Hazardous waste rotary kiln incineration process
A rotary kiln and hazardous waste technology, applied to incinerators, combustion methods, combustion types, etc., can solve problems such as heat loss, low air excess coefficient, low heat loss rate, etc., to achieve reduced heat loss, low air excess system , the effect of increasing the combustion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
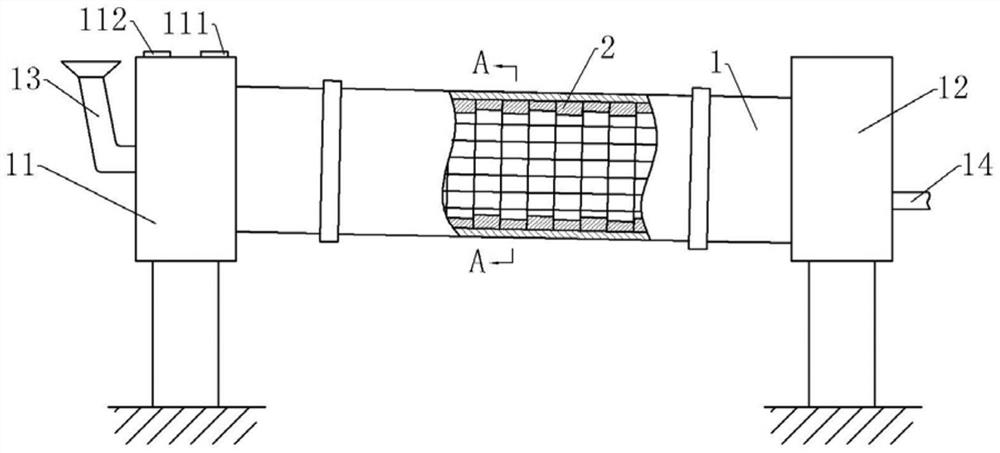
[0040]The incineration process of hazardous waste rotary kiln is realized by using hazardous waste rotary kiln. Hazardous waste rotary kiln is basically as attachedfigure 1 As shown, it includes a support frame and a cylinder 1 rotatably connected to the support frame. The cylinder 1 is inclined downwards from left to right. The inclination angle of the cylinder 1 is set according to actual needs. In this embodiment, the cylinder 1 The tilt angle is 10°. The support frame is also fixed with a motor, the drive shaft of the motor is coaxially fixed with a driving gear, and the cylinder 1 is coaxially fixed with a driven ring gear meshing with the driving gear, so the motor can drive the driving gear to rotate, and through the slave The transmission of the movable gear ring realizes the rotation of the cylinder 1.
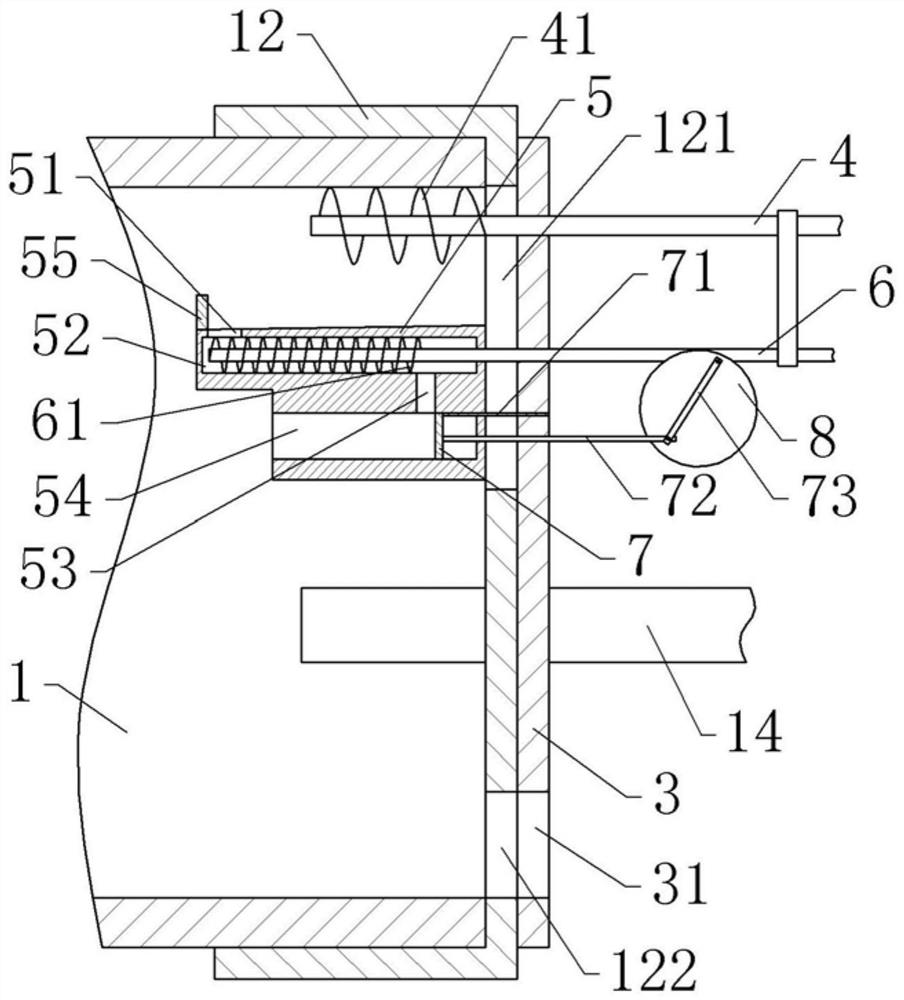
[0041]The left end of the cylinder 1 is rotatably connected with a kiln head cover 11, and the right end of the cylinder 1 is rotatably connected with a kiln tail cover 12. A ...
Embodiment 2
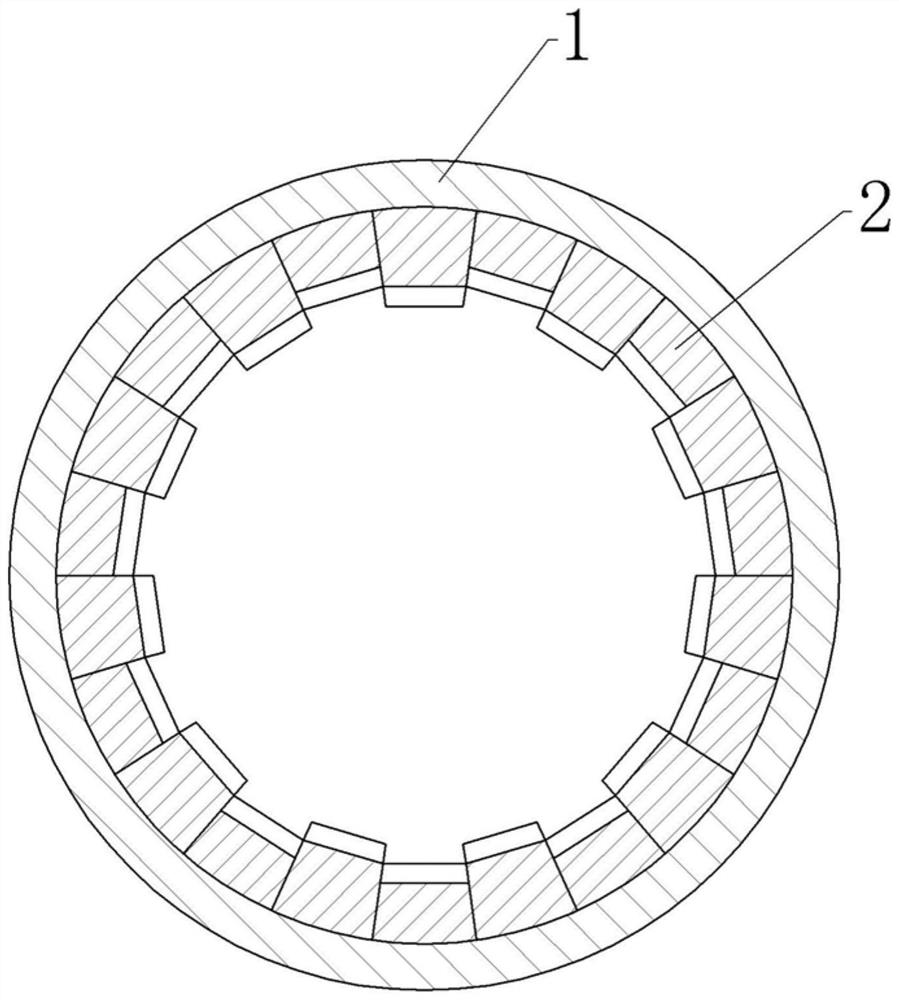
[0064]The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is only that, asFigure 5 As shown, in this embodiment, each material dispersion structure includes 8 groups of 2 groups of refractory bricks, and each group of 2 groups of refractory bricks includes one higher refractory brick 2 and three lower refractory bricks 2. The higher refractory brick 2 The height difference between the lower refractory brick 2 and the lower refractory brick 2 is 50mm or 100mm. This embodiment is preferably 50mm, and the adjacent higher refractory bricks 2 are the lower refractory bricks 2; that is, the structure of each material is dispersed Refractory bricks 2 are set in cycles of a, a, a, a+50mm, a...a+50mm, a, a, a, a+50mm.
[0065]CombineFigure 4 As shown, each group of material dispersion structure in this embodiment includes a higher material dispersion structure and three lower material dispersion structures. The height difference between the higher material dispersion structure and the lower ma...
Embodiment 3
[0068]The only difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that D=1.5d in this example; through model simulation calculations, a conclusion similar to Example 1 is reached, that is, the excess air coefficient of hazardous waste incineration is controlled within 0.8~ 1.0 to control the air supply, the rotary kiln's hazardous waste incineration heat loss rate is less than 3%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com