Method for improving corrosion resistance of neodymium-iron-boron waste recycled magnet
A technology of waste recycling and NdFeB, applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inductors/transformers/magnets, etc., can solve the problems of magnet main phase grain shedding, electrochemical corrosion, magnet corrosion, etc., to achieve uniform distribution, Effect of improving corrosion resistance and improving utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
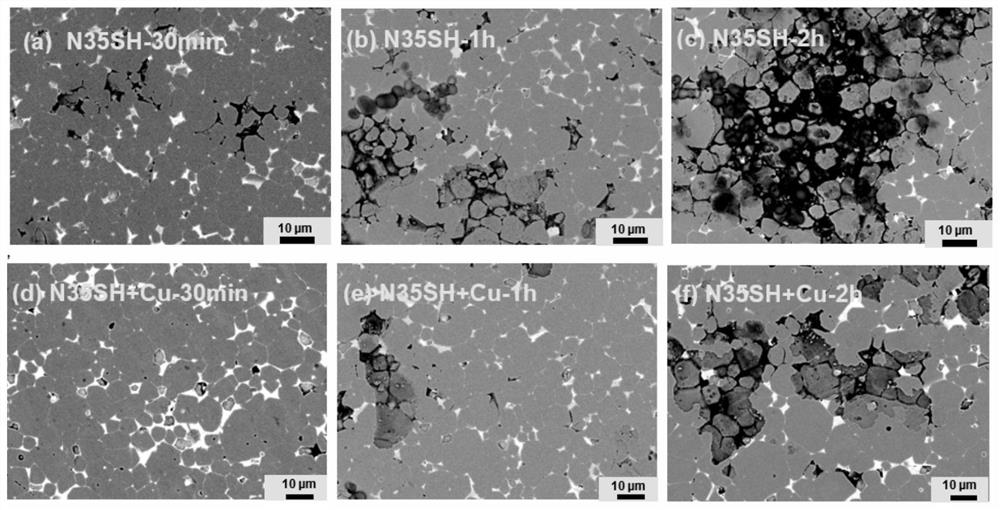
[0022] Step 1), with N35SH brand (H cj : 19~20kOe, (BH) max : 34~35MGOe, B r : 11 ~ 12kGs) NdFeB magnet as the main alloy, take the NdFeB magnet with a mass ratio of 99.7%, and carry out hydrogen cracking treatment at 590°C and 0.6MPa hydrogen pressure. After dehydrogenation, the mass ratio 0.3% copper powder with an average particle size of 1 μm was subjected to jet milling at a speed of 5000 rpm to prepare mixed magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3 μm.
[0023] Step 2), the mixed powder is subjected to compression molding orientation under a 2T orientation magnetic field, and then cold isostatic pressing under a pressure of 200MPa to obtain a green body of a magnet;
[0024] Step 3), sintering the obtained magnet green body at 1040°C for 2h, then heat-treating at 850°C for 3h in the next step, and then heat-treating in the second step at 550°C for 4h, to obtain a NdFeB grain boundary reconstructed magnet;
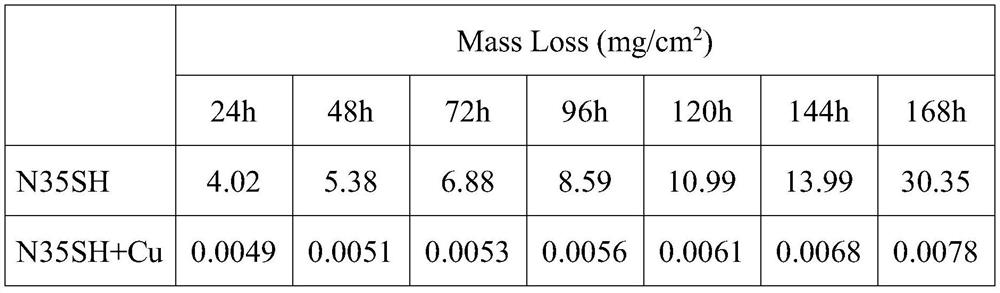
[0025] The weight loss data of the obtained grain b...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Step 1), with 38H grade (H cj : 15~18kOe, (BH) max : 35~38MGOe, B r: 12 ~ 13kGs) NdFeB magnets as the main alloy, take NdFeB magnets with a mass ratio of 99.8%, and carry out hydrogen cracking treatment at 590 ° C and 0.6 MPa hydrogen pressure. After dehydrogenation, the mass ratio 0.2% of copper powder with an average particle size of 1 μm is subjected to jet milling, and the jet mill speed is 5000 rpm to prepare mixed magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3 μm;
[0036] Step 2), the mixed powder is subjected to compression molding orientation under a 2T orientation magnetic field, and then cold isostatic pressing under a pressure of 200MPa to obtain a green body of a magnet;
[0037] Step 3), sintering the obtained magnet green body at 1040°C for 2h, then heat-treating at 850°C for 3h in the next step, and then heat-treating in the second step at 550°C for 4h, to obtain a NdFeB grain boundary reconstructed magnet;
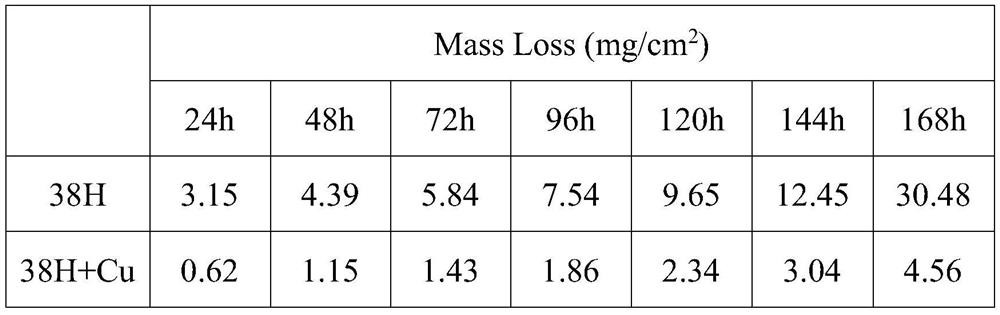
[0038] The weight loss data obtained b...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Step 1), with N40 brand (H cj : 10~15kOe, (BH) max : 38~40MGOe, B r : 12~13kGs) NdFeB magnets as the main alloy, take the NdFeB magnets with a mass ratio of 99.9%, and carry out hydrogen cracking treatment at 590°C and 0.6MPa hydrogen pressure. After dehydrogenation, the mass ratio 0.1% of copper powder with an average particle size of 1 μm is subjected to jet milling at a speed of 5000 rpm to prepare mixed magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3 μm;
[0048] Step 2), the mixed powder is subjected to compression molding orientation under a 2T orientation magnetic field, and then cold isostatic pressing under a pressure of 200MPa to obtain a green body of a magnet;
[0049] Step 3), sintering the obtained magnet green body at 1040°C for 2h, then heat-treating at 850°C for 3h in the next step, and then heat-treating in the second step at 550°C for 4h, to obtain a NdFeB grain boundary reconstructed magnet;
[0050] The weight loss data obtained by exposing th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com