Negative electrode, lithium ion secondary battery and preparation method of lithium ion secondary battery
A secondary battery, lithium ion technology, used in secondary batteries, negative electrodes, battery electrodes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
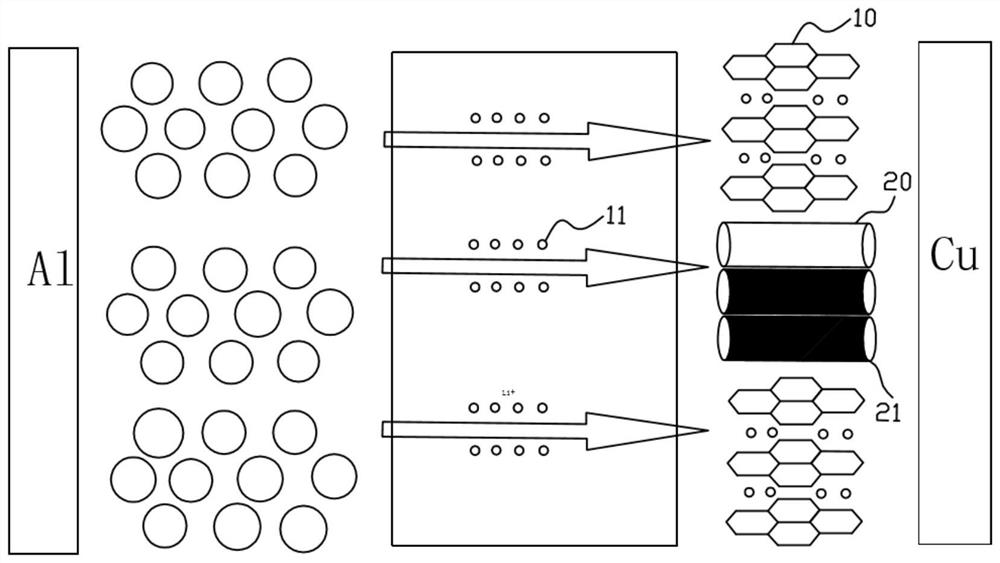
[0053] This embodiment also provides a method for preparing a lithium-ion secondary battery as described above, comprising the steps of:
[0054] Mix the first negative electrode active material, conductive agent, binder, hole support material and solvent uniformly to make a negative electrode mixture, and apply the negative electrode mixture on the negative electrode current collector to make a negative electrode sheet; wherein, the hole support material constitutes The conductive network structure of the negative electrode sheet.
[0055] Mix the positive electrode active material, conductive agent, binder and solvent uniformly to make a positive electrode mixture, and apply the positive electrode mixture on the positive electrode current collector to make a positive electrode sheet;
[0056] Assemble the positive electrode sheet, negative electrode sheet, separator and electrolyte into a cell;
[0057] Charge the cell to the upper limit voltage to make lithium ions excessi...
no. 1 example
[0062] 35wt% MCMB (mesophase carbon microspheres), 10wt% conductive carbon black, 30wt% conductive carbon fiber, 25wt% PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) and appropriate amount of NMP (N-methylpyrrolidone) were stirred and homogenized The negative electrode material layer, wherein MCMB is used as a first negative electrode active material, conductive carbon black is used as a conductive agent, conductive carbon fiber is used as a hole support material, PVDF is used as a binder, and NMP is used as a solvent.
[0063] Then, the negative electrode material layer is double-sided coated on the negative electrode current collector (area density 160g / cm 2 ), dried in an oven; then rolled and compacted with a compacted density of 0.8g / cc; anode sheets meeting the size requirements were obtained by cutting.
[0064] Figure 2a It is a structural schematic diagram of the conductive network structure under the electron microscope in the first embodiment of the present invention. Please com...
no. 2 example
[0066] Stir 35wt.% of MCMB (mesophase carbon microspheres), 10wt.% of conductive carbon black, 30wt.% of conductive carbon fiber, 25wt.% of PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) and appropriate amount of NMP (N-methylpyrrolidone) The homogenate is made into mixture; The mixture is double-sidedly coated on the negative electrode current collector (area density 160g / cm 2 ), dried in an oven; then rolled and compacted with a compacted density of 0.96g / cc; a negative electrode sheet meeting the size requirements was obtained by cutting.
[0067] Figure 2b It is a schematic structural diagram of the conductive network structure under the electron microscope in the second embodiment of the present invention. Please combine Figure 2b , there are also continuous and a large number of conductive holes in the figure, that is to say, the second embodiment of the present invention also constitutes a negative electrode structure that can deposit all lithium metal into the holes in the conduct...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Areal density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compaction density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com