Cr (VI) removal and recovery method based on electrochemical oxidation-reduction sequential conversion
A recycling method, electrochemical technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, contaminated groundwater/leachate treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problem of difficult recovery of chromium resources, large chromium-containing sludge, and high treatment and disposal costs. problems, to achieve the effect of automatic control and equipment, easy automatic control and equipment, and beneficial to recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
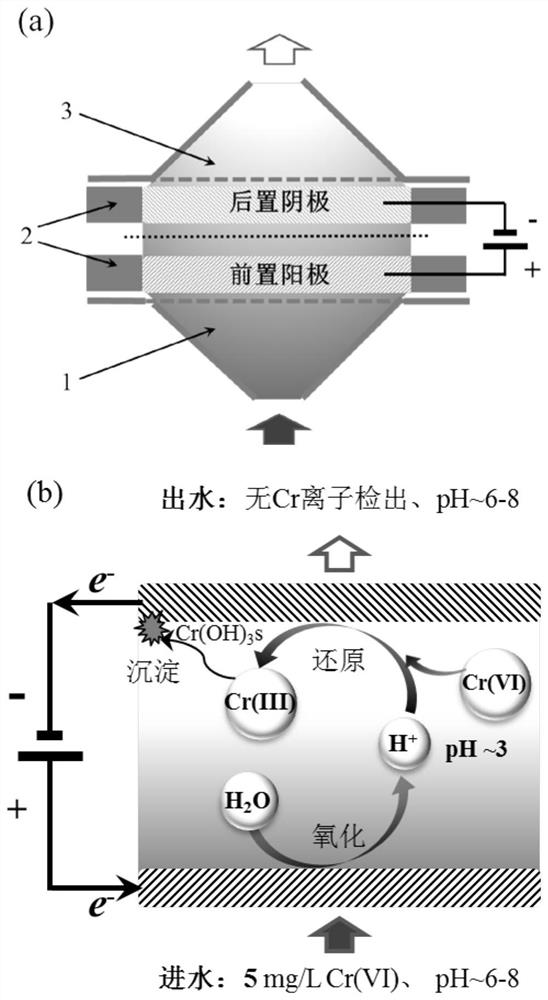
[0027] Using a graphene sponge with a thickness of 5mm as the cathode and anode electrodes, a 5cm-diameter internal filter device based on sequential oxidation-reduction reactions was constructed. The schematic diagram of the device is shown in figure 1 Figure a in. Supply voltage 3.0V, flux 1000L / h / m 2 Under continuous treatment of 5 mg / L Cr(VI) solution (pH 7), no Cr ions (including Cr(VI) and Cr(III)) can be detected in the effluent within 24 hours of continuous operation. When the total Cr ion concentration in the effluent water is higher than 50 μg / L, immediately turn off the pump and the voltage power supply, then connect the cathode and anode of the device to the positive and negative poles of the power supply respectively, apply a reverse voltage of 3V, and let it stand for 10 minutes to react. The solution in the electrode is discharged from the reactor to obtain a Cr(III) solution that is about 3000 times concentrated (compared with the concentration of Cr(VI) in th...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Using graphitized carbon felt with a thickness of 10mm as the cathode and anode electrodes, an in-electrode filter electrochemical device with a diameter of 10cm based on sequential oxidation-reduction reactions was constructed. Supply voltage 3.5V, flux 1000L / h / m 2 Under continuous treatment of 5 mg / L Cr(VI) solution (pH 8), no Cr ions (including Cr(VI) and Cr(III)) can be detected in the effluent within 40 hours of continuous operation. When the total Cr ion concentration in the effluent water is higher than 50 μg / L, immediately turn off the pump and the voltage power supply, then connect the cathode and anode of the device to the positive and negative poles of the power supply respectively, apply a reverse voltage of 3V, and let it stand for 5 minutes to react. The solution in the electrode is discharged from the reactor to obtain a Cr(III) solution that is about 1500 times concentrated (compared with the concentration of Cr(VI) in the feed water), which is convenien...
Embodiment 3
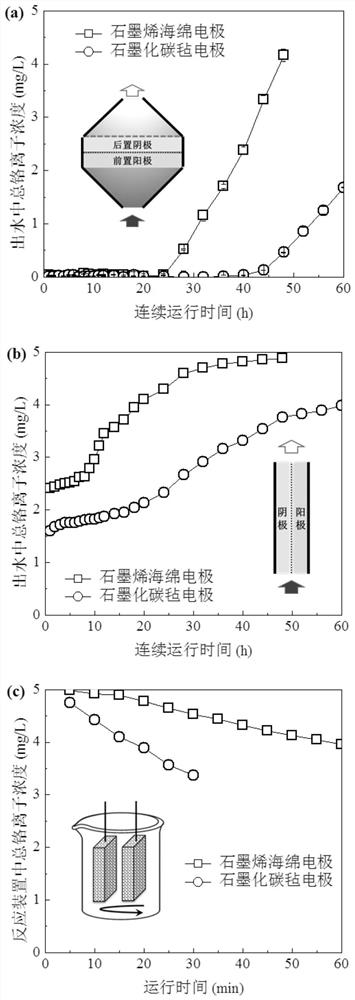
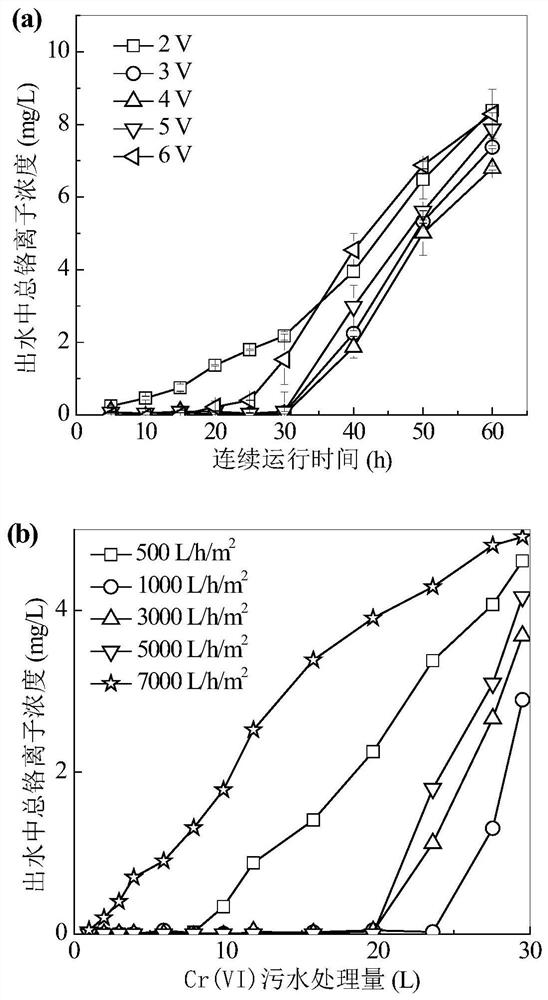
[0035] Using a graphene sponge with a thickness of 5mm as the cathode and anode electrodes, a 5cm-diameter internal filter device based on sequential oxidation-reduction reactions was constructed. The schematic diagram of the device is shown in figure 1 Figure a in. Investigate the influence of operating supply voltage and flux on Cr(VI) (5mg / L Cr(VI) and pH is 6)) removal ability, such as image 3 As shown in a in the figure: as the supply voltage increases, the Cr(VI) removal performance of the device first increases and then decreases. With a supply voltage of 3-5V, it can achieve no Cr ions in the water within 30 hours of continuous operation ( Including Cr(VI) and Cr(III)) detection. The device was compared at 3.0V and flux 500-7000L / h / m 2 Under the treatment performance of Cr(VI) sewage (sewage treatment capacity = flux * treatment time * electrode area), such as image 3 As shown in b in the figure: as the flux increases, the device's Cr(VI) processing capacity first...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com