Voltage and current quasi-fixed-frequency control device and method
A technology of control device and voltage detection circuit, which is applied in the direction of control/regulation system, output power conversion device, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of wide range of switching frequency variation and the influence of output capacitor equivalent series resistance on stability, etc., to achieve The switching frequency range is small, the effect of overcoming low light load efficiency and small output voltage ripple
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
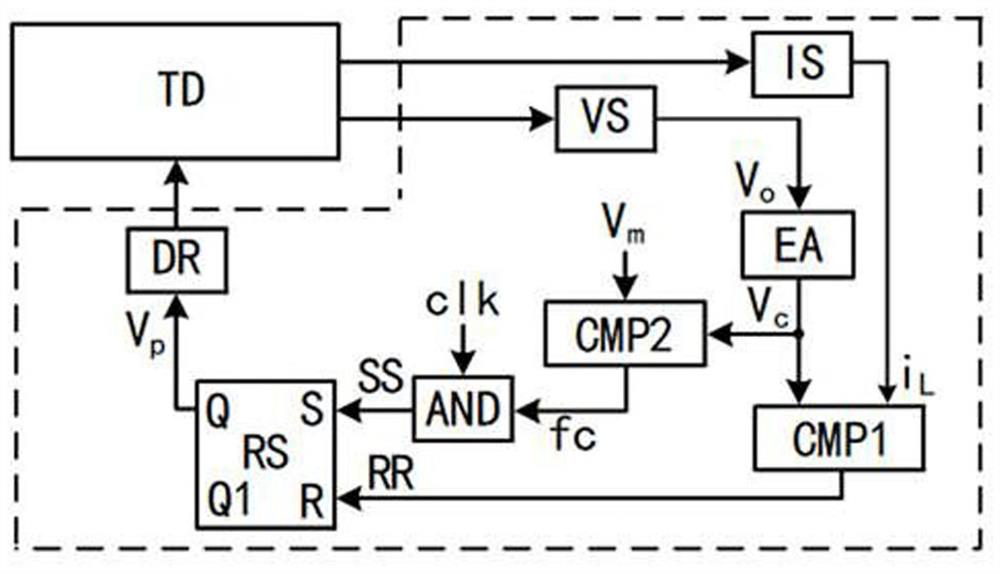
[0021] combined with figure 1 As shown, a voltage and current quasi-fixed frequency control device includes a voltage detection circuit VS, a current detection circuit IS, an error amplifier EA, a first comparator CMP1, a second comparator CMP2, an AND gate AND, a flip-flop RS and a driving circuit DR, the voltage detection circuit VS, the current detection circuit IS and the drive circuit DR are respectively connected to the voltage output terminal of the converter TD, the current output terminal of the converter, and the switch tube of the converter, and the voltage detection circuit VS is connected to the error amplifier EA; The detection circuit IS is connected to the input terminal of the first comparator CMP1; the output terminal of the error amplifier EA is connected to the input terminal of the first comparator CMP1 and the input terminal of the second comparator CMP2; the preset error signal reference value V m It is connected with the input end of the second comparat...
Embodiment 2
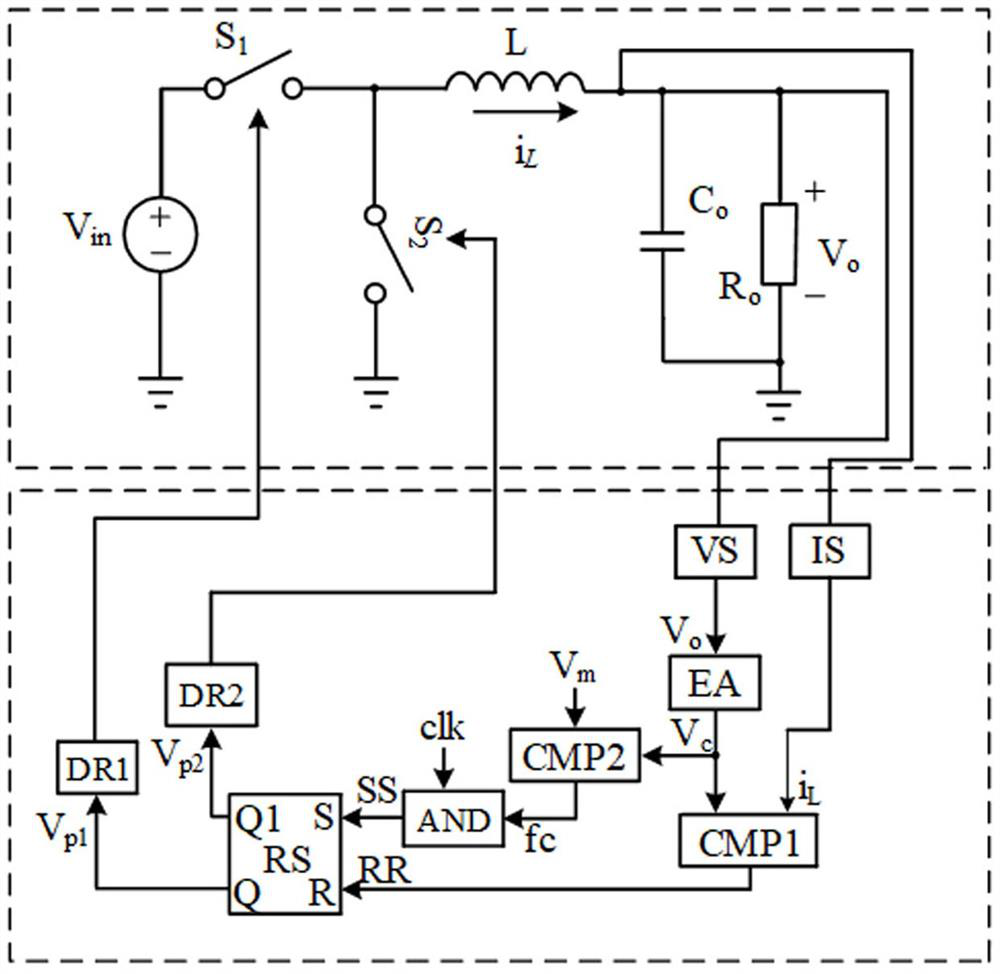
[0025] A quasi-fixed-frequency control method for voltage and current, realized based on the above-mentioned control device, the embodiment of the present invention replaces the converter TD in the above-mentioned embodiment with a synchronous rectification Buck converter, such as figure 2 As shown, the control method is:
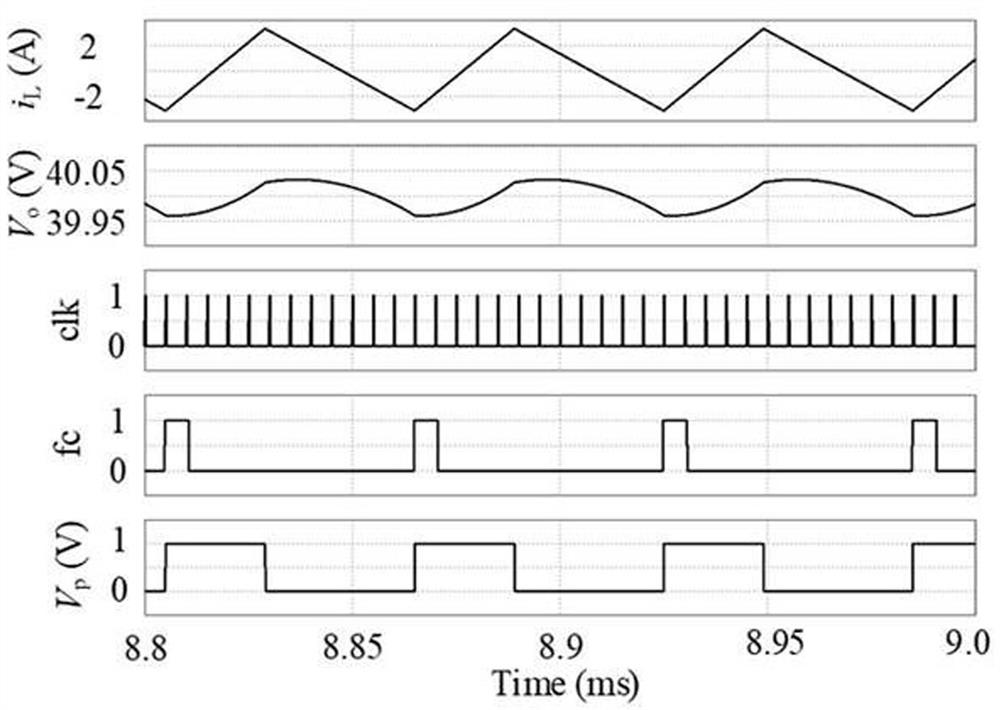
[0026] At the beginning of any period, the converter TD output voltage V o and inductor current i L , output voltage V o with reference voltage V ref1 The voltage control signal V is generated through the error amplifier EA c ;Inductor current i L connected to one input terminal of the first comparator CMP1, and the voltage control signal V c After comparison, the signal RR is generated as the input signal of the R terminal of the flip-flop RS; the preset error signal reference value V m with voltage control signal V c Also connected to the input terminal of the second comparator CMP2, the preset error signal reference value V m with voltage contro...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Such as Figure 9 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention replaces the converter TD in the above embodiments with a Boost converter. In the figure, V in is the input voltage, L is the power inductor, S is the power switch tube, C o is the output capacitance, R o is the load resistance, VS is the output voltage detection circuit, IS is the inductor current detection circuit, V p1 It is the pulse control signal of the switch tube S.
[0036] The invention can also be used in various circuit topologies such as Buck-Boost converters, Flyback converters, and Forward converters, and is suitable for switching converters of various topological structures.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com