A drug-eluting intraocular lens with sustained-release function and its preparation method
An intraocular lens and drug technology, used in intraocular lens, drug devices, eye implants, etc., can solve the problems of difficult control of coating quality, effect greatly affected by coating stability, damage to structural strength, etc. Good drug release and biocompatibility, ensure foldability and stability, and prevent inflammation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0045] The preparation method provided by the invention is carried out sequentially according to the following steps:
[0046] 1) Prepare the intraocular lens according to the design plan, and use it after ultrasonic cleaning;
[0047] 2) Preparation of drug-eluting coating: dissolve the degradable polymer and drug powder in an organic solvent; in the obtained spray solution, the concentration of the degradable polymer is 0.1-10%, preferably 5%; the concentration of the drug is 0.01%- 5%, preferably 0.2%; stand-by;
[0048] 3) Preparation of drug-eluting intraocular lens:
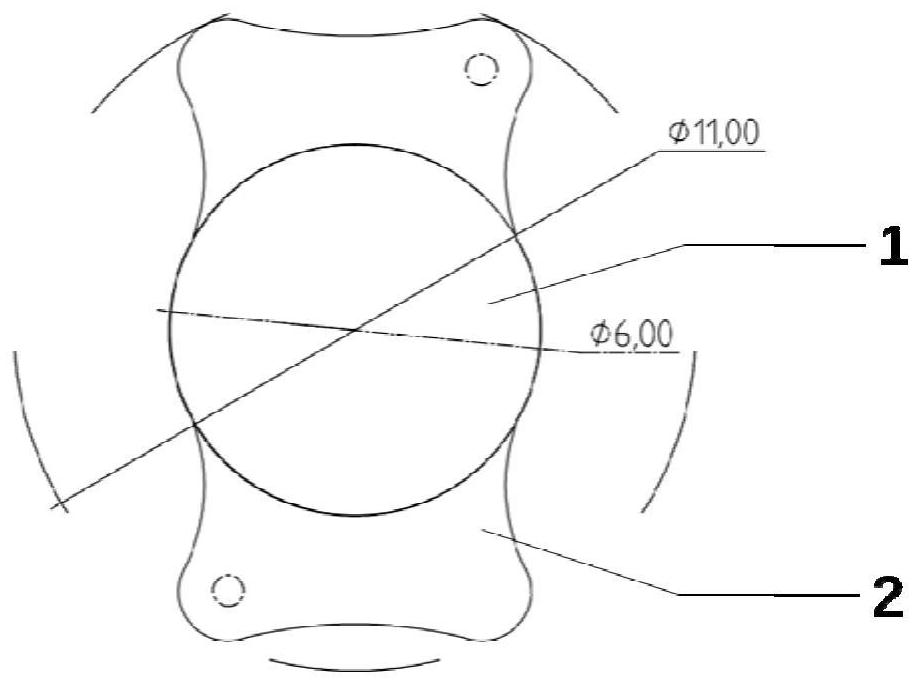
[0049] (1) Block the optics of the intraocular lens in step 1), and the haptics of the intraocular lens are selected as the spraying area;
[0050] (2) Apply the solution prepared in step 2) to the haptics of the intraocular lens accurately by using an ultrasonic atomization spraying system to form a drug coating on the surface, while keeping the optical part of the intraocular lens smooth and transparent...
Embodiment 1
[0061] The intraocular lens in this embodiment is made of hydrophobic polyacrylate material, and the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug bromfenac sodium is used as the drug.
[0062] Bromfenac sodium is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug commonly used in ophthalmology. It mainly exerts anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2, and has low cytotoxicity. Brookshire et al. found that IOLs pretreated with bromfenic acid were more effective at inhibiting the development of posterior capsule opacities in laboratory dogs than IOLs pretreated with prednisolone acetate.
[0063] Concrete manufacturing method comprises the following steps:
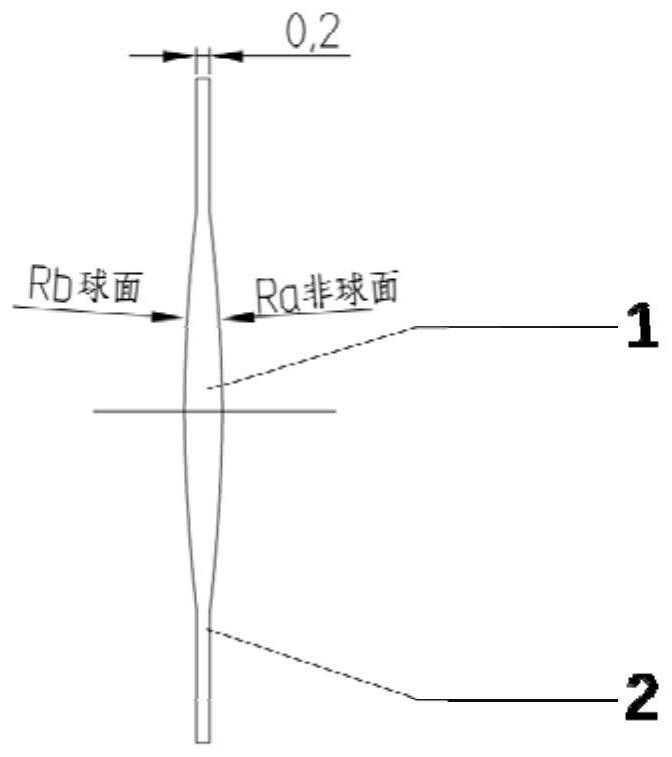
[0064] Apply hydrophobic polyacrylate material as per figure 1 The planar planar haptic intraocular lens produced by the design shown has two wide and symmetrically arranged flat haptics about the optic, which can provide a sufficient drug-loading platform for the drug-eluting coating. The optical part is designed with one sph...
Embodiment 2
[0068] This example is made of hydrophobic polyacrylate material, and the difference from Example 1 is that the drug used is indomethacin.
[0069] Indomethacin is a hydrophobic drug, which has a higher drug-loading potential than bromfenac sodium in Example 1. Recent studies have shown that indomethacin can not only exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting cyclooxygenase-2, but also inhibit cell proliferation by inducing autophagy.
[0070] The preparation method of the intraocular lens is the same as that in Example 1. The PLGA and indomethacin powders are dissolved in ethyl acetate solution, the PLGA concentration is 5%, the drug concentration is 0.5%, and the loop of the intraocular lens is set as the spraying area. The drug PLGA solution was precisely sprayed onto the intraocular lens loop by using an ultrasonic atomization spraying system. The drug loading amount of each intraocular lens indomethacin was 100 μg or 500 μg, sterilized with ethylene oxide and sealed and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com