Human gallbladder stem cell acquisition and long-term in-vitro culture method
An acquisition method and in vitro culture technology, which are applied in cell dissociation methods, artificial cell constructs, cell culture active agents, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing preparation costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
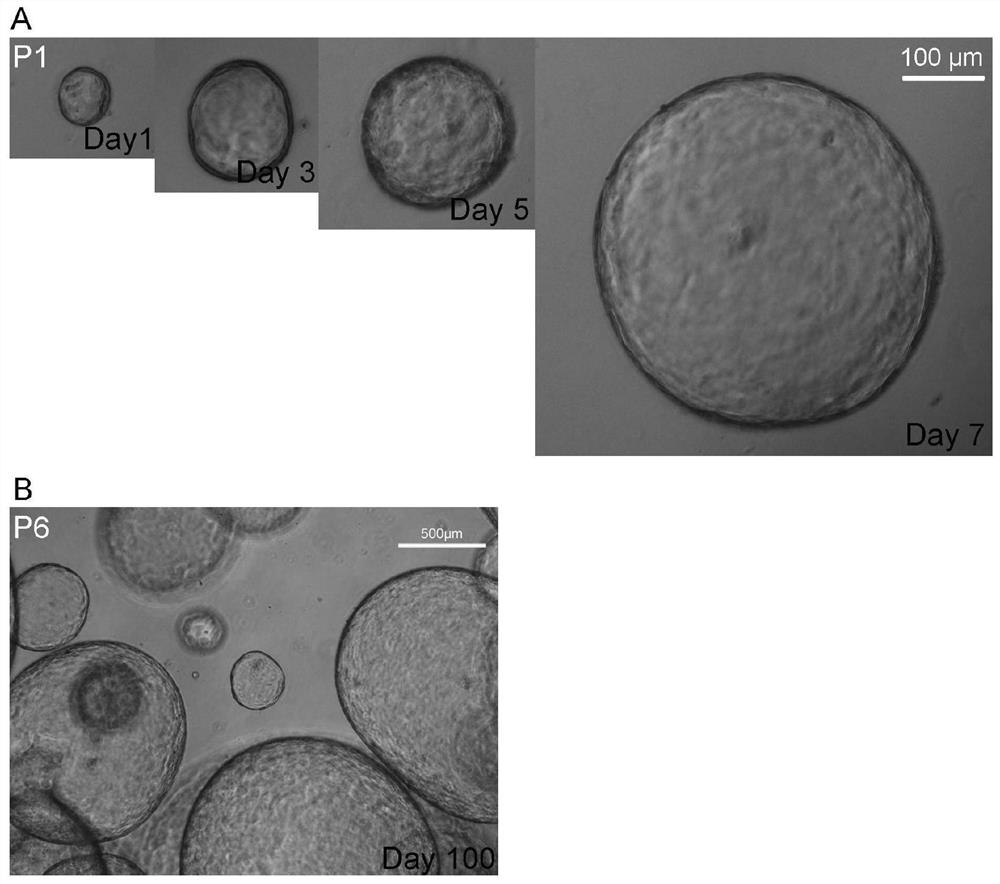
[0051] Example 1. Rapid isolation of human gallbladder stem cells
[0052] A. Obtaining cells from the mucosal layer of the inner wall of the gallbladder
[0053] After the human gallbladder tissue is obtained (removed by hospital surgery), it is stored in liquid basal medium and transported to the laboratory; the tissue is taken out in a sterile environment, cut longitudinally along the tissue and fully expanded, and washed repeatedly with sterile PBS Tissue until the color of the solution is clear and bloodless; transfer the tissue to a 10cm culture dish containing pre-cooled basal medium, scrape off the mucosal layer cells of the inner wall of the gallbladder with a sterile disposable scalpel blade, wash the inner wall of the gallbladder with the basal medium, Gallbladder tissue was discarded.
[0054] B. Obtain single cells from the mucosal layer of the inner wall of the gallbladder
[0055] Pipette the culture medium containing the cells into a 50ml centrifuge tube, cen...
Embodiment 2
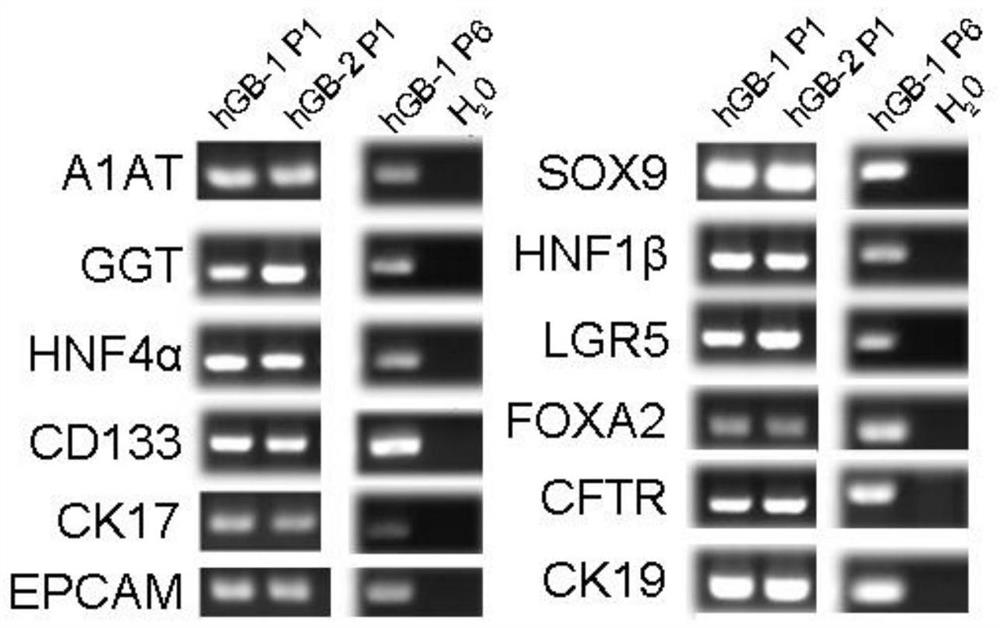
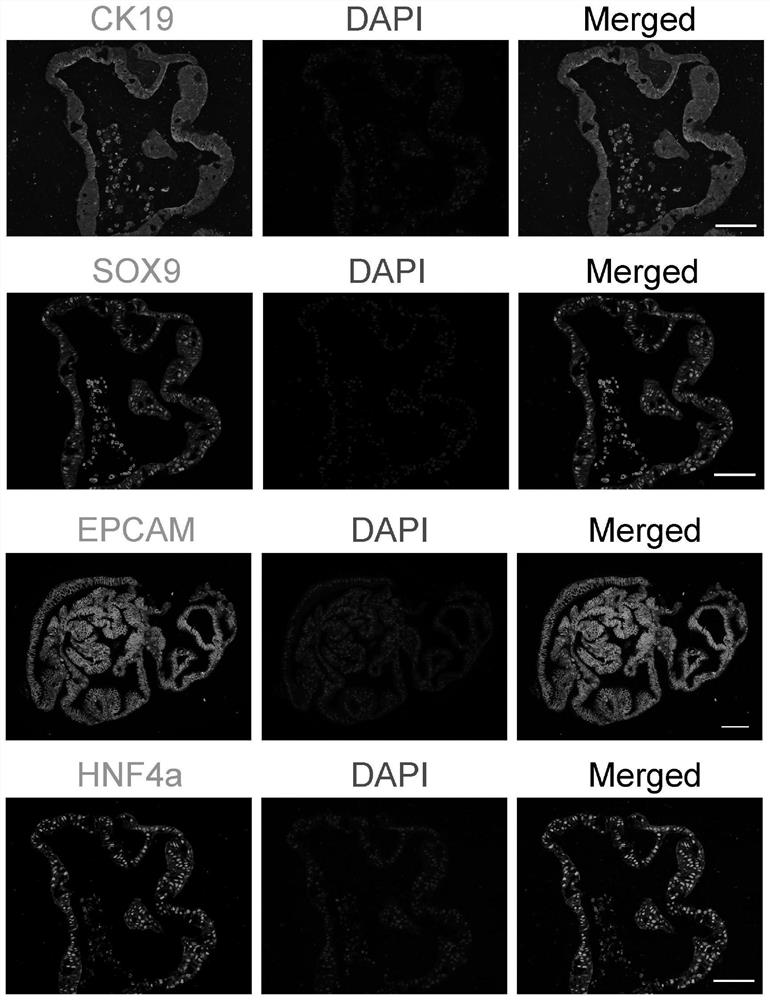
[0061] Example 2. Expansion and culture of human gallbladder stem cells
[0062] 1. Expansion of cells
[0063] When the cell clones are full (7-10 days), they can be digested and passaged. The specific steps are: (A) Take out the supernatant and discard it, add pre-cooled liquid basal medium, use a 1ml pipette gun to absorb the Matrigel containing cells, and blow repeatedly until the colloid is broken, so that the clumps are evenly distributed in the liquid . (B) Pipette the cell suspension in each three wells into a 15ml centrifuge tube, make up the liquid to 14ml, and use a 25ml pipette to mix the cell suspension evenly. Centrifuge at 400g for 5 minutes and discard the supernatant as much as possible. Add TrypLE digestion solution, place in a 37°C water bath for 10 minutes for digestion, and shake appropriately during the period. (C) After digestion, add liquid basal medium to 14ml, mix well, centrifuge at 400g for 5 minutes, discard the supernatant, repeat washing 2 ti...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3. Inducing human gallbladder stem cells to differentiate into cells with mature hepatocyte function
[0075] When the cell growth density is about 50%, replace with hepatic differentiation medium. The differentiation medium includes N-acetylcysteine, R-spondin, nicotinamide, recombinant human epidermal growth factor, recombinant human hepatocyte growth factor, TGFβ inhibitor, dexamethasone and oncostatin M to induce mature hepatocytes required components.
[0076] After two weeks of culture, the differentiated cells can differentiate and have the ability to take up low-density lipoprotein, store glycogen and synthesize fat ( Figure 6 ).
[0077] The above results show that the hepatic differentiation system established in the present invention can induce the differentiation of human gallbladder stem cells into cells with the function of mature hepatocytes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com