Hypochlorous acid preparation device for preparing epoxide by monoacid chlorohydrin method and use method
A technology of epoxy and monoacid chlorohydrins, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, chemical/physical/physical chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of inability to guarantee the balance of chlorine gas in the chlor-alkali industry, rising total product costs, Enterprise survival difficulties and other problems, to achieve the effect of complete recovery, reduce equipment investment, and less corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
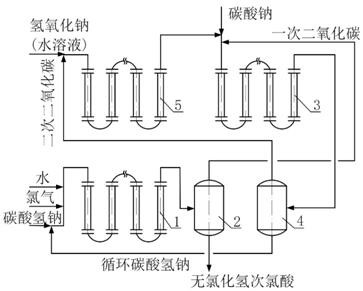
[0033]A hypochlorous acid preparation device for the production of epoxides by the single-acid chlorohydrin method described in this embodiment includes a hypochlorous acid reactor 1, a first gas-liquid separation device 2, a first carbon dioxide reactor 3, and a second gas-liquid Separation device 4, second carbon dioxide reactor 5, connecting pipelines between equipment, valves, medium delivery devices, control and display instruments and accessories; hypochlorous acid reactor 1, first carbon dioxide reactor 3, and second carbon dioxide reactor 5 are A heat-exchanging jacketed tubular reactor with chemical fillers provided continuously or intermittently; hypochlorous acid reactor 1 is provided with water, chlorine, sodium bicarbonate and circulating sodium bicarbonate inlets and the reactor reactant outlet, the first The gas-liquid separation device 2 is provided with a hypochlorous acid reactor 1 material inlet, a primary carbon dioxide outlet and a hydrogen chloride-free hy...
Embodiment 2
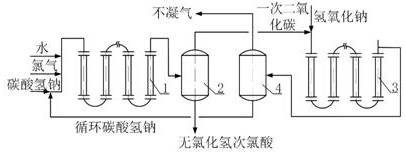
[0045] Embodiment 2 is substantially the same as Example 1, and the difference is that the second carbon dioxide reactor 5 is not provided with the device, and the sodium carbonate inlet of the first carbon dioxide reactor 3 is changed into an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide inlet, and the aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and Once carbon dioxide enters the first carbon dioxide reactor 3, sodium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide to generate sodium carbonate, and the process of sodium carbonate further reacting with carbon dioxide to generate sodium bicarbonate is carried out in the first carbon dioxide reactor 3. The secondary carbon dioxide outlet of the second gas-liquid separation device 4 is used as the non-condensable gas outlet.
[0046] The schematic diagram of the device in this embodiment is shown in figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
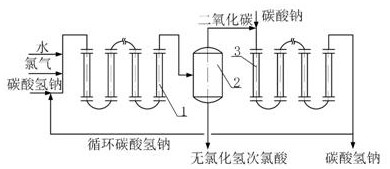
[0048] Embodiment 3 is substantially the same as Example 1, and the difference is that the device used is not provided with the second carbon dioxide reactor 5 and the second gas-liquid separation device 4, and adopts sodium carbonate aqueous solution in the first carbon dioxide reactor 3 with the first carbon dioxide reactor 3 from the first The primary carbon dioxide reaction of the gas-liquid separation device 2 generates sodium bicarbonate, and a part of the aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution from the first carbon dioxide reactor 3 enters the hypochlorous acid reactor 1 instead of adding sodium bicarbonate, and the other part is used to make commercial sodium bicarbonate .
[0049] The schematic diagram of the device in this embodiment is shown in image 3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com