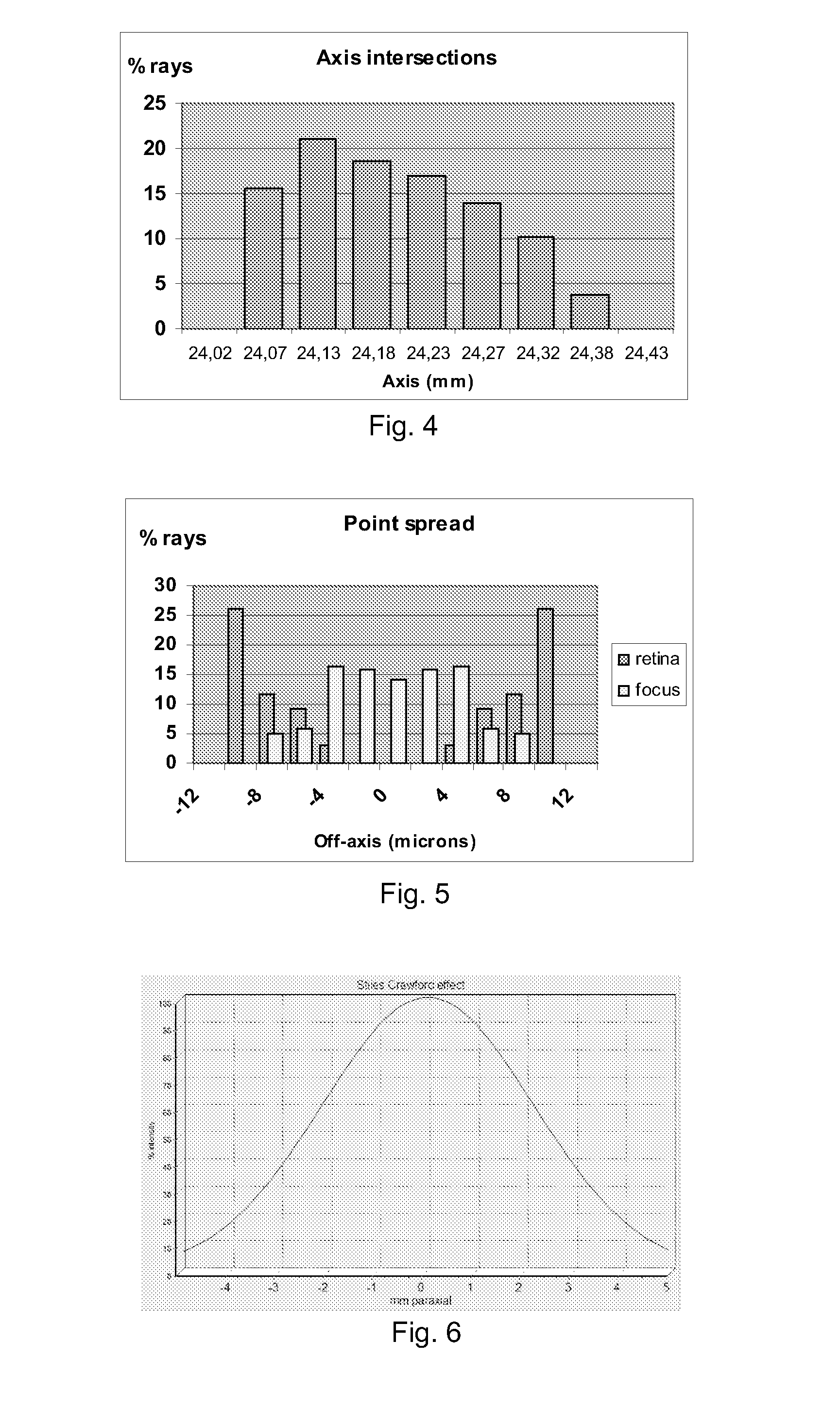
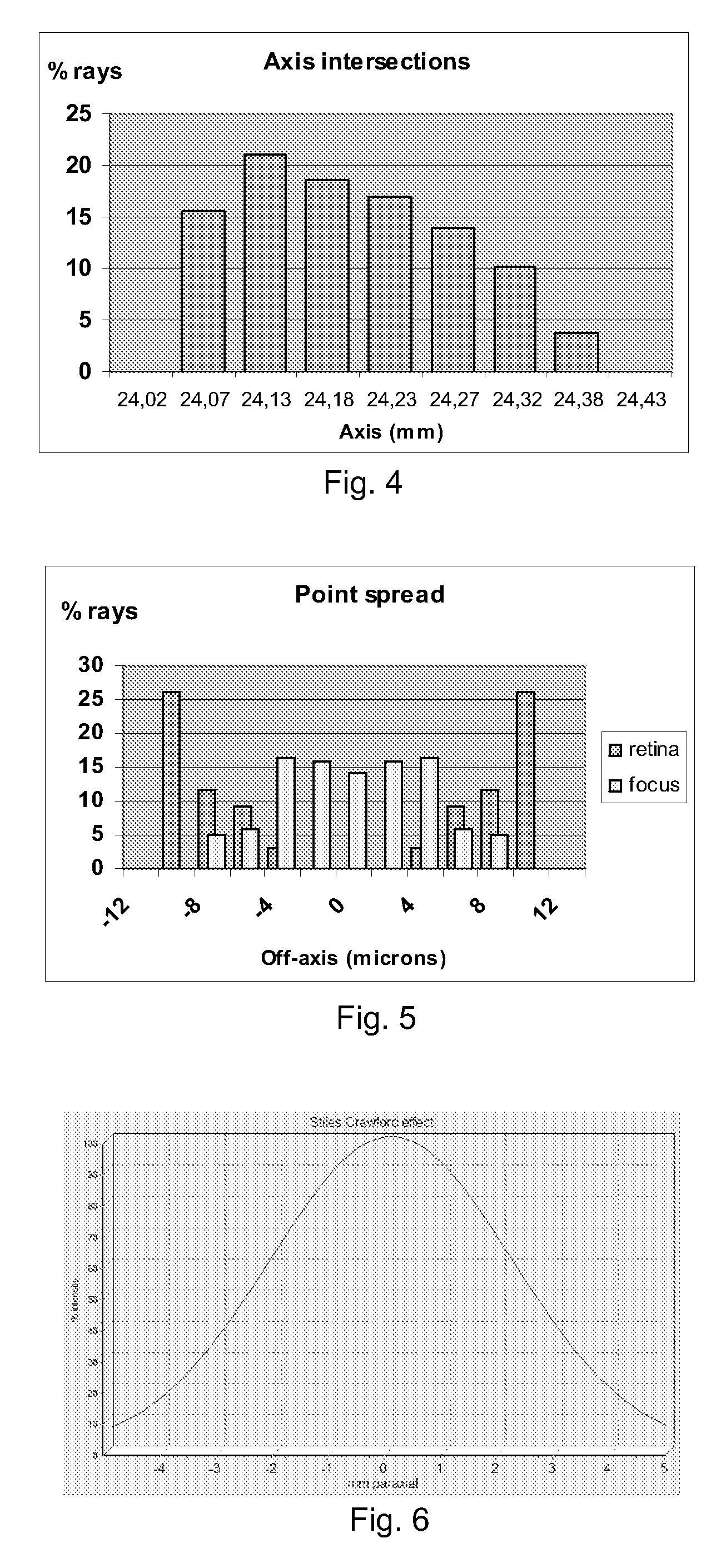
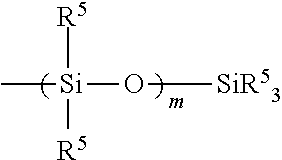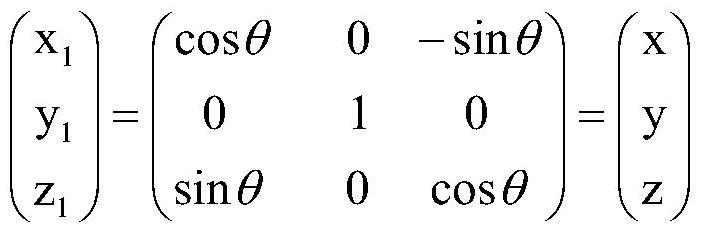Patents
Literature
84 results about "Artificial intraocular lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
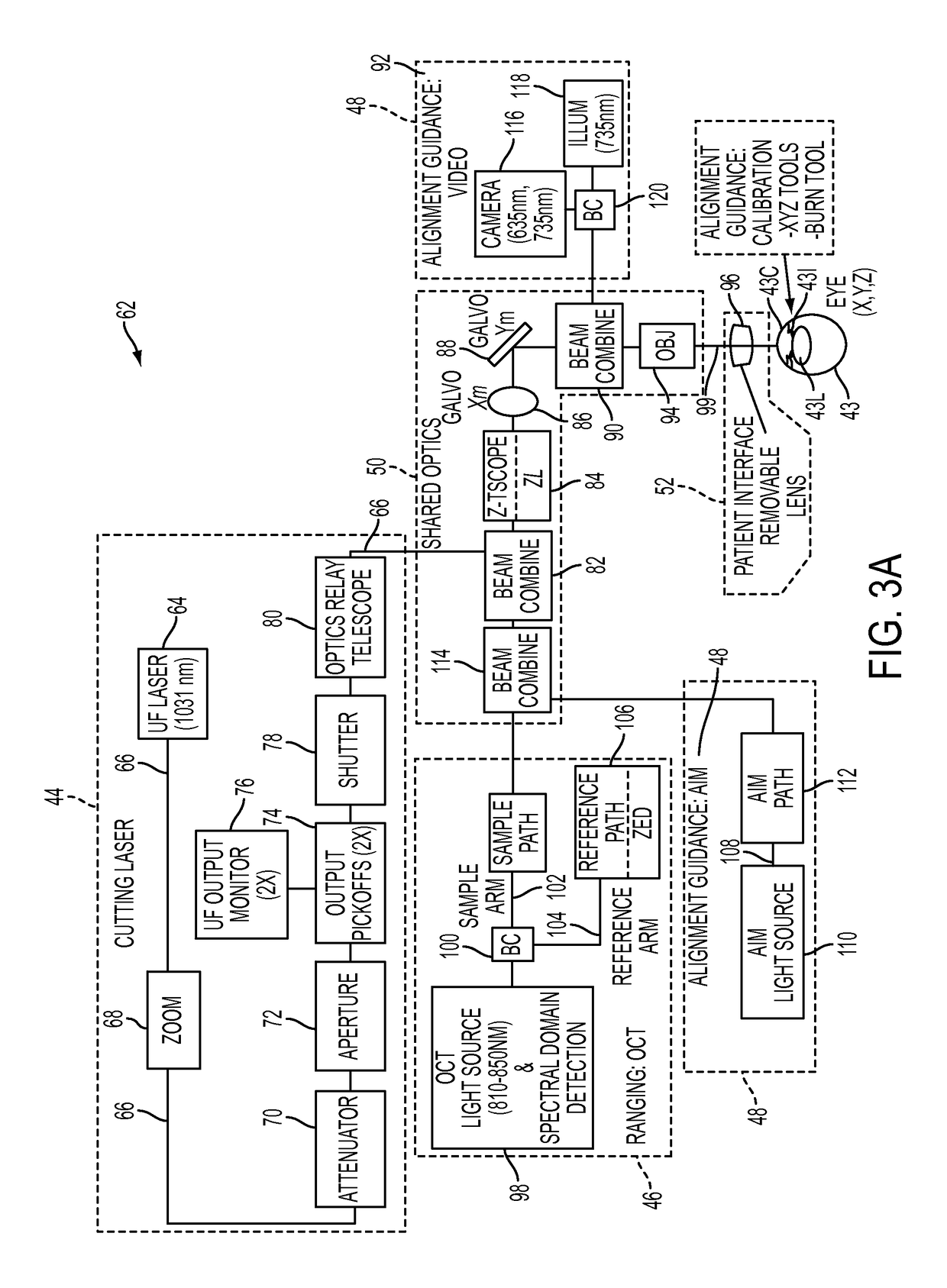
May. An intraocular lens (or IOL) is a tiny, artificial lens for the eye. It replaces the eye's natural lens that is removed during cataract surgery. The lens bends (refracts) light rays that enter the eye, helping you to see.
Rapid exchange iol insertion apparatus and methods of using
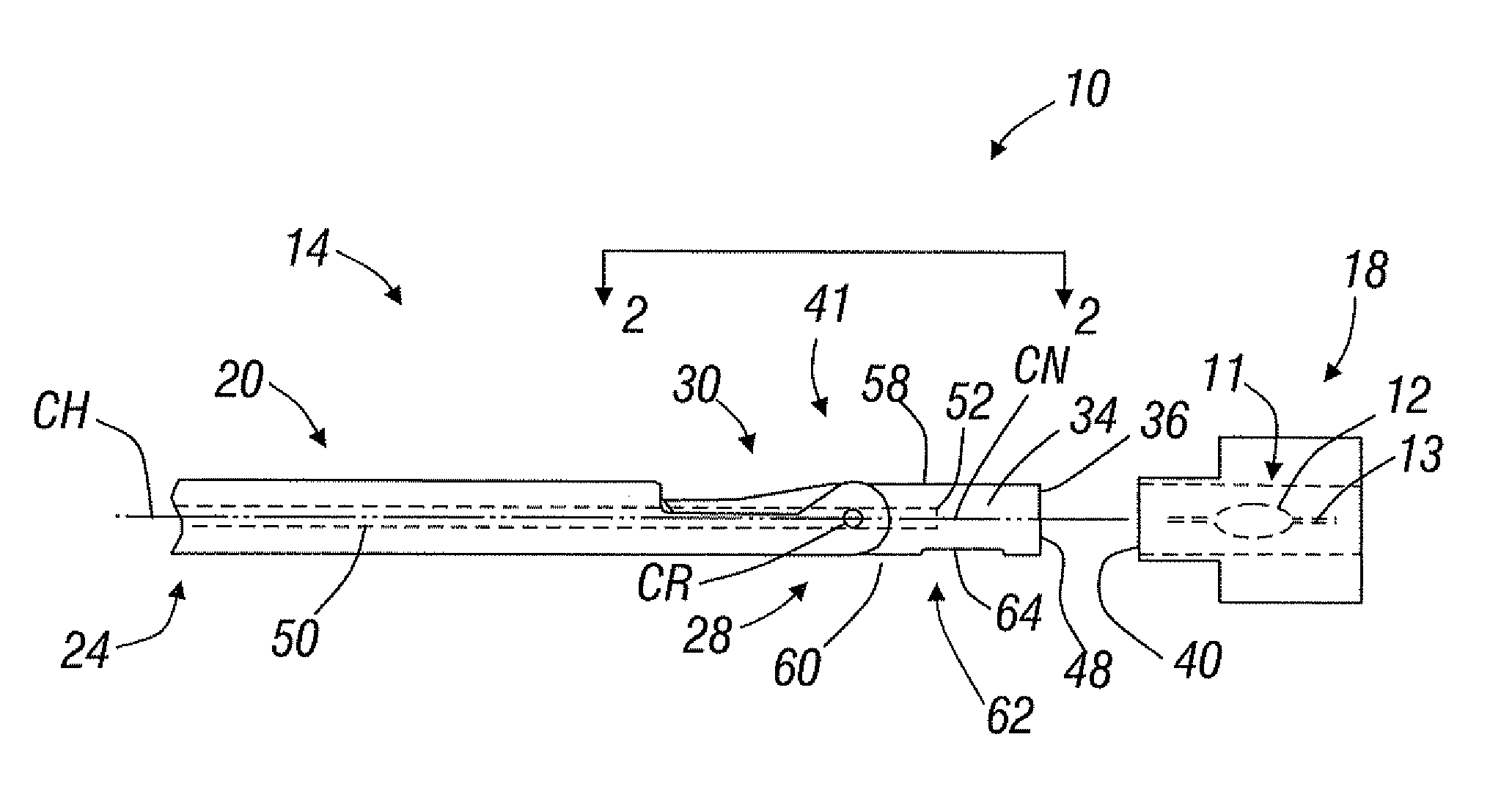
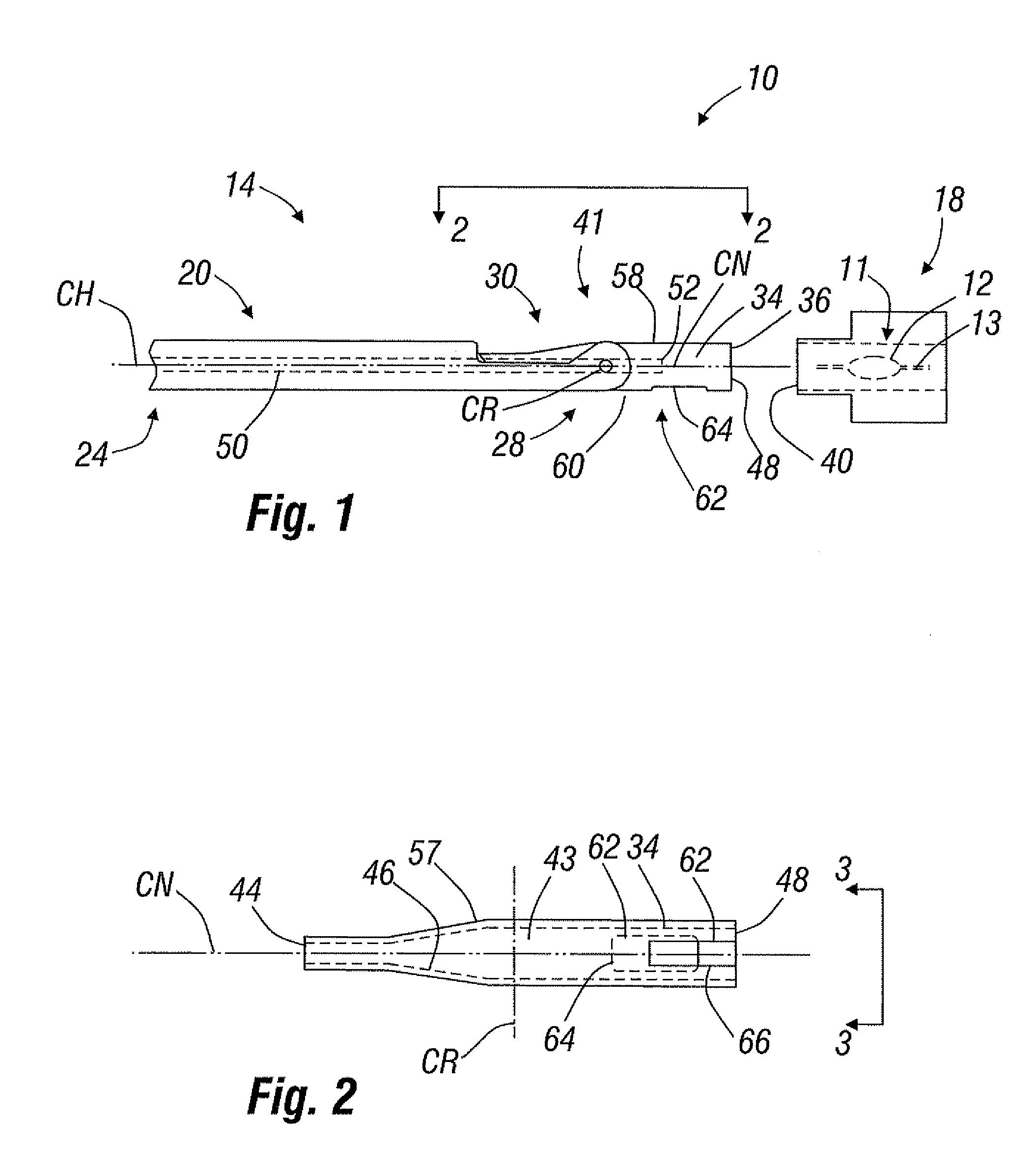
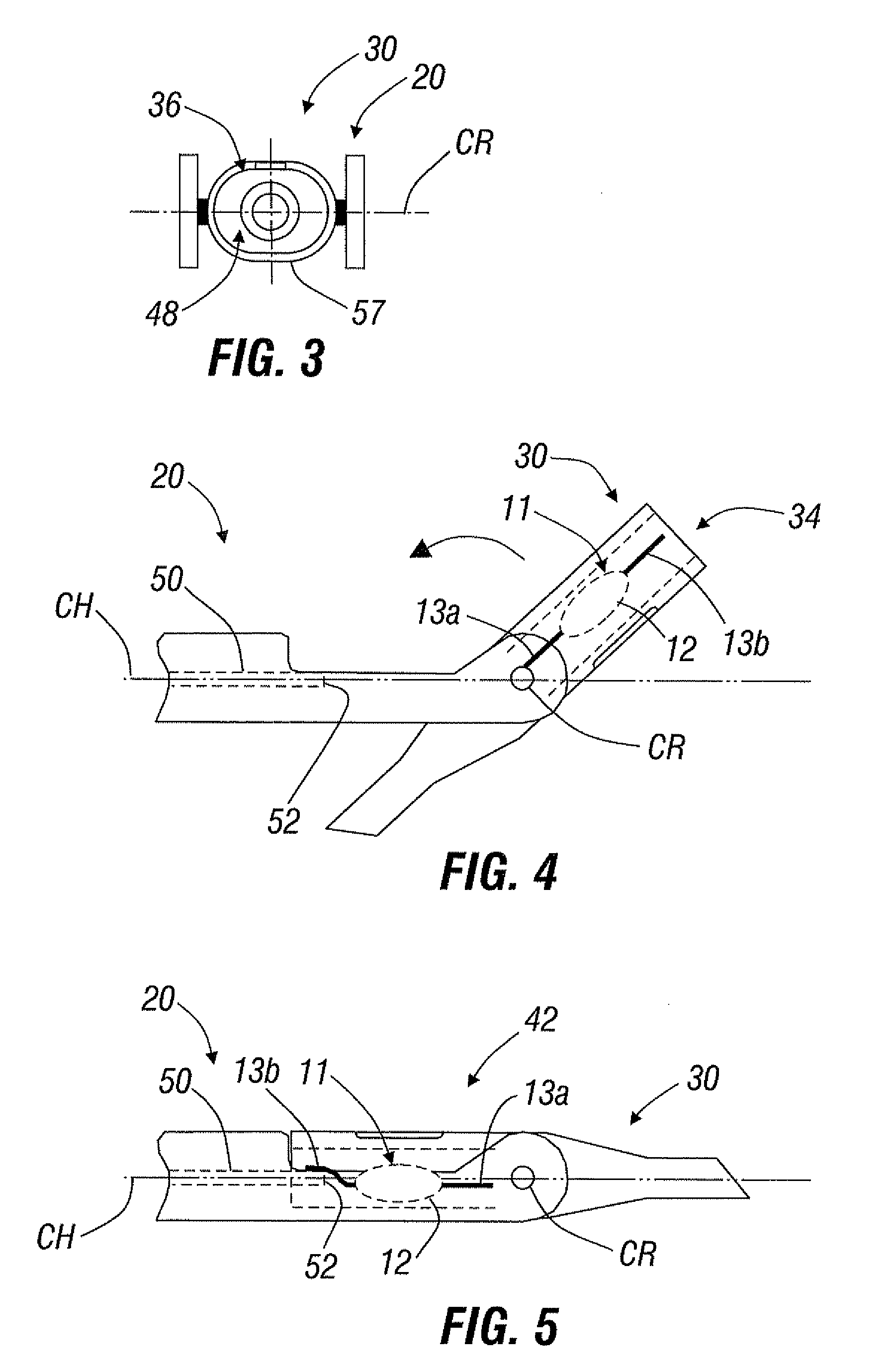
A system for easily transferring an intraocular lens (IOL) from a lens case to an inserter, and then into a patient's eye. The lens case has a transfer mechanism therein which retains the IOL until engagement with the inserter. The transfer mechanism may include jaws having a closed configuration for retaining the IOL and an open configuration for releasing the IOL. Engagement of the inserter with the lens case automatically opens the jaws and transfers the IOL to the inserter. The IOL is transferred into a load chamber of a nosepiece rotatably coupled to a handpiece. After transfer of the IOL, the nosepiece is rotated from a load position to a delivery position. The IOL may have an optic and a haptic coupled to the optic, and the lens case may be capable of configuring the haptic as desired to facilitate its transfer into an inserter and / or into the eye. For instance, the lens case may fold one or both of the haptics over the optic. Preferably, the lens case maintains the haptic in this position during transfer of the intraocular lens into an inserter and / or inserter cartridge. A manifold for easily distributing a viscoelastic medium to the load chamber of the inserter is also provided.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Artificial lens, in particular a contact or intraocular lens, for correcting presbyopia, possibly associated with other visual defects, and relative production method
InactiveUS20070279585A1High of long vision acuityDrawback can be obviatedSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensVisual perception
An artificial lens (1) (contact lens or intraocular lens) for correcting presbyopia, possibly associated with other refractive defects, has at least one region (5) having a fourth-order spherical aberration in OSA notation greater than −1.5 μm and less than zero μm, and possibly associated with a basic vertex power for correcting refractive defects, and with higher-order aberrations for improving vision acuity. The lens is produced by ablating a surface of a base body of the lens by means of an appropriately controlled laser device, and according to a given photoablative pattern to induce the desired aberration.
Owner:STUDIO BOL DI GIUSEPPE BOLLINI +1
System and Method for Determining and Predicting IOL Power in Situ
InactiveUS20110242482A1Accurately reflectAccurate explanationMedical simulationEye diagnosticsDiseaseOphthalmology
The present invention relates to a system and a method for determining the power of an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) in situ. The invention furthermore relates to a system and a method for predicting the optical outcome of IOL surgery. Use of the system may provide prevention, treatment, or amelioration of diseases and disorders affecting the lens of the eye and which may benefit from IOL surgery. Moreover, the invention relates to a computer-readable medium for implementing such a system on a computer.
Owner:IOL INNOVATIONS
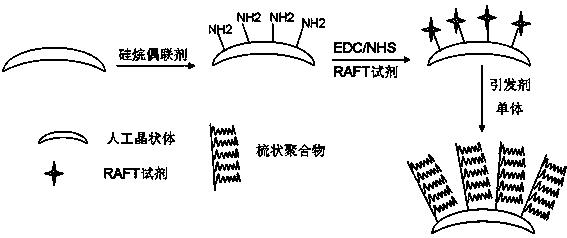
Surface comblike polymer hydrophilic modified artificial lens and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103405807AGood anti-adhesion characteristicsResistance to adhesion proliferationCoatingsIntraocular lensHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The invention relates to a surface comblike polymer hydrophilic modified artificial lens and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the surface comblike polymer hydrophilic modified artificial lens comprises the following process steps of carrying out surface treatment on a clean artificial lens by using an amino functional group contained silane coupling agent to enable the surface of the clean artificial lens to have an amino group; grafting a carboxyl functional group contained RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Transfer) chain transfer agent on the artificial lens by using a chemical method; and carrying out in-situ polymerization on a hydrophilic monomer molecule on the surface of the artificial lens by using an RAFT polymerization reaction method initiated on the surface of the artificial lens to form a hydrophilic comblike polymer to obtain the surface comblike polymer hydrophilic modified artificial lens. The surface comblike polymer hydrophilic modified artificial lens has the advantages that the condition that the artificial lens has toxic and side effects to non-targeting cells when being applied to a traditional drug coating is avoided, and the artificial lens with high biocompatibility is obtained.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Lens oil having a narrow molecular weight distribution for intraocular lens devices
A silicone oil having a mean molecular weight average greater than about 20,000 Daltons, with no more than about 3% to about 4% of the total silicone oil by weight being comprised of components having a molecular weight less than about 15,000 Daltons. In some embodiments, the silicone oil is used in intraocular lens devices.
Owner:LENSGEN INC
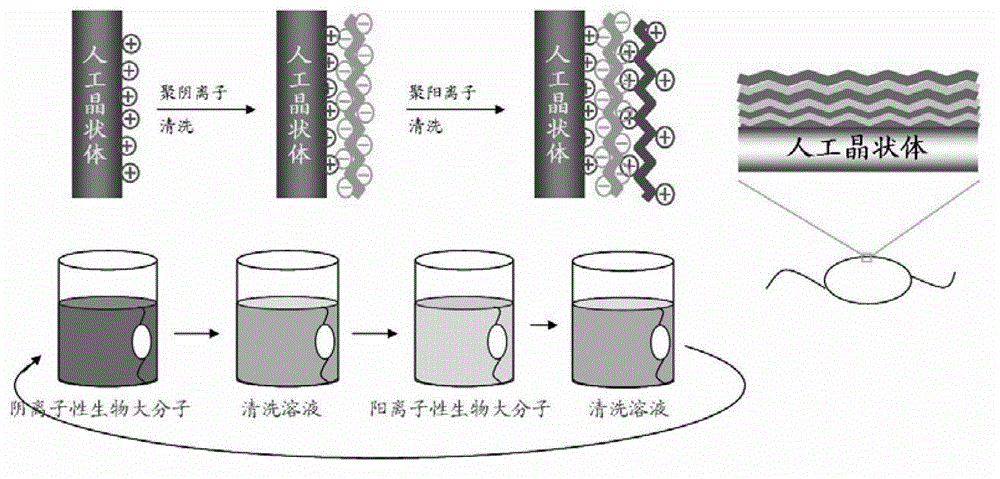
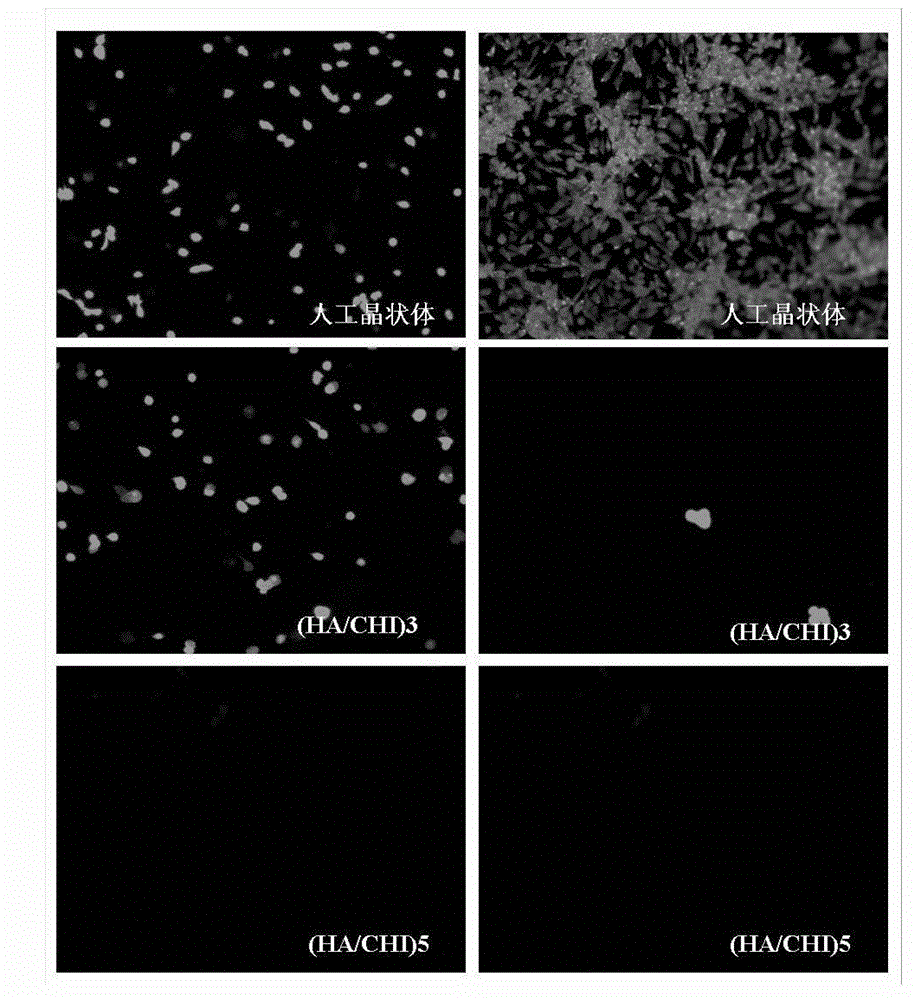
Modification process of surface bionic self-assembly multilayer film of artificial lens and artificial lens provided with surface bionic self-assembly multilayer film
InactiveCN103146010AGood biocompatibilityEasy to disinfectCoatingsProsthesisPolyelectrolyteLens epithelial cell
The invention relates to a modification process of a surface bionic self-assembly multilayer film of an artificial lens and the artificial lens provided with the surface bionic self-assembly multilayer film. The modification process of the surface bionic self-assembly multilayer film of the artificial lens comprises the following steps: the well cleaned artificial lens is provided with positive charge through surface pre-treatment, soaked into biomacromolecule polyelectrolyte solution provided with negative charge, placed still for electrostatic adsorption for a period of time, taken out and cleaned; then the artificial lens is soaked into biomacromolecule polyelectrolyte solution provided with positive charge, placed still for electrostatic adsorption for a period of time, taken out and cleaned; the alternative electrostatic assembly process is repeated for several times, at last the artificial lens is dried at room temperature, and the artificial lens modified by the surface bionic self-assembly multilayer film is obtained. The modification process of the surface bionic self-assembly multilayer film of the artificial lens and the artificial lens provided with the surface bionic self-assembly multilayer film have the advantages that a bionic modification layer formed by an artificial lens surface bionic lens envelope is obtained through a simple, convenient and rapid bionic method, adhesion and breeding of impedance lens epithelial cells are achieved, toxic and side effects on non-target cells existing in the application of a drug coating artificial lens are avoided, and the obtained artificial lens is high in biological compatibility.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Lens oil having a narrow molecular weight distribution for intraocular lens devices
Owner:LENSGEN INC
System and method for determining and predicting IOL power in situ
InactiveUS8657445B2Accurately reflectAccurate explanationMedical simulationEye diagnosticsDiseaseOphthalmology
The present invention relates to a system and a method for determining the power of an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) in situ. The invention furthermore relates to a system and a method for predicting the optical outcome of IOL surgery. Use of the system may provide prevention, treatment, or amelioration of diseases and disorders affecting the lens of the eye and which may benefit from IOL surgery. Moreover, the invention relates to a computer-readable medium for implementing such a system on a computer.
Owner:IOL INNOVATIONS
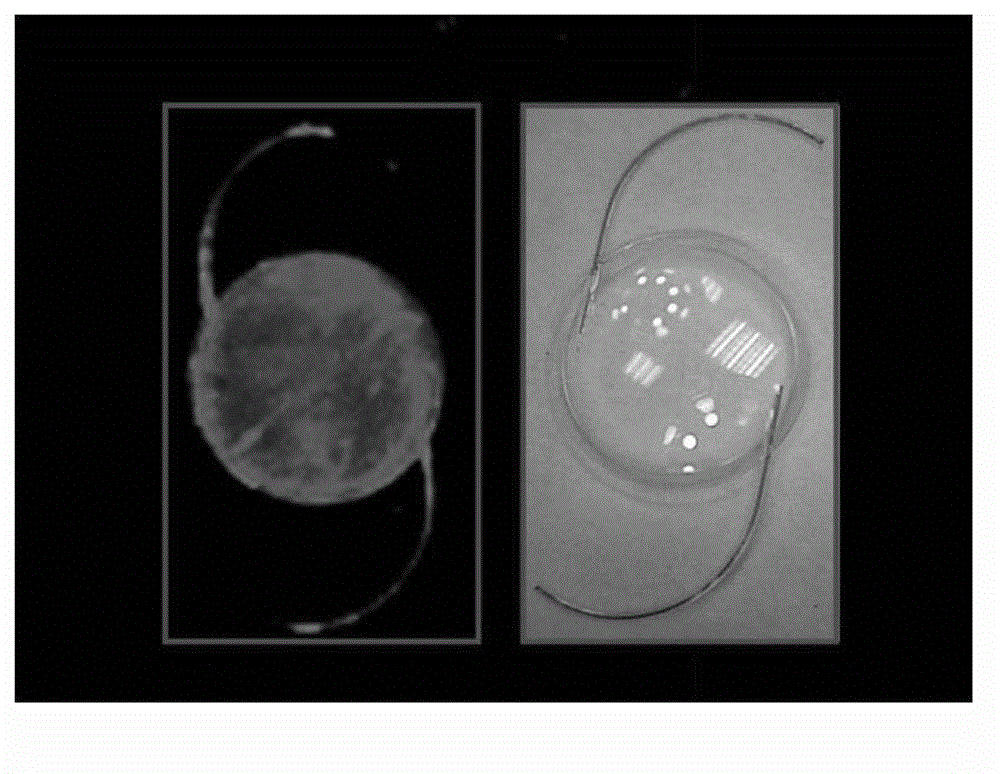
Posterior chamber intraocular lens
ActiveUS20140358225A1Increase spacingPromote lowerIntraocular lensPosterior capsule opacificationAnterior surface
The present invention relates to a posterior chamber intraocular lens (IOL), comprising: an optic consisting of an effective optical area and an effective optical area edge; at least two haptics connected to the optic, wherein a posterior surface of the effective optical area is a convex surface, and a basic spherical surface thereof has a radius of curvature in a range of 6.6 mm-80.0 mm. The effective optical area of the posterior chamber IOL adopts a design with the posterior surface obviously convex, which reduces the distance between the posterior surface of the effective optical area of the IOL and the posterior capsule, improves the stability of a spatial position of the IOL in a capsule bag, and reduces an incidence rate of posterior capsule opacification (PCO) after implantation of the IOL; since the effective optical area anterior surface is relatively flat, the IOL haptics will not be tightly pressed on the effective optical area anterior surface upon folding, the haptics are more easily unfolded after implantation into the eye and the support haptics are not mutually adhered to the effective optical area, and meanwhile the IOL imaging quality can be improved and / or the visual quality of the astigmatism sufferer is enhanced.
Owner:EYEBRIGHT MEDICAL TECH BEIJING
Artificial sac
The invention discloses an artificial sac which comprises a front-layer envelope and a rear-layer envelope. The peripheral edge of the front-layer envelope and the peripheral edge of the rear-layer envelope are fixedly connected with each other, a fixing portion for fixing the artificial sac is arranged on the outer periphery of a joint, the front-layer envelope and the rear-layer envelope are soft transparent envelopes, and an avoiding hole for bringing convenience for artificial lens implantation is formed in the middle of the front-layer envelope. The artificial sac has the advantages thatthe peripheral edge of the front-layer envelope and the peripheral edge of the rear-layer envelope are fixedly connected with each other to form a complete sealed bag, the front-layer envelope and therear-layer envelope are the soft transparent envelopes, and accordingly the artificial sac can be implanted into an eye via a small incision and can be fixed to the eye of a patient by the aid of thefixing portion; the location of an artificial lens can be guaranteed by the artificial sac after the artificial lens is implanted into the artificial sac from the avoiding hole, and the artificial lens is positioned in the middle of the visual axis and is perpendicular to the visual axis, so that light rays which are transmitted into the eye can be focused and can be guided onto the retina.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIESHI MEDICAL TECH
Accommodating intraocular lens device
An intraocular lens (IOL) device comprising a first lens, a second lens and a circumferential haptic. The first lens comprises a pair of opposing and deformable surfaces and a cavity defined therebetween. The first lens has a first lens diameter. The second lens has a second lens diameter. The circumferential haptic has an outer peripheral edge and couples the first lens and the second lens. A main IOL cavity is defined by the circumferential haptic, the first lens and the second lens. The IOL device is resiliently biased to an unaccommodated state, characterized by the IOL device having a first diameter d1 in the absence of radial compressive forces exerted on the outer peripheral edge. The IOL device actuates to an accommodated state being characterized by a second diameter d2 in response to radial compressive forces exerted on the outer peripheral edge, wherein d1>d2.
Owner:LENSGEN INC
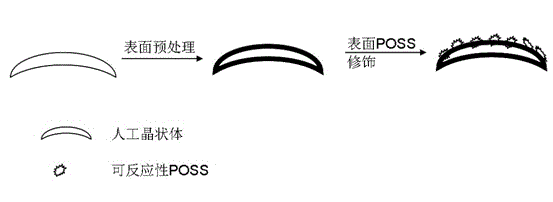
Artificial lens with polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-modified surface and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104382673AGood biocompatibilitySimple preparation processIntraocular lensPolymer scienceBiocompatibility
The invention relates to an artificial lens with a polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-modified surface and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the artificial lens with the polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-modified surface includes the following process steps: a clean artificial lens is chosen, and by surface pretreatment, a chemically active surface is obtained; the chemically active surface chemically reacts with POSS (polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) containing reactable functional groups, so that the artificial lens, on the surface of which is the POSS is grafted, is obtained. The invention has the advantage that a surface composite micronanostructure is obtained by nano POS modification, so that the super-hydrophobic surface is obtained to inhibit the adhesion of epithelial cells on the lens, and thereby the highly biocompatible artificial lens is obtained.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
A kind of intraocular lens with surface comb polymer hydrophilic modification and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103405807BGood anti-adhesion characteristicsResistance to adhesion proliferationCoatingsIntraocular lensHydrophilic monomerOphthalmology
The invention relates to an intraocular lens whose surface is hydrophilically modified by a comb polymer and a preparation method thereof. A method for preparing an intraocular lens with a surface hydrophilically modified by a comb polymer, comprising the following process steps: taking a clean intraocular lens, and treating the surface with an amino functional group-containing silane coupling agent to bring amino groups on the surface; The intraocular lens is chemically grafted with a RAFT chain transfer agent containing carboxyl functional groups; the intraocular lens is polymerized in situ by hydrophilic monomer molecules on the surface of the intraocular lens through surface-induced RAFT polymerization to form a hydrophilic comb polymer. The intraocular lens with surface comb polymer hydrophilic modification was obtained. The invention has the advantages of avoiding the toxic and side effects on non-target cells existing in the application of the drug-coated intraocular lens in the past, and obtaining the highly biocompatible intraocular lens.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
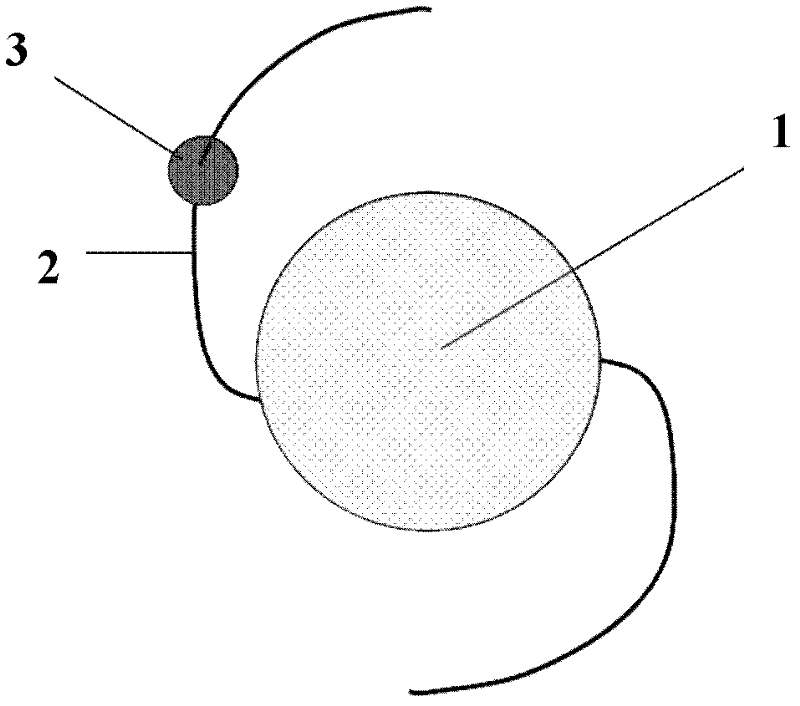
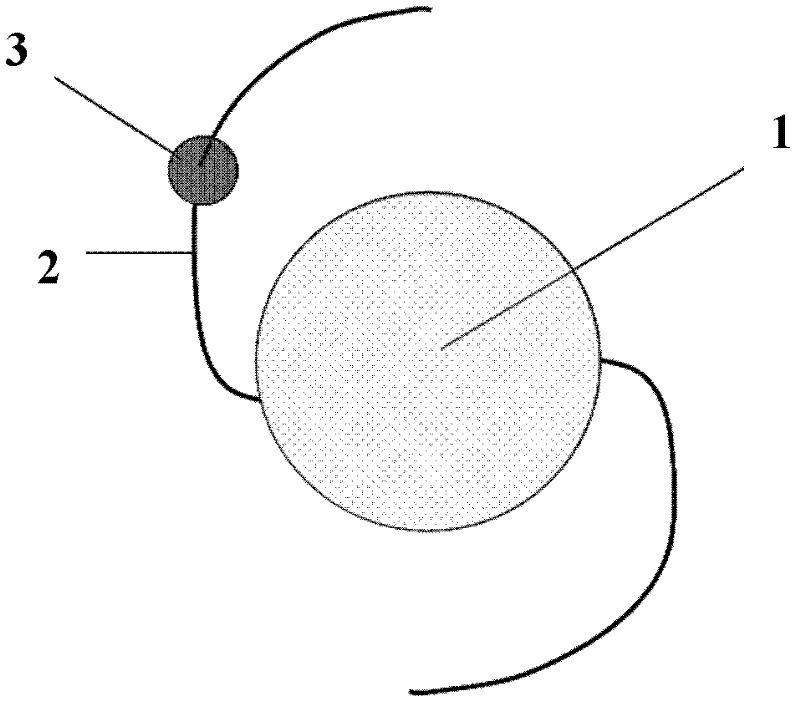
Variable multi-focus artificial lens
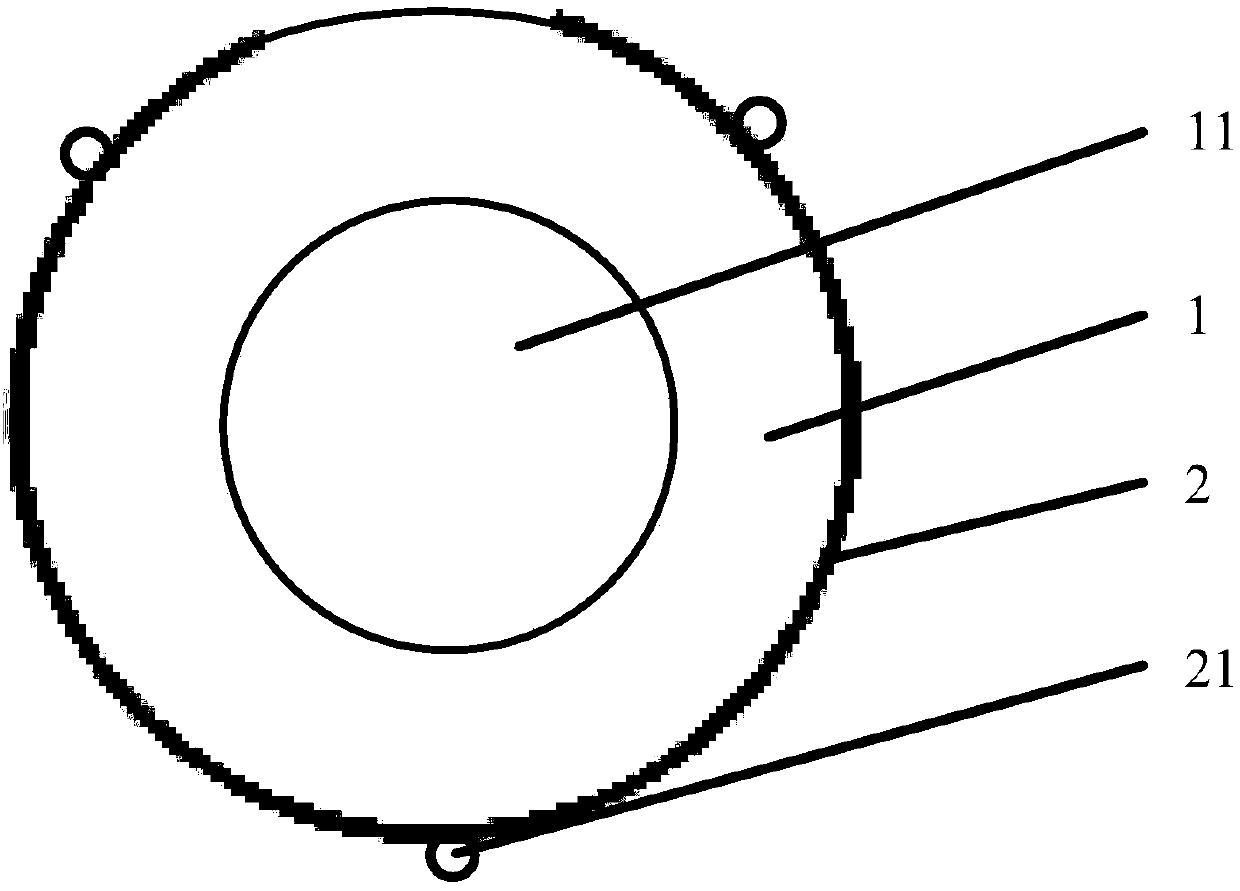
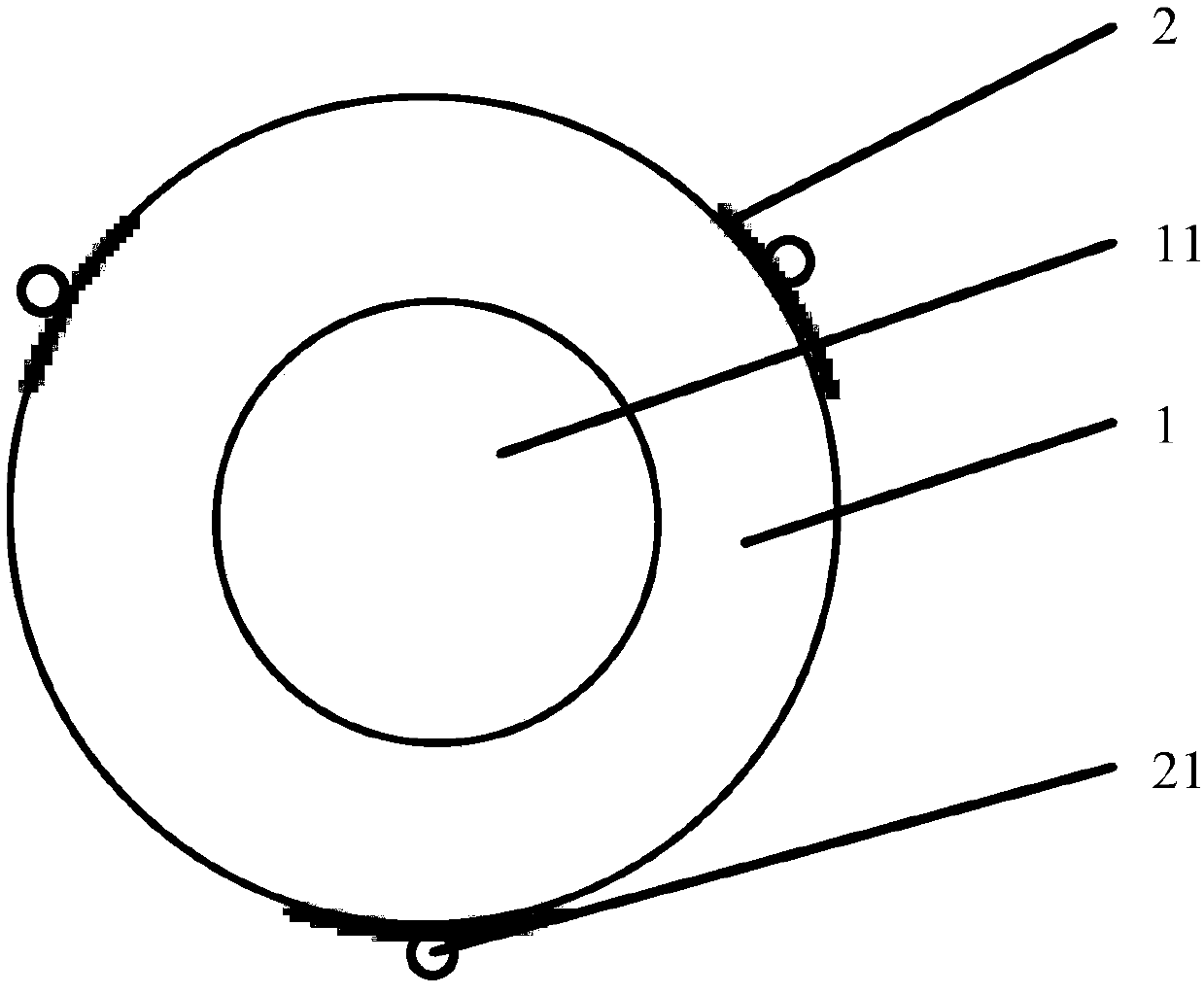
InactiveCN106667623AIncrease elasticityEffective forward and backward movementIntraocular lensEngineeringSilica gel
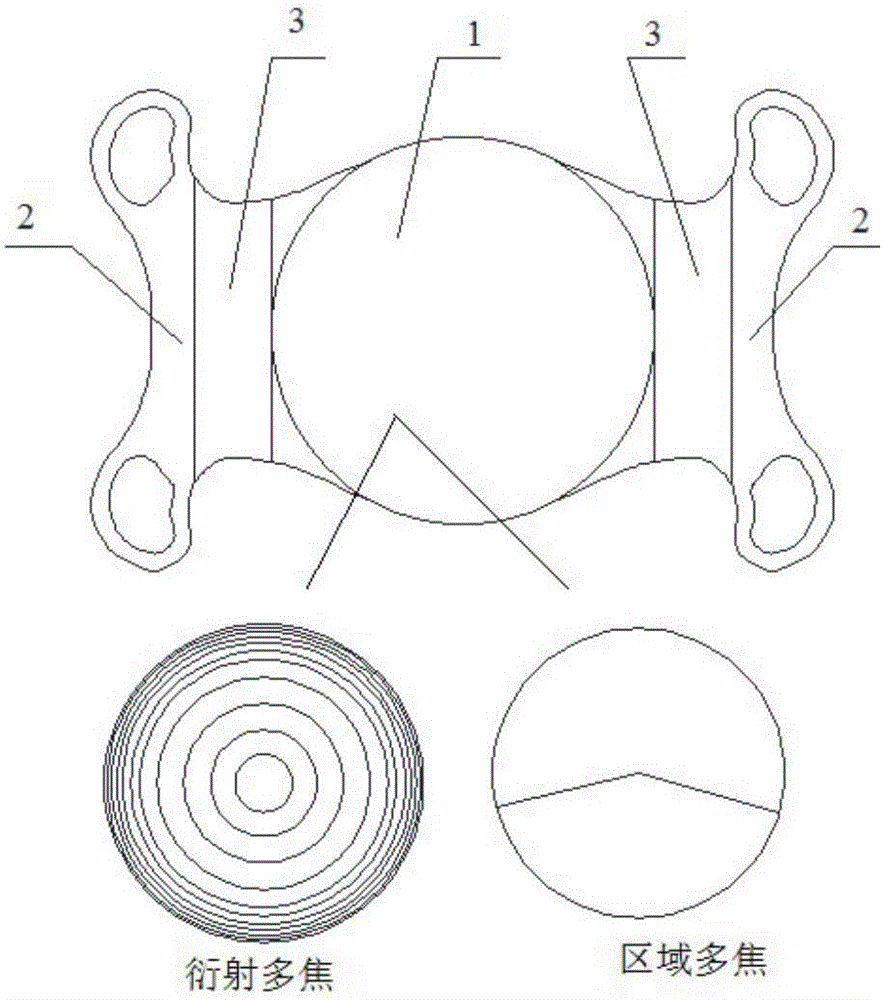
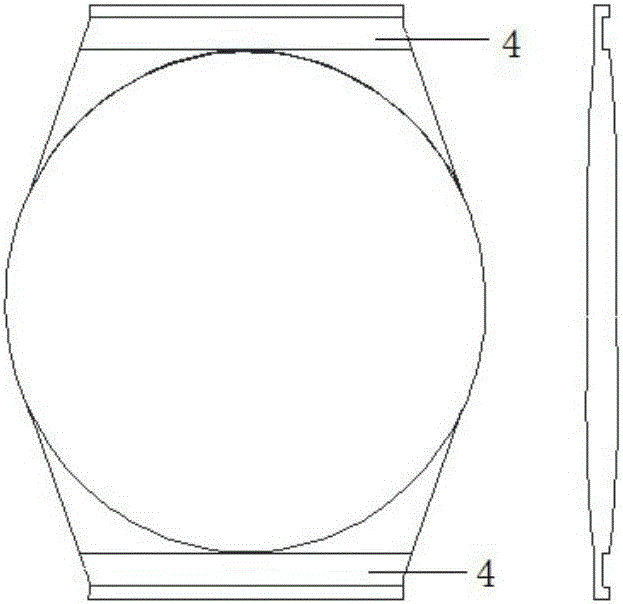
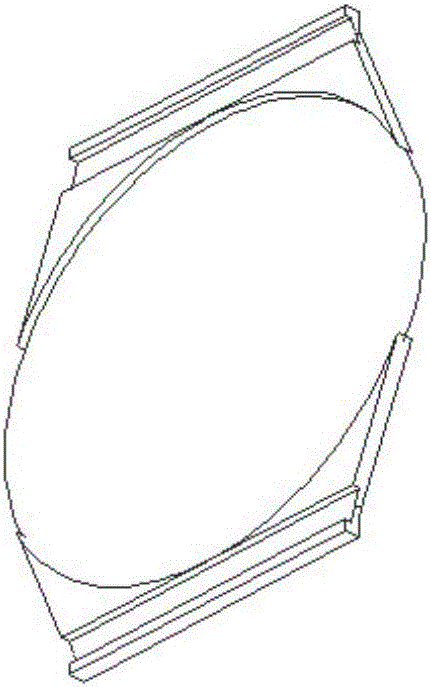
The invention discloses a variable multi-focus artificial lens. The artificial lens comprises an optical body (1), loops (2) and silica gel connecting pieces (3), wherein the silica gel connecting pieces (3) are located between the optical body (1) and the loops (2), and the optical body (1) and the loops (2) are combined together through concave and convex grooves in a spliced manner. Grooves (4) are formed in two ends of the optical body (1), and grooves (5) are formed in the ends, combining with the optical body (1), of the loops (2). The convex grooves are formed in two ends of each of the silica gel connecting piece (3) respectively in the width direction, including the convex groove (6) and the convex groove (7). The optical body is a multi-focus optical zone, and focal power change of the multi-focus artificial lens can be effectively increased through back-and-forth movement in the multi-focus optical zone.
Owner:WUXI VISION PRO
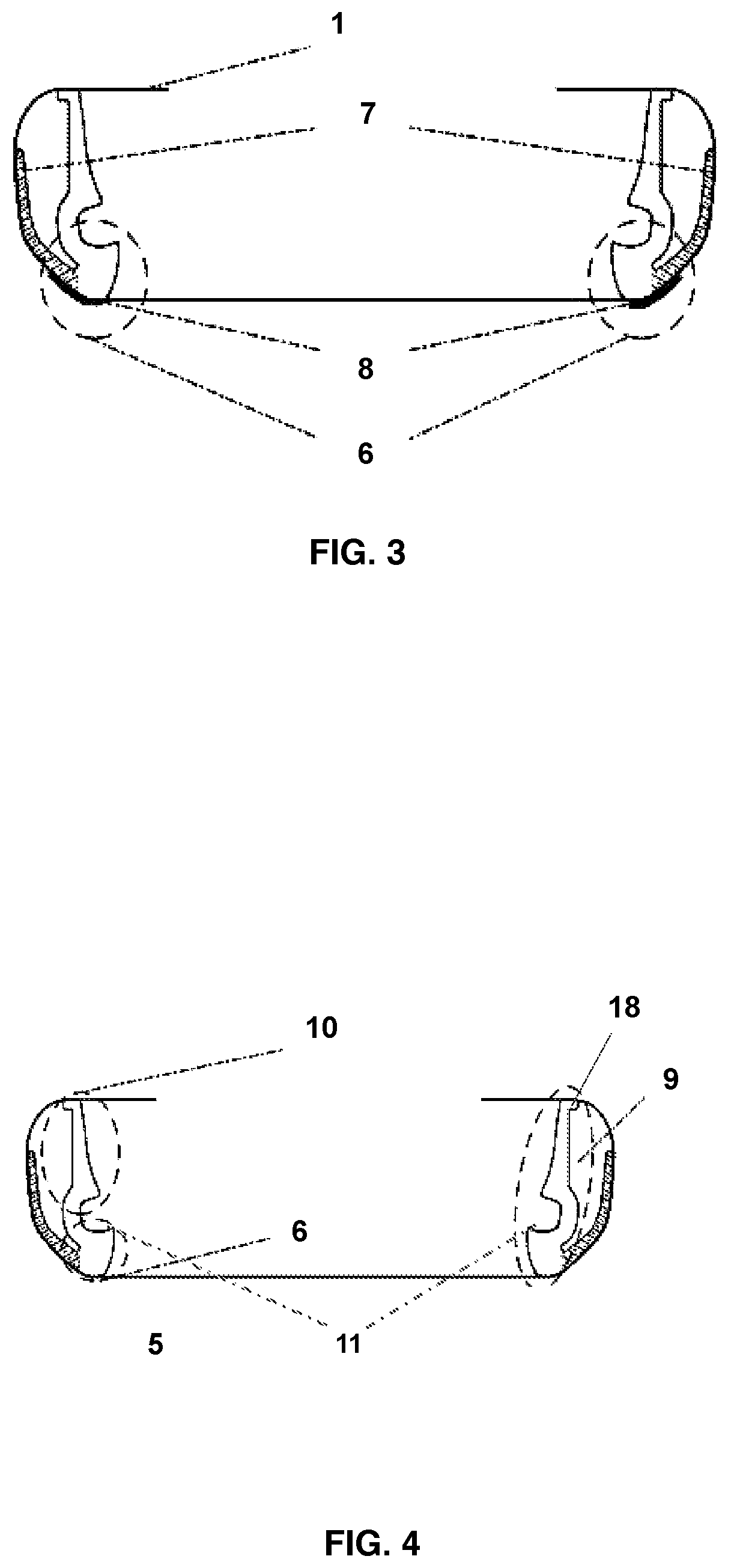
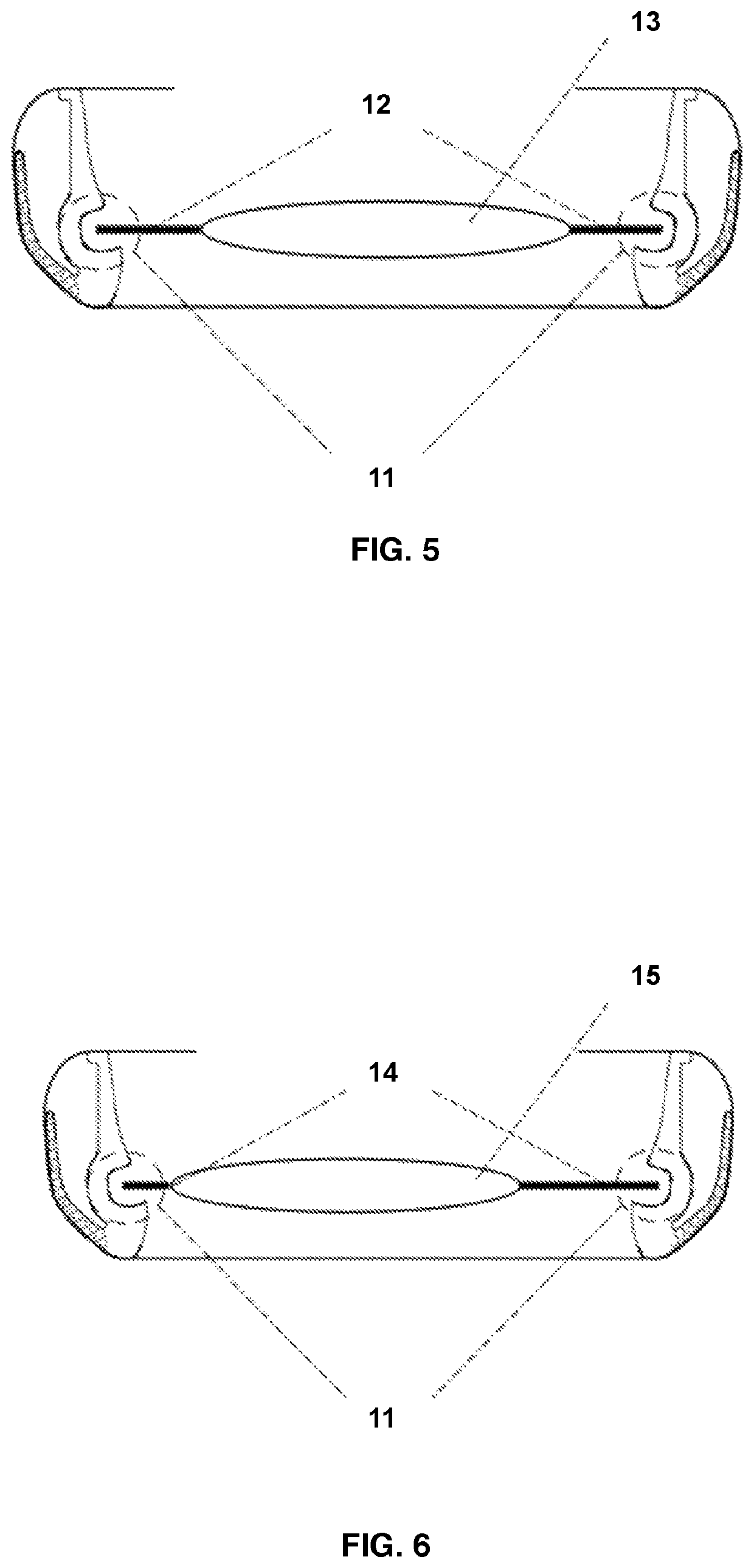
Laser fiducials for axis alignment in cataract surgery
A fiducial is generated on an internal anatomical structure of the eye of a patient with a surgical laser. A toric artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is positioned so that a marker of the toric IOL is in a predetermined positional relationship relative to the fiducial. This positioning aligns the toric IOL with the astigmatic or other axis of the eye. The toric IOL is then implanted in the eye of the patient with high accuracy.
Owner:眼力健发展有限责任公司
Intraocular lens and associated design and modeling methods
A multifocal IOL (M-IOL) has a phase-altering characteristic that can control the diffraction and interference of light propagating there through to effect multifocality and extended depth of focus (EDOF). The embodied IOLs include engineered, discrete phase profiles on one or both of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the lens to intentionally manipulate the light in a designated manner. A design method for defining the discrete phase profile on the lens surface. The engineered phase profile is constructed by concentric annular zones having an abrupt step jump at the trailing circumferential edge of each zone. An optical modeling method to simulate the optical performance of the embodied IOLs in an optical ray tracing environment.
Owner:河南赛美视生物科技有限公司
Multifocal intraocular lens with extended depth of field
ActiveUS20170290657A1Small apertureInhibitionSpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensOptical axisDepth of field
Multifocal intraocular lens with extended depth of field that comprises, in at least one of the surfaces (2), a small zone with a multifocal profile with a defined optical axis (3) and, in the peripheral region and coaxial to the multifocal zone, a ring-shaped opaque mask (1) that partially or totally block light to produce a small aperture effect and, therefore, the multifocal profile has a radius equal or larger than the internal radius of the mask (1), and there is at least one transition between focal zones or one diffractive step inside the internal radius of the mask (1).
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Intraocular lens resistant to eccentricity and inclination clinically
PendingCN111658232AReduce sensitivityPlay a compensatory roleIntraocular lensOphthalmology departmentImaging quality
The invention belongs to the technical field of ophthalmic lenses, and particularly relates to an intraocular lens resistant to eccentricity and inclination clinically. The intraocular lens resistantto eccentricity and inclination clinically is a high-order aspheric intraocular lens with weak negative spherical aberration, and the intraocular lens is placed in a posterior chamber of the human eyeto replace a turbid natural lens. The intraocular lens has the weak negative spherical aberration of-0.1 micron - 0, and plays a role in compensating the positive spherical aberration of the human cornea. The intraocular lens comprises an anterior optical surface and a posterior optical surface, wherein at least one of the anterior optical surface and the posterior optical surface is an asphericoptical surface. The intraocular lens provided by the invention has better contrast sensitivity under a dark light condition (namely under a large-aperture diaphragm), and can improve the overall imaging quality of an intraocular lens eye under a real postoperative clinical condition.
Owner:XIAN PILLAR BIOSCI CO LTD
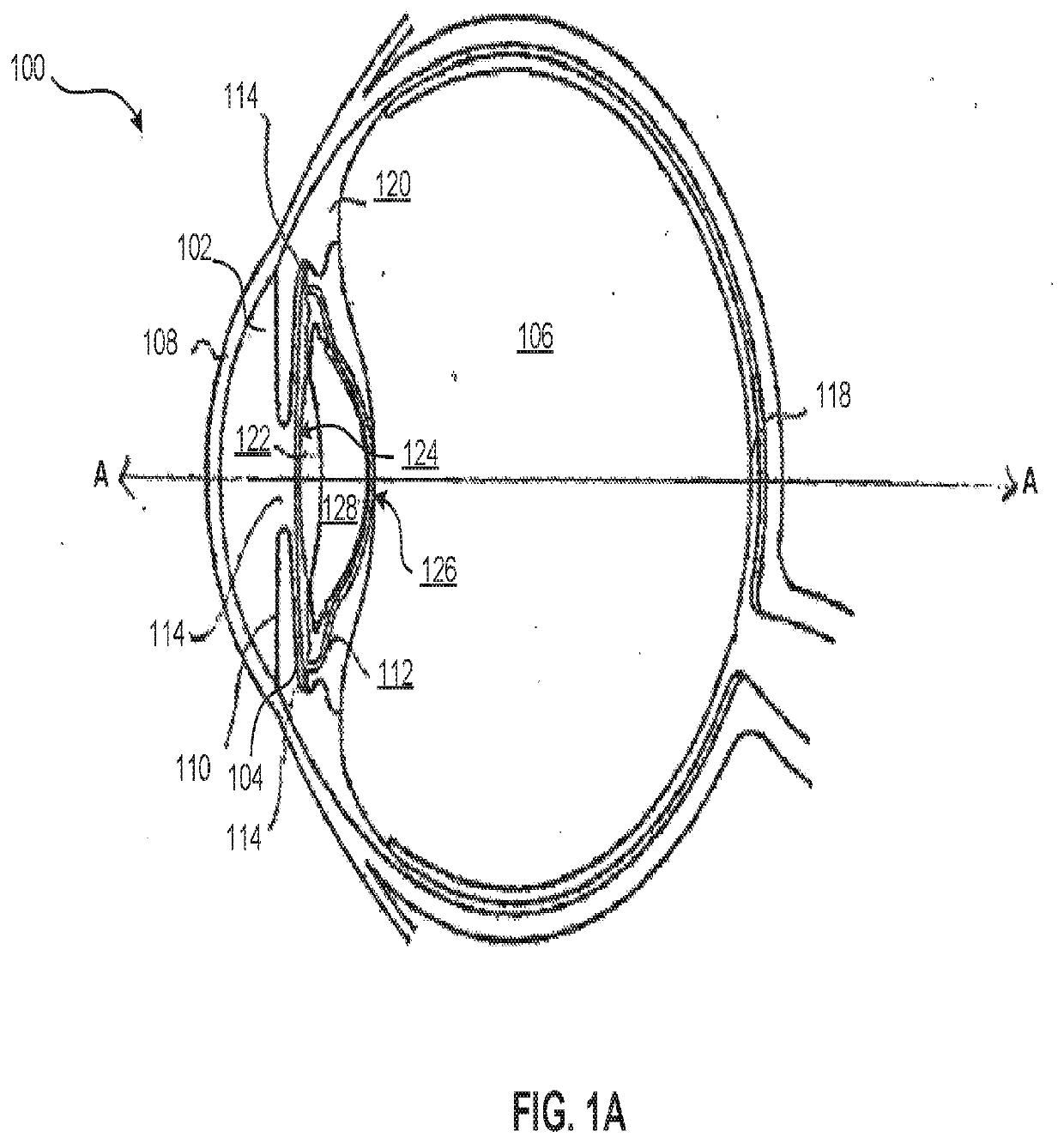
Devices for reconstruction of a lens capsule after cataract surgery
Provided herein are devices used to reconstruct a natural lens capsule after a cataract surgery. The device flexibly adapts to the tension of the lens capsule as it is relaxed or contracted. This device comprises a ring-shaped rigid component. The rigid component comprises a distal end in contact with an anterior surface of the capsule and a proximal end disposed on a posterior surface of the capsule and disposed against a Wieger's ligament of the eye. A ring-shaped flexible component substantially concentric with the rigid component is flexibly fitted against an inner surface of the capsule. The ring-shaped flexible component comprises a proximal end formed on an outer surface of a proximal end of the rigid component, and a distal end extending away from the rigid component. A groove is disposed on an inner surface of the rigid component configured to receive haptics on an intraocular lens.
Owner:EYE PCR BV
Laser fiducials for axis alignment in cataract surgery
ActiveUS10219945B2Facilitate surgical procedureLaser surgeryDiagnostic markersAnatomical structuresCataract surgery
A fiducial is generated on an internal anatomical structure of the eye of a patient with a surgical laser. A tonic artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is positioned so that a marker of the tonic IOL is in a predetermined positional relationship relative to the fiducial. This positioning aligns the tonic IOL with the astigmatic or other axis of the eye. The toric IOL is then implanted in the eye of the patient with high accuracy.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Triamcinolone acetonaide acetate nano controlled-release formulation, preparation method thereof and artificial lens containing same
InactiveCN102327212ATurbidity preventionImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticPolyvinyl alcoholLate complication
The invention relates to a triamcinolone acetonaide acetate nano controlled-release formulation, a preparation method thereof and an artificial lens containing the same for preventing inflammation and late complication after cataract operation, wherein the triamcinolone acetonaide acetate nano controlled-release formulation is prepared from the triamcinolone acetonaide acetate-chloroform solution with the triamcinolone acetonaide acetate concentration of 1%-3%, the lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA)-dichloromethane solution with the lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (PLGA) concentration of 2%-5%, and the polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with the concentration of 0.5%-1.5%. The invention provides the preparation method of the triamcinolone acetonaide acetate nano controlled-release formulation which can effectively prevent posterior capsular opacity, has simple preparation process, and is convenient to use and the artificial lens containing the triamcinolone acetonaide acetate nano controlled-release formulation.
Owner:严宏 +1
Intraocular lens and process for producing the same
Provided is an intraocular lens that inhibits secondary cataract which occurs after insertion of an intraocular lens and that is free from the adherence and deposition of a protein, etc., to / on the front surface of the lens, and the intraocular lens has an optic portion with a front surface and a back surface, said front surface and said back surface being different from each other in the property of adhering to a protein and satisfying the relationship of the expression (x),PAF<PAB (x)wherein PAF is the property of adherence of said front surface to fibronectin and PAB is the property of adherence of said back surface to fibronectin in a fibronectin adherence test.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Controlled axial displacement posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens
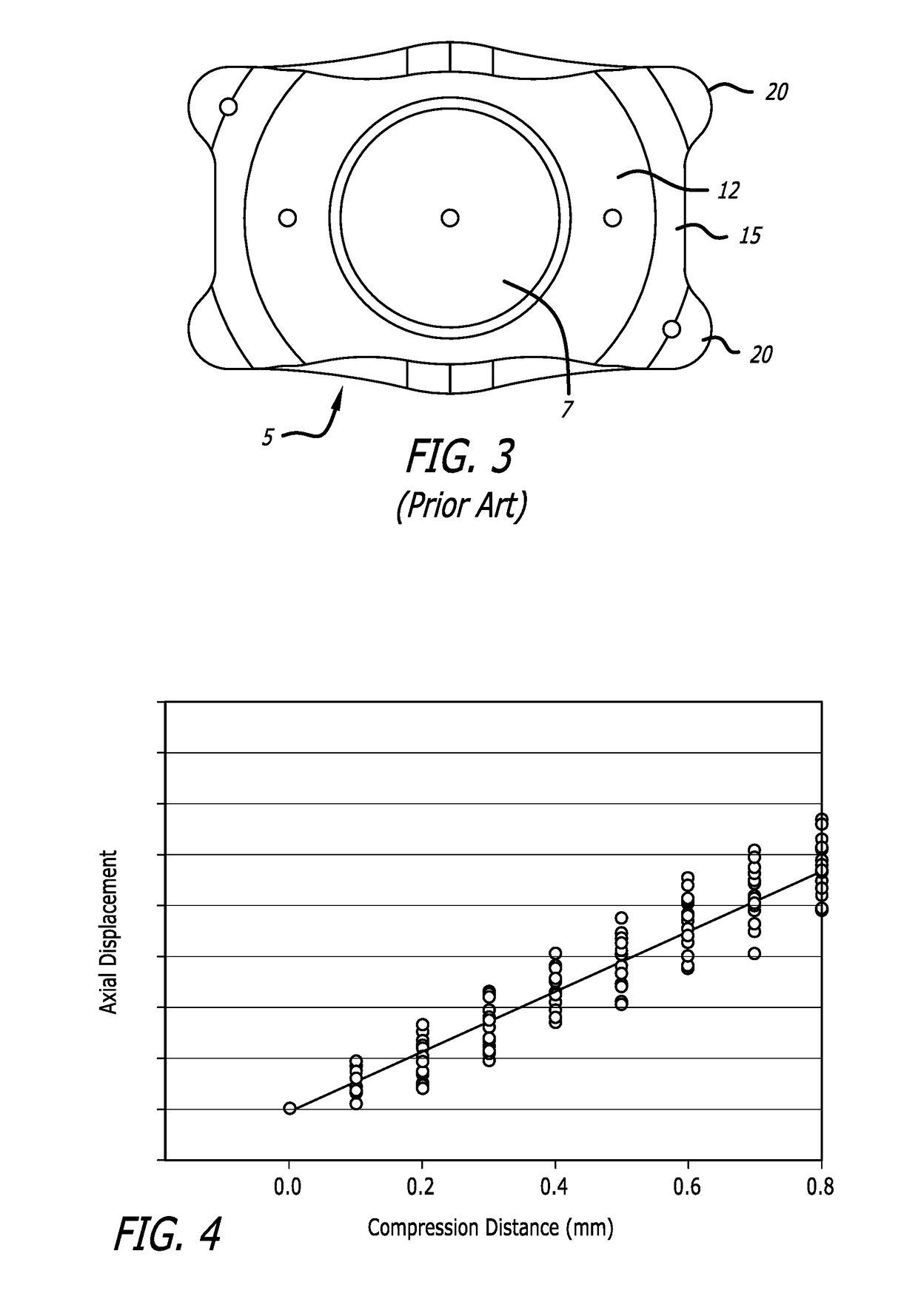
InactiveUS20180318064A1Minimize and eliminate axial displacementReduce in quantityIntraocular lensAxial displacementMedicine
Owner:STAAR SURGICAL COMPANY INC
Vision correction systems and methods for using an intraocular lens enclosed in an inner capsulated bag
A intraocular lens system includes an artificial capsular bag adapted for implantation within a natural capsular bag of an eye and an intraocular lens adapted to be received within the artificial capsular bag. At least a portion of the intraocular lens tilts and moves forwards within the artificial capsular bag under gravitational force with respect to a cornea and retina of the eye to create myopia.
Owner:INGRAM RONALD WILLIAM
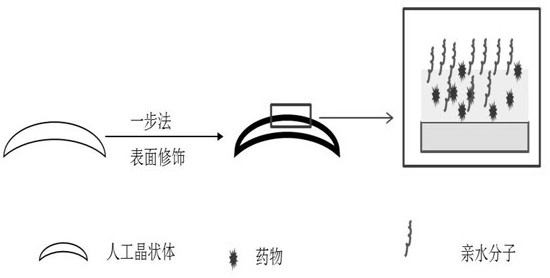
A kind of intraocular lens with hydrophilic-drug sustained-release synergistic function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107754018BEasy to disinfectEasy to packCoatingsIntraocular lensCell adhesionPosterior capsule opacification
The invention relates to an artificial lens with a hydrophilic-medicine sustained release synergistic function, and a preparation method thereof. A medicine-loading-hydrophilic multifunctional coatingis modified on the surface of the artificial lens, and the synergistic effect of resisting cell adhesion at an early stage after implantation and resisting lens epithelia cell proliferation at middleand late stage is achieved, so that the occurrence rate of posterior capsule opacification can be reduced and a high-biocompatibility artificial lens is obtained; a hydrophilic-medicine-loading multifunctional modification layer is constructed on the surface of the artificial lens by a one-pot method, the manufacturing process is simple and low in cost, the tedious steps required by surface modification in the past are avoided, and the artificial lens can be applied to the surface of a three-dimensional implantable device with various complex shape structures. The manufactured zwitterionic modified artificial lens is convenient to disinfect, packaging and transport, and is an artificial lens industrialized product which is low in cost, convenient and practical.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
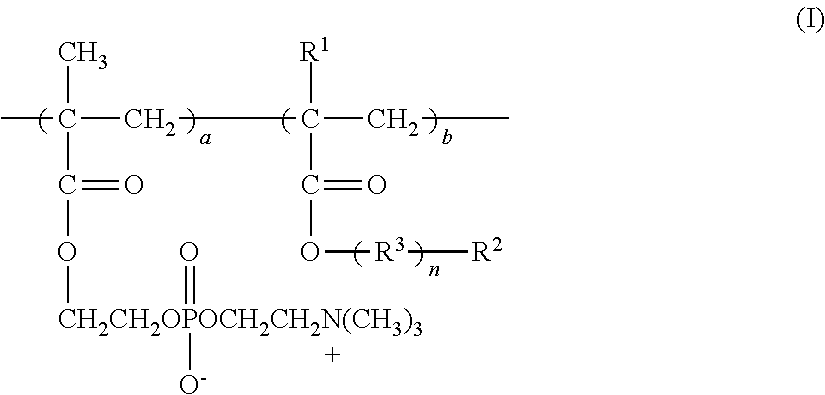
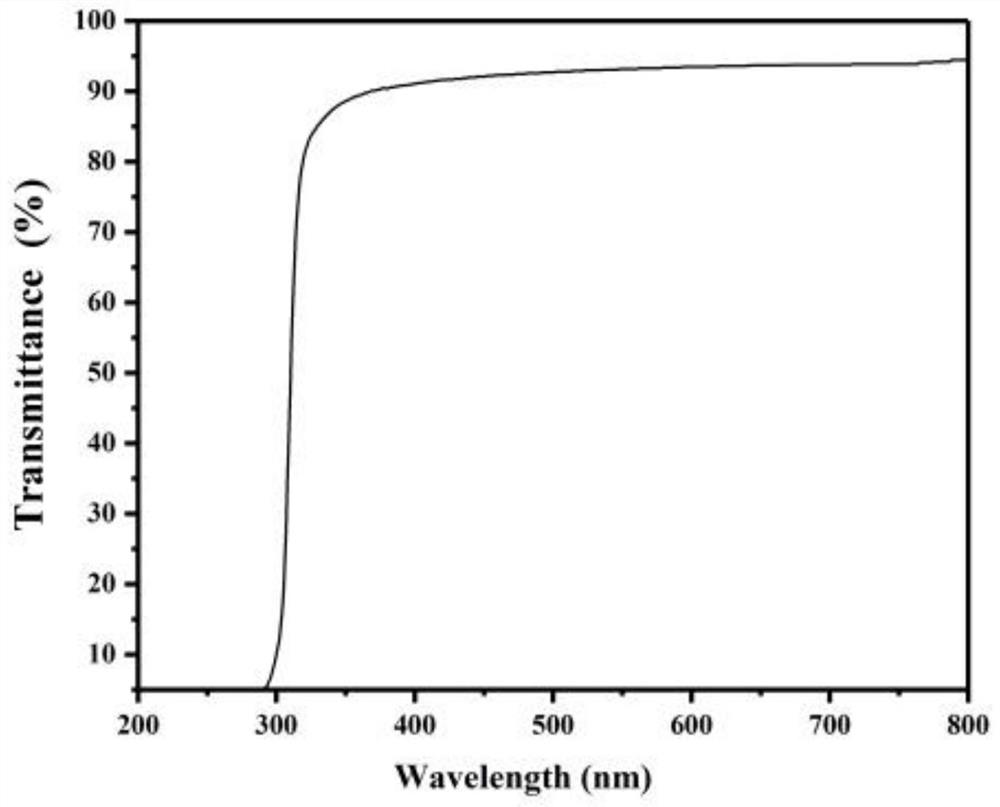
A kind of high refractive index hydrophobic foldable intraocular lens material and its preparation method
ActiveCN110003385BGood optical performanceEasy to manufactureTissue regenerationProsthesisMethacrylatePolymer science
The invention provides a high-refractive-index hydrophobic foldable intraocular lens material, which consists of three parts of monomers formed by free radical polymerization. The first part of monomer B is a polymerizable monomer containing phenyl, specifically including B1 and B2 Two parts, wherein B1 accounts for 50%-60% of the total monomer content, B2 accounts for 30-40% of the total monomer content, and the B1 and B2 are different; the second part of the monomer C is a branched alkyl chain acrylic acid or methacrylate, accounting for 1-10% of the total monomer content; the third part monomer D is a crosslinking agent, accounting for 1.5-2.5% of the total monomer content; the total monomer content is three parts The sum of monomers B+C+D. Compared with common intraocular lens materials, the intraocular lens material provided by the present invention has higher key optical performance parameters such as transmittance and refractive index. required material properties.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
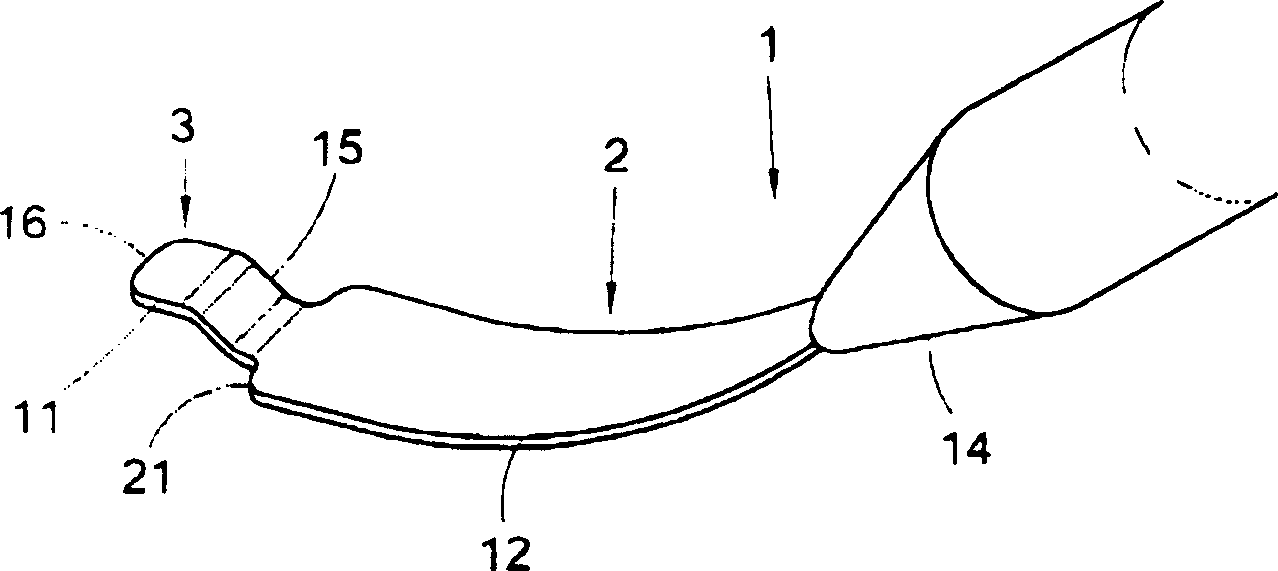
Artificial crystalline for transplanting in eyes and appliance and method for inserting such crystalline
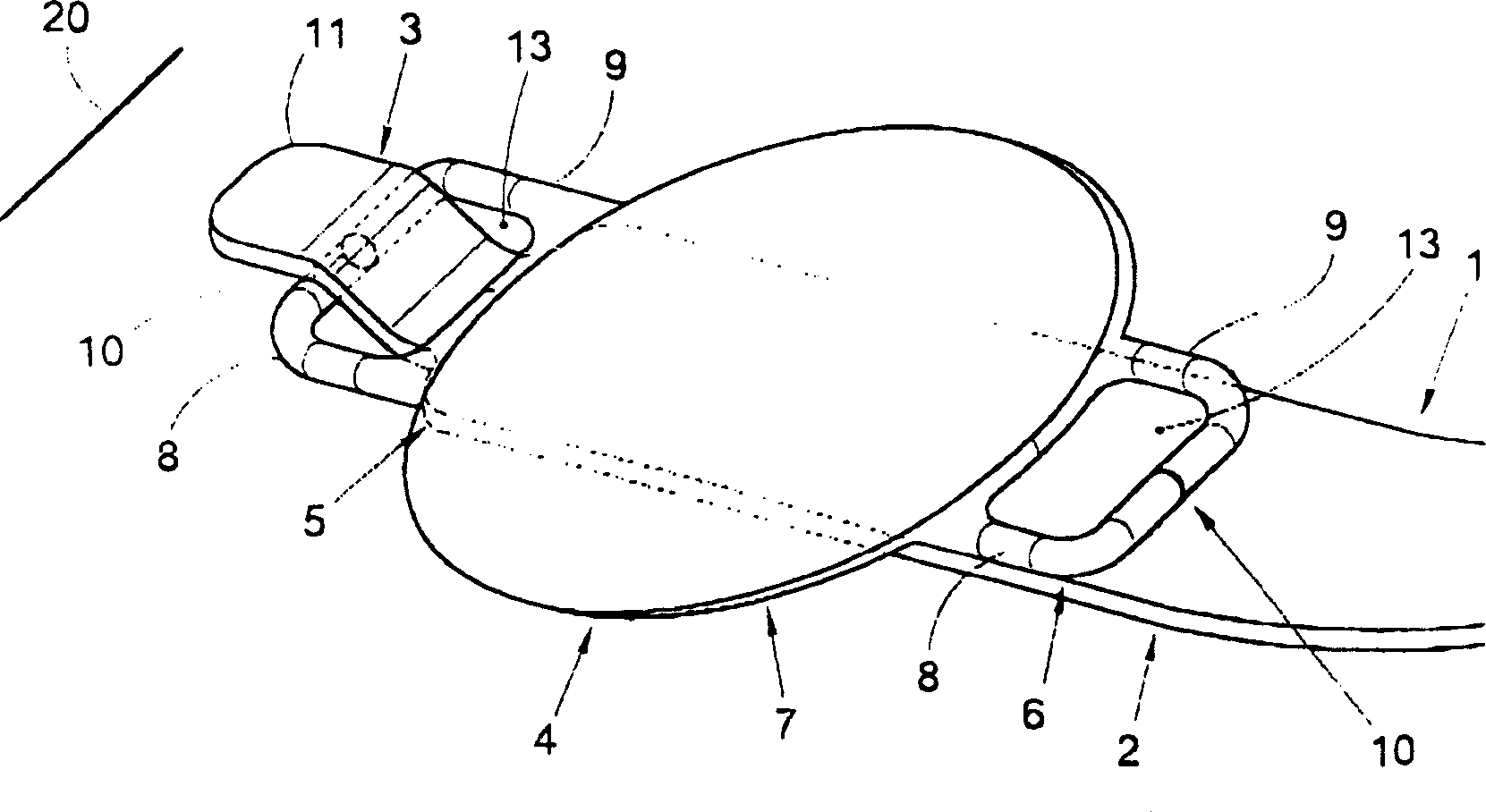
InactiveCN1446523AHelp to deal withReduced risk of contact with sensitive tissues in the eyeEye surgeryIntraocular lensHigh stiffnessIntraocular lens
An intraocular lens includes an optical portion (7; 607; 907; 1107) of a transparent, deformable material, at least one haptic (5, 6; 205, 206; 405, 406, 706; 806; 905; 1005; 1105; 1205) radially projecting from the optical portion for supporting the optical portion in a position parallel to and against an anterior iris surface plane (936; 1136), and at least one aperture (13; 213; 713; 913; 1013; 1113) bounded by the haptic. At least a stiff portion of the haptic has a higher stiffness against bending about an axis in the radial direction than the optical portion. Furthermore, the stiff portion has a width ( a ) measured parallel to the plane and perpendicular to the radial direction, which is smaller than the size ( b ) of the optical portion in the direction of the width. An instrument for carrying out insertion of such a lens are also described.
Owner:オフテックビーブイ
Extraocular-zooming-combined focal length adjusting method for artificial lens
PendingCN112370212ALarge adjustment rangeEasy to adjustIntraocular lensAccommodative amplitudeVisual acuity
The invention provides an extraocular-zooming-combined focal length adjusting method for an artificial lens. A creative part lies in that an entire adjustable design is divided into two parts, i.e., an intraocular part and an extraocular part, a relatively large range of adjustment is achieved with a relatively small amplitude of adjustment, the adjusting effect is good, and the limitation of thetraditional artificial lenses that only intraocular adjustment is available. The intraocular part is a spherical, non-spherical or other-optical-designed artificial lens, is used for partially correcting aberration of human eyes and has micro-adjustment capability. The extraocular part is an Alvarez or zoom lens with zooming capability, functions similar to those of a natural lens can be achievedthrough matching between the intraocular part and the extraocular part, namely stepless zooming from proximal places to distant places, and continuous clear vision is provided for a sufferer.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
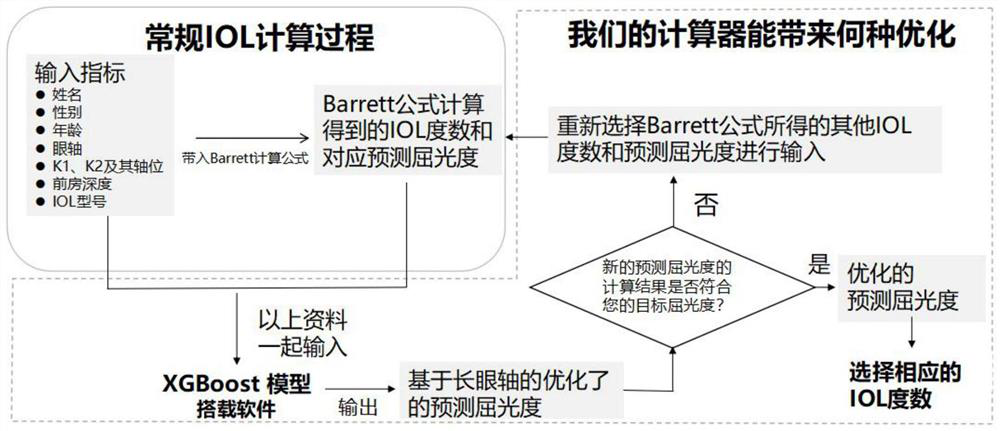
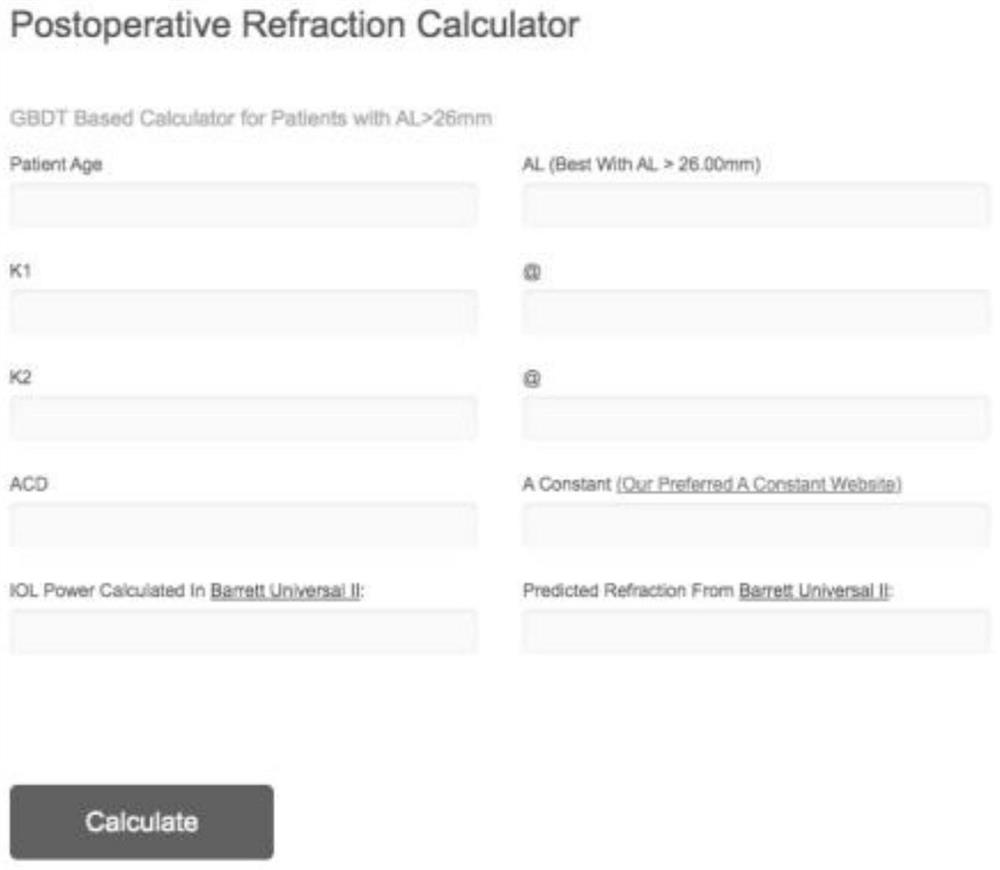
Artificial intelligence assisted optimized highly myopia intraocular lens degree calculator
PendingCN114300136AEasy to useImprove visual effectsMathematical modelsMedical data miningOphthalmologyIntraocular lens implantation procedure
The invention relates to an artificial intelligence-assisted optimized highly myopia intraocular lens degree calculator using method, which comprises the following steps: S1, inputting basic information of a patient, and substituting the basic information into a Barrett calculation formula to obtain an IOL degree and a corresponding predicted diopter; s2, inputting the obtained IOL degree and diopter into XGBoost model carrying software; s3, outputting the optimized predicted diopter based on the long eye axis; and S4, comparing the optimized predicted diopter with the target diopter. The method has the advantages that the degree of the intraocular lens can be accurately calculated and the postoperative reserved diopter can be predicted before the high-myopia intraocular lens implantation operation, myopia drift or hyperopia drift occurring after the operation can be effectively reduced, and the visual effect after the intraocular lens implantation operation is improved; the postoperative refraction state of a patient with high myopia can be accurately predicted, and the satisfaction degree of the patient is increased.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
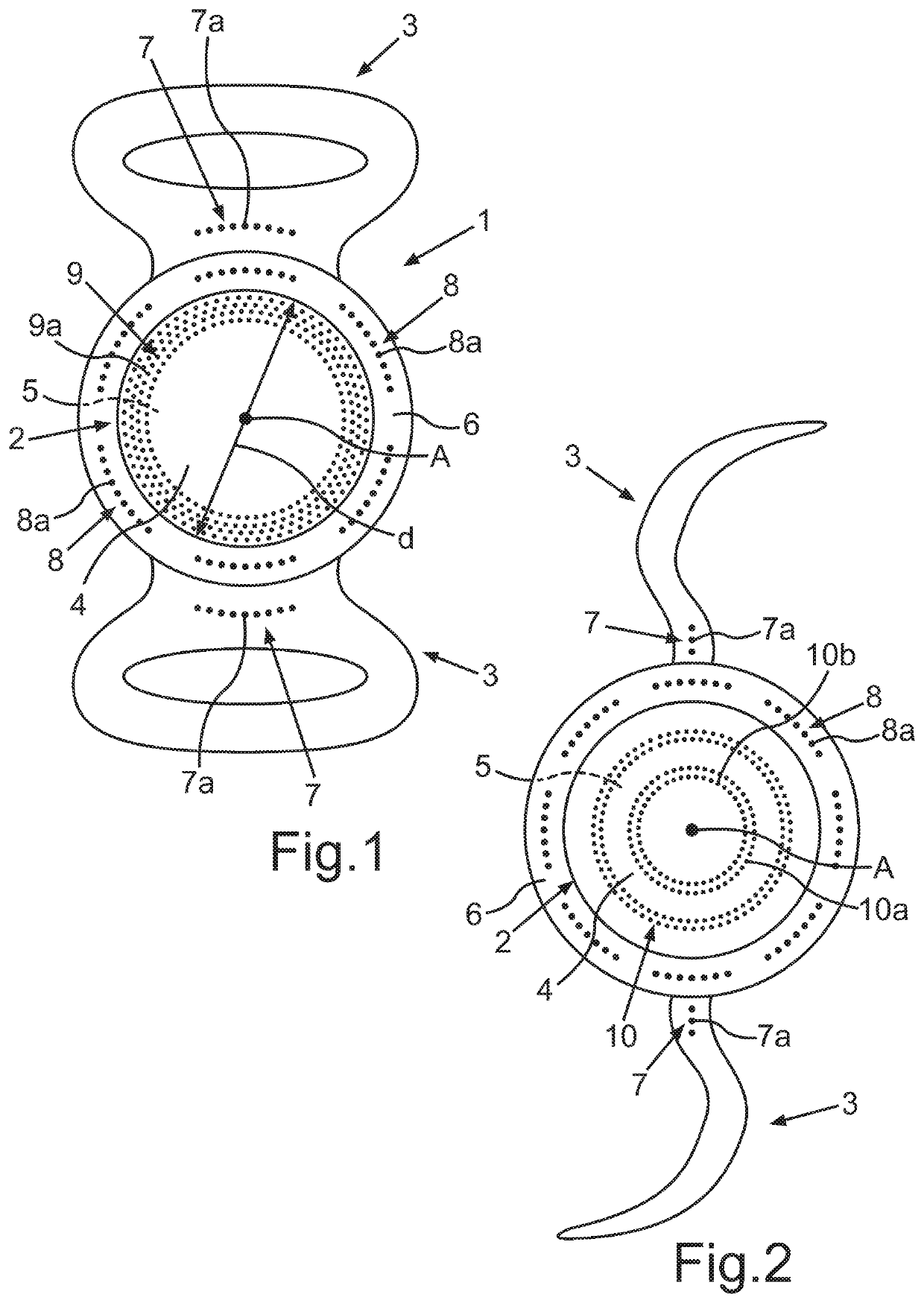
Artificial eye lens having medicine repository formed therein, and method for producing an artificial eye lens
ActiveUS20210161655A1Good blood pressureDesigning can be facilitatedOptical articlesIntraocular lensOphthalmologyArtificial Eyes
The invention relates to an artificial eye lens comprising an optical part, which has a first optical side as viewed in a direction of an optical principal axis of the artificial eye lens and an opposite second optical side, wherein a structure with at least one depression is formed in a haptic arrangement of the artificial eye lens and / or in a surround that surrounds the optical part at least in certain areas and that differs from the haptic arrangement, wherein the structure is formed as a micro-perforation with a multiplicity of perforation zones and at least some perforation zones are filled at least in certain areas with at least one medicament for the purposes of producing a medicament repository. The invention also relates to a method for producing such an artificial eye lens.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com