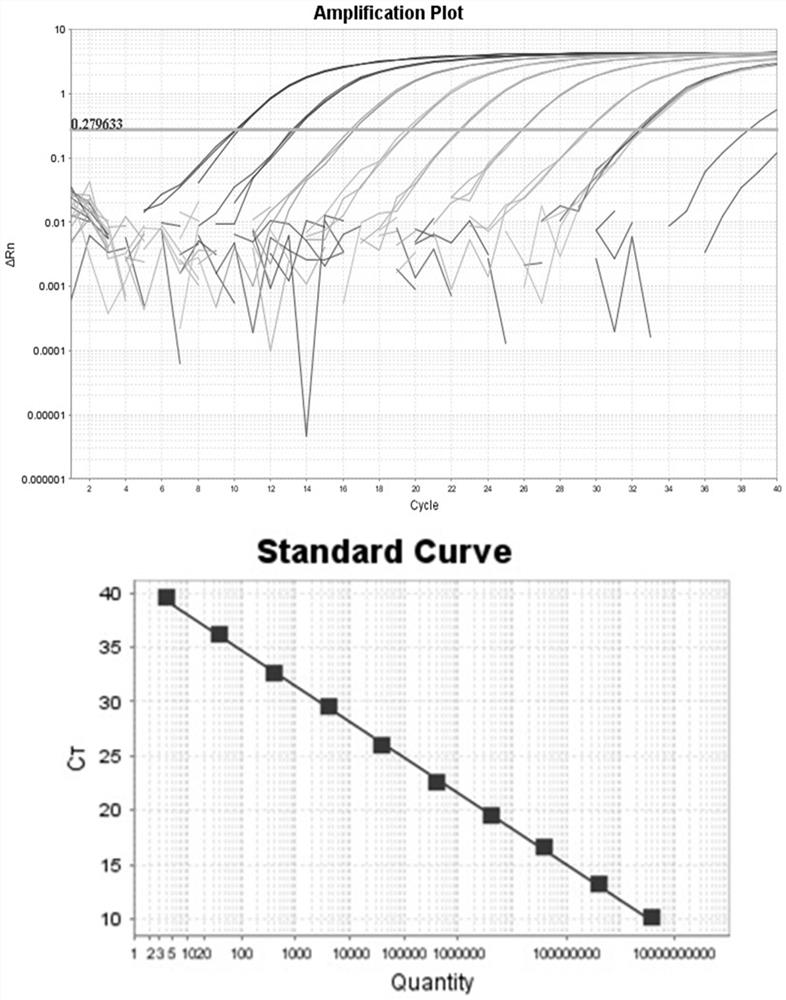
[0081] Utilize embodiment 1 to determine specific primers and probes and the detection method determined in embodiment 2 to analyze the sensitivity of three kinds of Clostridium difficile toxin gene detection, take the lg value of standard concentration template as the abscissa, and take the corresponding Ct value as The vertical axis is to establish the detection standard curve of the detection method against the three toxin coding genes. details as follows:
[0082] 1. Toxin A gene (tcdA)
[0083] The concentration of recombinant plasmid DNA was 123 μg / μL, and the calculated plasmid copy number concentration was 5.53×10 10 copies / μL, the plasmid was diluted 10 times to obtain 5.53×10 0~ 5.53×10 9 Copies / μL total of 10 gradient standard plasmids. These 10 gradient standards were used as templates for fluorescence quantitative PCR amplification, and t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com