Method for exciting polaritons of two-dimensional Van der Waals material
A polariton, chemical vapor deposition technology, applied in electrical components, antennas and other directions, can solve the problem of difficult excitation of polariton
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] This embodiment provides a method for exciting a single-layer hexagonal boron nitride polariton, and the method includes the following steps:
[0049] The single-layer hexagonal boron nitride is irradiated with 60keV high-energy electrons to realize the excitation of the single-layer hexagonal boron nitride polaritons.
[0050] Using 60keV high-energy electrons to irradiate a single layer of hexagonal boron nitride, ultra-high-resolution images can be obtained.
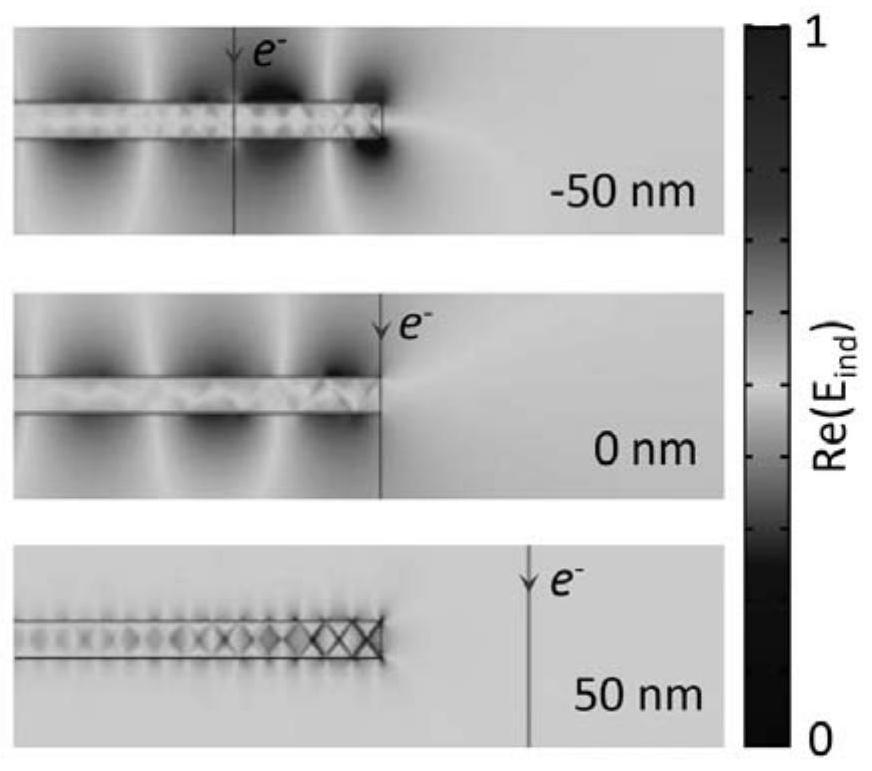
[0051] Moreover, due to the very short wavelength of high-energy electrons, higher momentum compensation can be improved. The momentum compensation provided when irradiating monolayer hexagonal boron nitride can obtain monolayer hexagonal boron nitride signals in a wide momentum range, so it can efficiently excite monolayer Phonon polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride.
Embodiment 2
[0053] This embodiment provides a method for exciting multilayer hexagonal boron nitride polaritons, the method comprising the following steps:
[0054] The multilayer hexagonal boron nitride is irradiated with high-energy electrons of 60 keV to realize the excitation of polaritons of the multilayer hexagonal boron nitride, and the thickness of the multilayer hexagonal boron nitride is 10 nm.
[0055] Using 60keV high-energy electrons to irradiate multi-layer hexagonal boron nitride, ultra-high-resolution images can be obtained.
[0056] Moreover, due to the very short wavelength of high-energy electrons, higher momentum compensation can be improved, and the momentum compensation provided when irradiating multilayer hexagonal boron nitride can obtain multilayer hexagonal boron nitride signals in a wide momentum range, so it can efficiently excite multilayer Phonon polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride.
Embodiment 3
[0058] This embodiment provides a method for exciting a single-layer hexagonal boron nitride polariton, and the method includes the following methods:
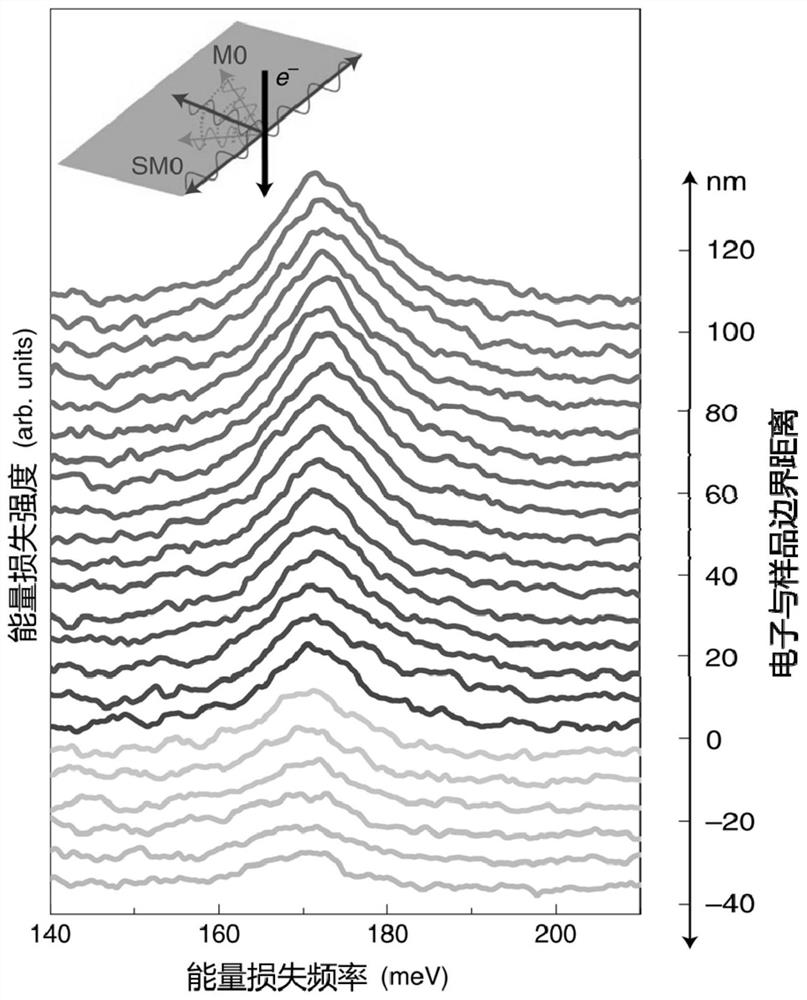
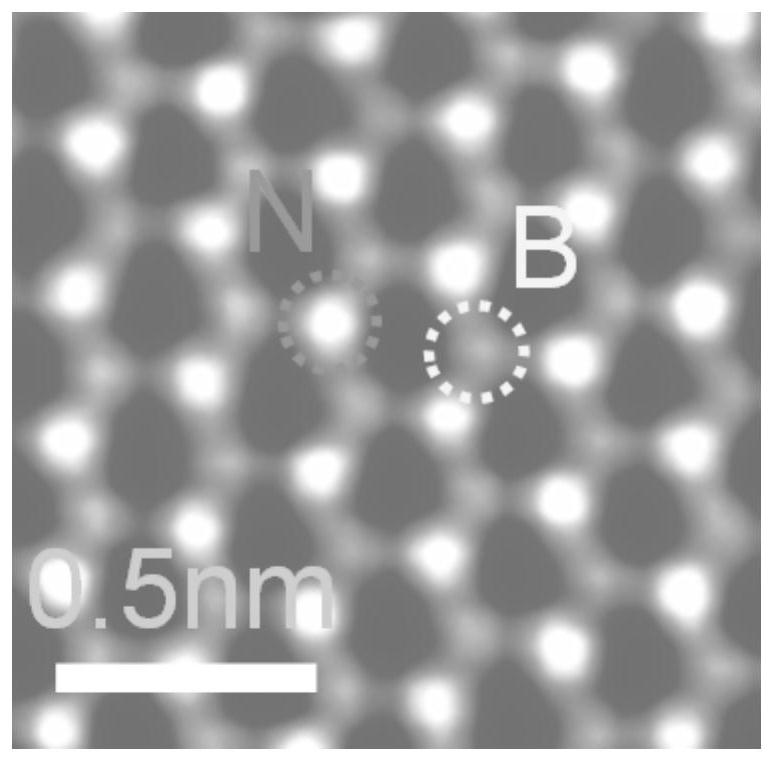
[0059] The single-layer hexagonal boron nitride prepared by the chemical vapor deposition method is placed on a copper substrate, and the copper substrate is evenly covered with square through holes, the side length of the square through holes is 100 μm, and a carbon support film is arranged in the through holes , the surface of the carbon support film is provided with a support hole with an equivalent diameter of 2 μm, and the air in the support hole makes the monolayer hexagonal boron nitride in a suspended state in the support hole; then use 60keV high-energy electrons to irradiate the single layer of the suspended part A layer of hexagonal boron nitride is used to realize the excitation of polaritons in a single layer of hexagonal boron nitride.
[0060] The electron energy loss spectrum when irradiating a single layer of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com