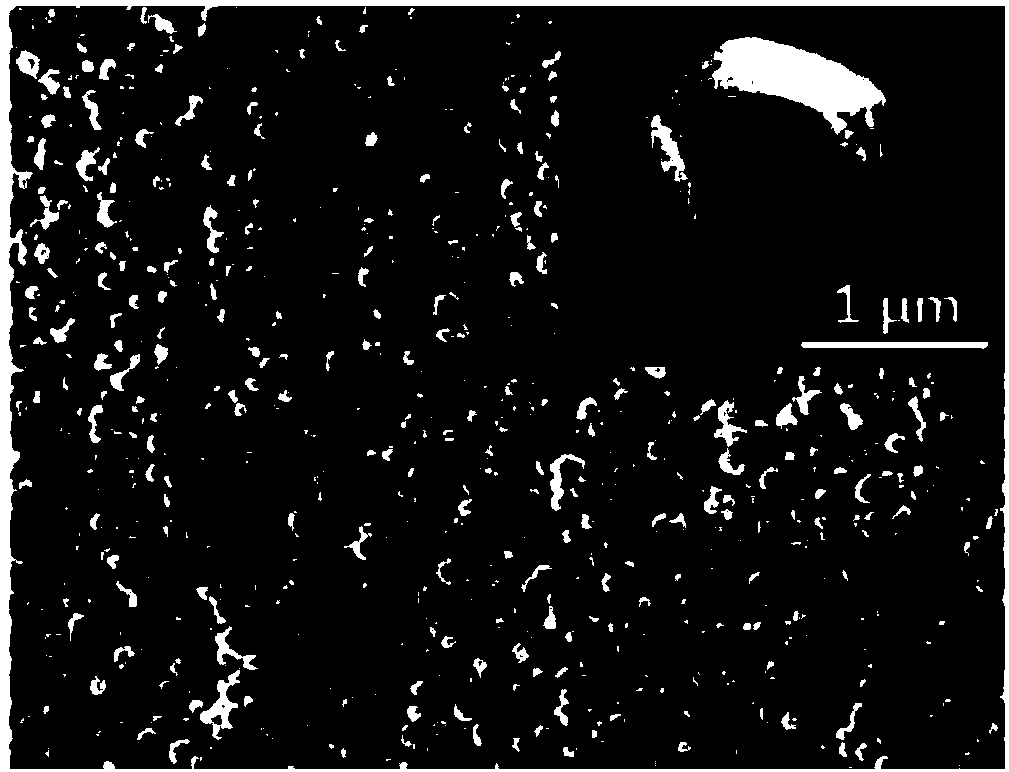
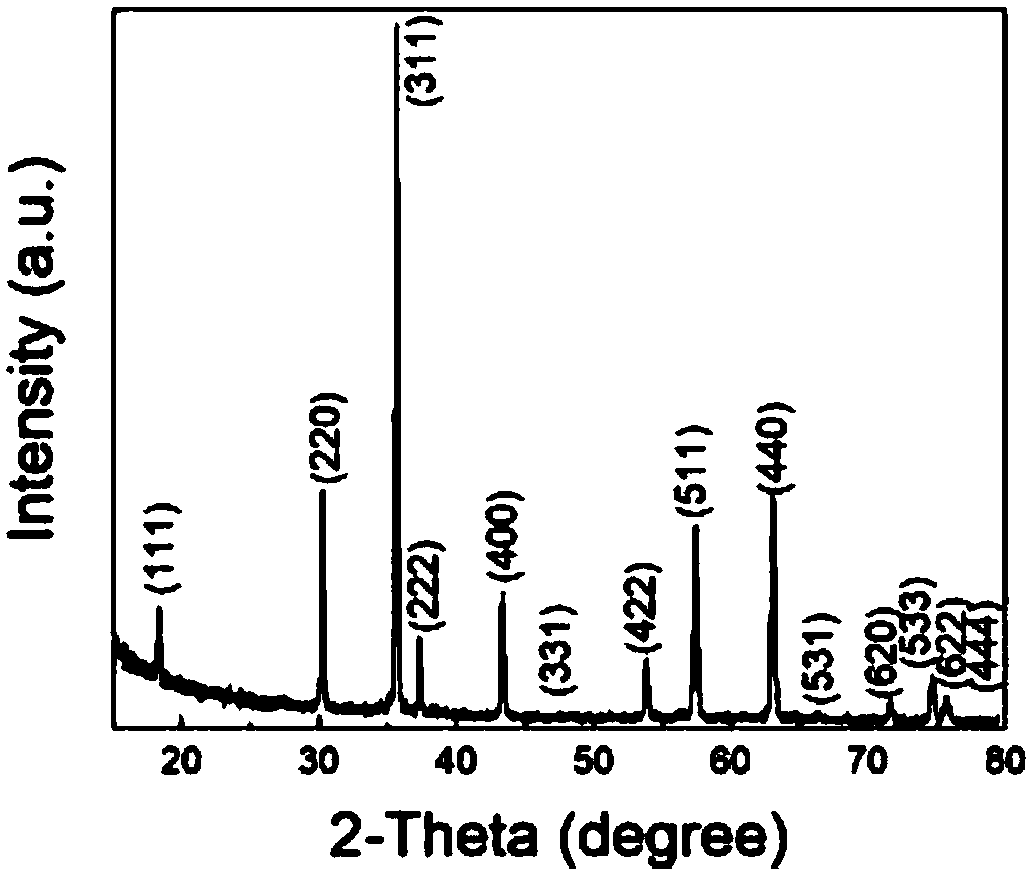
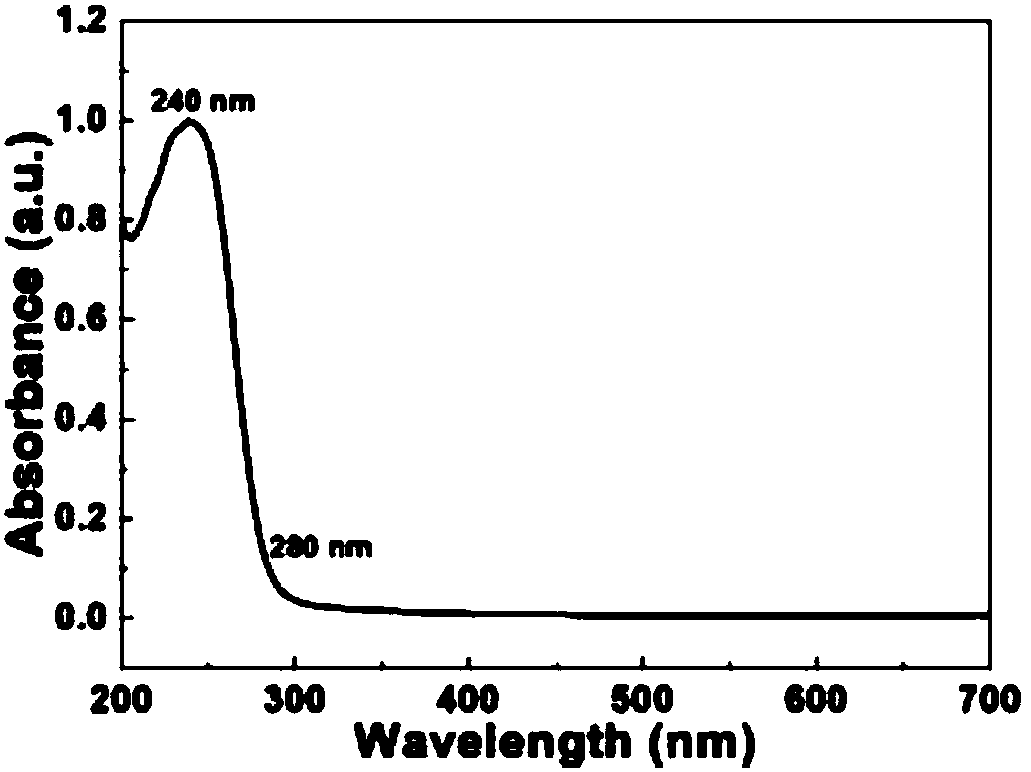
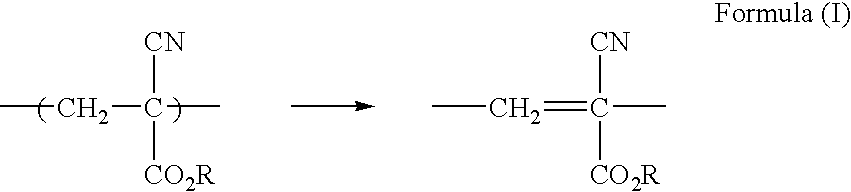Patents
Literature
120 results about "Photo ablation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
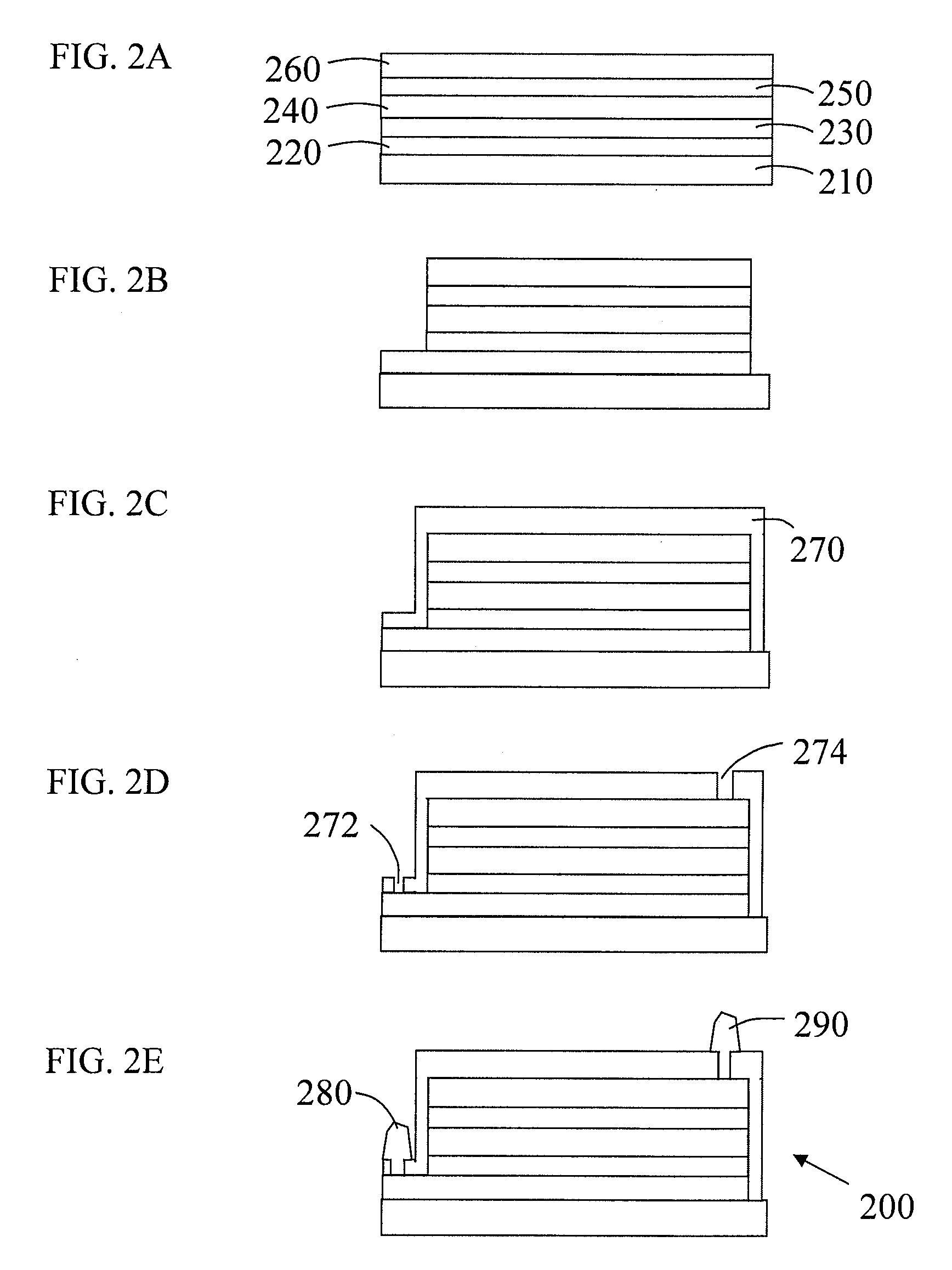
Ophthalmic surgery method using non-contact scanning laser
InactiveUSRE37504E1Low-powerLow-cost and effectiveLaser surgeryDiagnosticsSystem parametersOphthalmic surgery
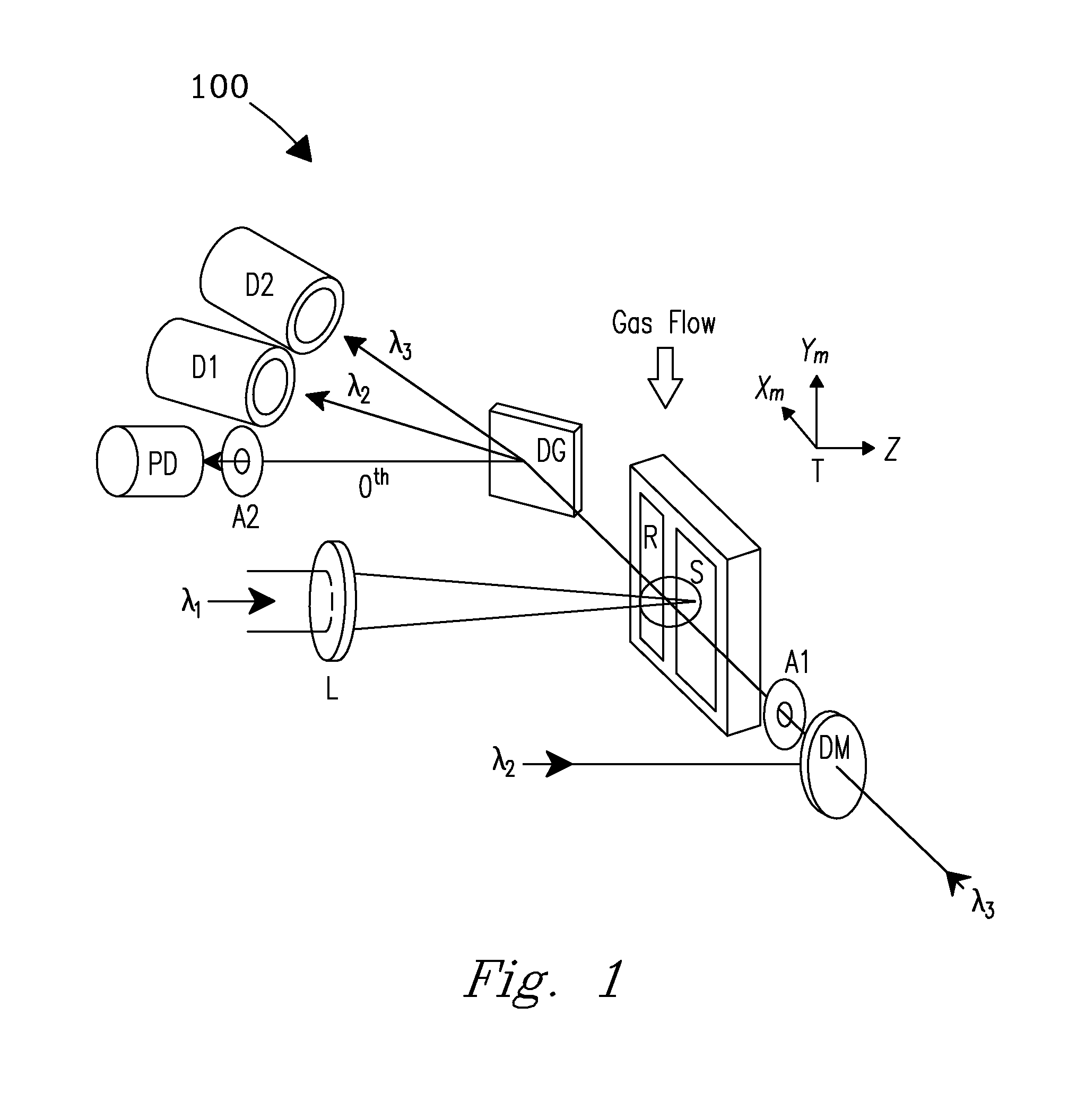
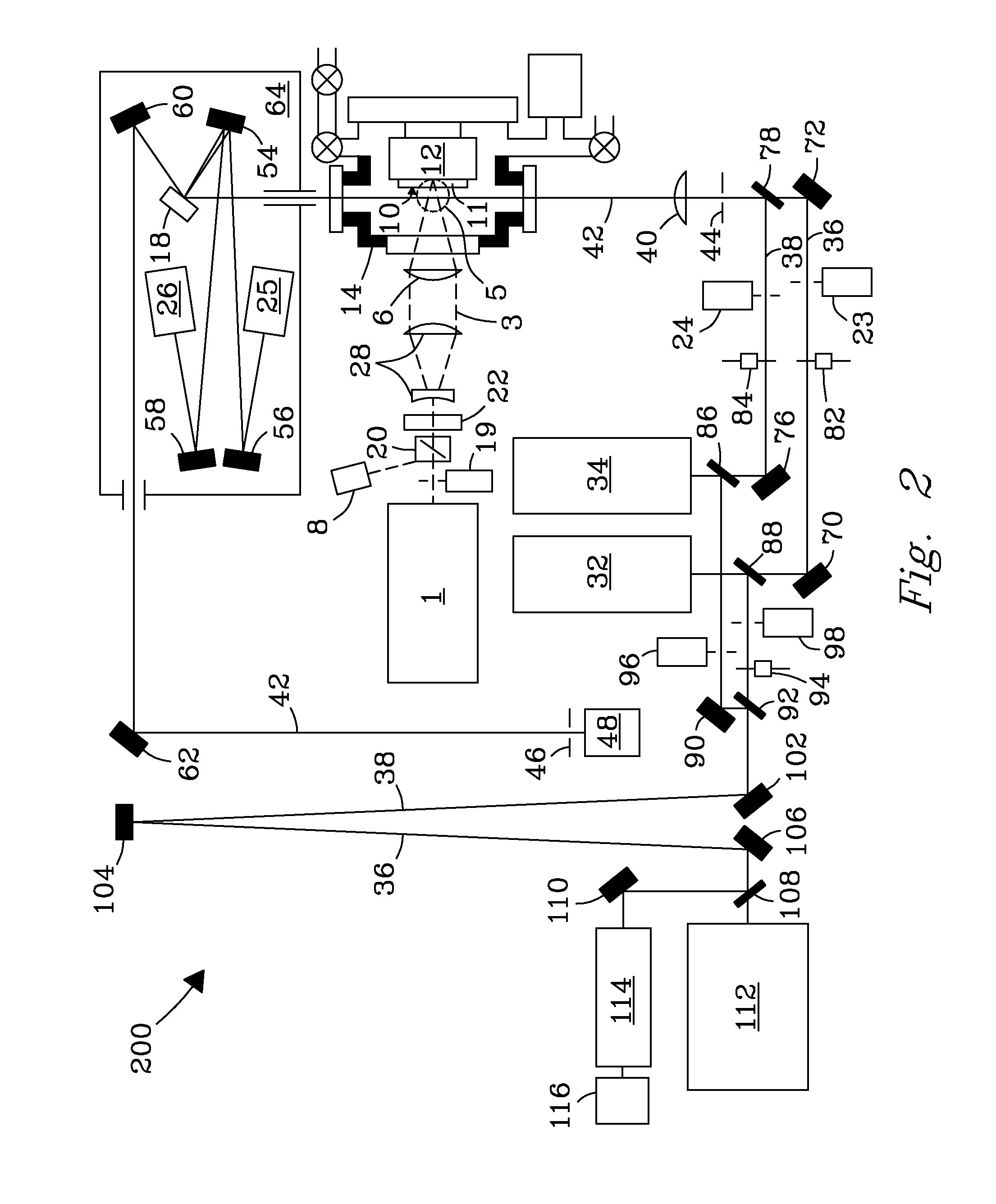
A refractive laser surgery process is disclosed for using compact, low-cost ophthalmic laser systems which have computer-controlled scanning with a non-contact delivery device for both photo-ablation and photo-coagulation in corneal reshaping. The basic laser systems may include flash-lamp and diode pumped UV solid state lasers (193-215 nm), compact excimer laser (193 nm), free-running Er:glass (1.54 microns), Ho:YAG (2.1 microns), Q-switched Er:YAG (2.94 microns), and tunable IR lasers, (750-1100) nm and (2.5-3.2) microns. The advantages of the non-contact, scanning device used in the process over other prior art lasers include being safer, reduced cost, more compact and more precise and with greater flexibility. The theory of beam overlap and of ablation rate and coagulation patterns is also disclosed for system parameters. Lasers are selected with energy of (0.01-10) mJ, repetition rate of (1-10,000), pulse duration of 0.01 nanoseconds to a few hundreds of microseconds, and with spot size of (0.05-2) mm for use with refractive laser surgery.
Owner:LASERSIGHT TECH
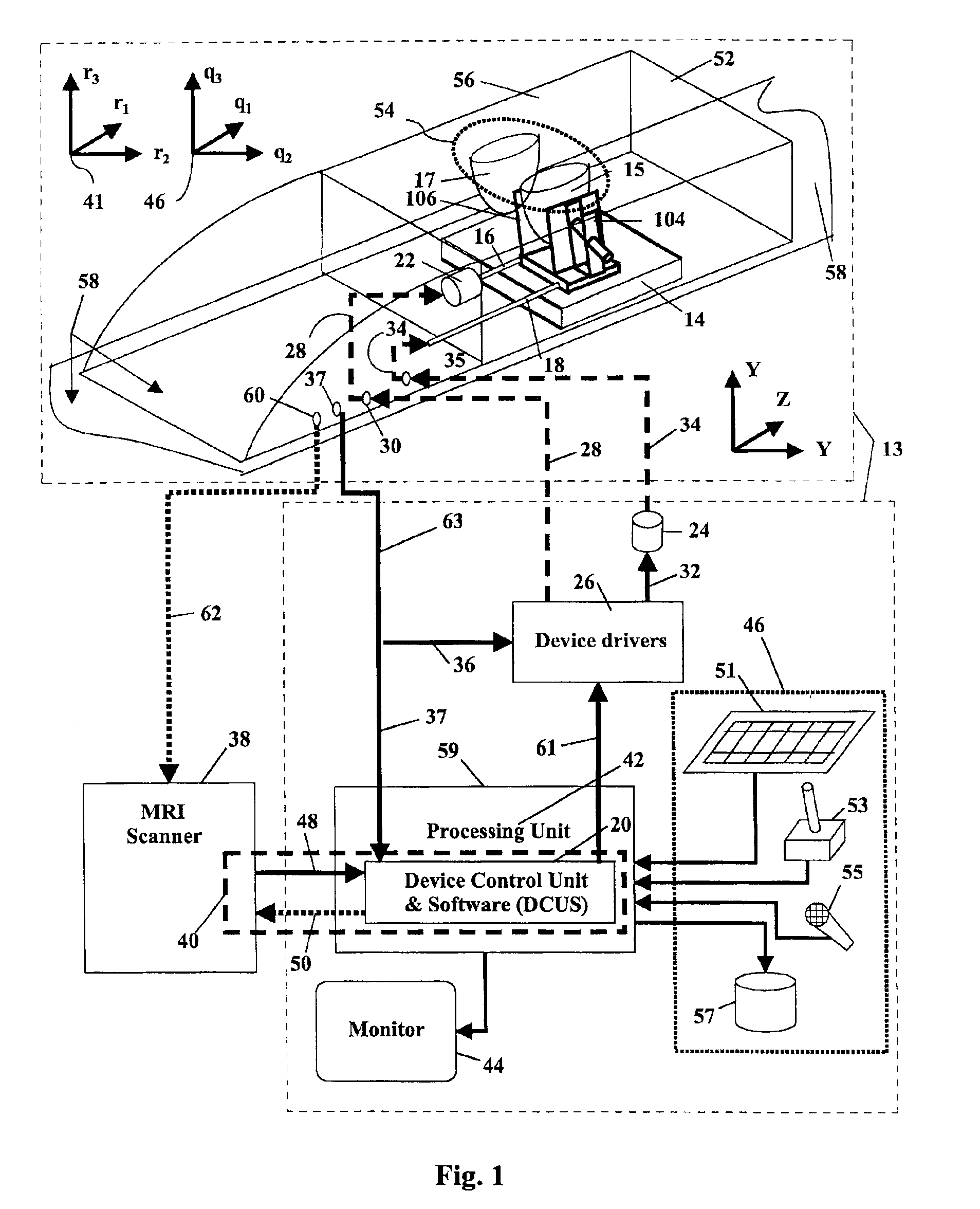
System for MRI-guided interventional mammary procedures
InactiveUS6904305B2Enhanced magnetic resonance imagingProvide flexibilitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsContrast-enhanced Magnetic Resonance ImagingSingle injection
The combination of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and MR-guided subcutaneous core biopsy can be used as a robust approach for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. MRI provides the means to accurately position and monitor interventional procedures such as biopsy, removal of tissue or other transcanular procedures. MRI may also be used in this invention to position and monitor the progress of breast conserving therapies (BCT), such as laser photo-ablation, cryoablation and localized hyperthermia. The general practice of this invention is to provide a remotely controlled apparatus for MR-guided interventional procedures in the breast. The apparatus allows the practice of a method that provides flexibility in conditioning the breast, i.e. orientation and degree of compression, and in setting the trajectory of the intervention. To that end, a robust conditioning / positioning device, fitted with the appropriate degrees of freedom, enhances the efficacy and efficiency of breast interventions by providing the flexibility in planning and executing an appropriate procedure strategy that better suits interventional procedures, either those in current use or yet to be developed. The novelty and potential commercial success of the device originates from its high maneuverability to set and perform the procedure strategy and its adaptability to accommodate an array of interventional probes. Remote control of this device can allow planning the operation and performing the relevant tasks in a short period, for example, within the contrast window provided by a single injection of a contrast agent, and this feature can be operator-independent.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Method for manufacturing electrochromic devices
ActiveUS20090304912A1Improve manufacturabilityReduce complexityRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesDevice materialLaser patterning
This invention contemplates the use of laser patterning / scribing in electrochromic device manufacture, anywhere during the manufacturing process as deemed appropriate and necessary for electrochromic device manufacturability, yield and functionality, while integrating the laser scribing so as to ensure the active layers of the device are protected to ensure long term reliability. It is envisaged that the laser is used to pattern the component layers of electrochromic devices by directly removing (ablating) the material of the component layers. The invention includes a manufacturing method for an electrochromic device comprising one or more focused laser patterning steps. To minimize redeposition of laser ablated material and particulate formation on device surfaces a number of approaches may be used: (1) ablated material generated by the focused laser patterning may be removed by vacuum suction and / or application of an inert gas jet in the vicinity of the laser ablation of device material; (2) spatial separation of the edges of layers and patterning of lower layers prior to deposition of upper layers; and (3) the laser patterning step may be performed by a laser beam focused directly on the deposited layers from above, by a laser beam directed through the transparent substrate, or by a combination of both.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
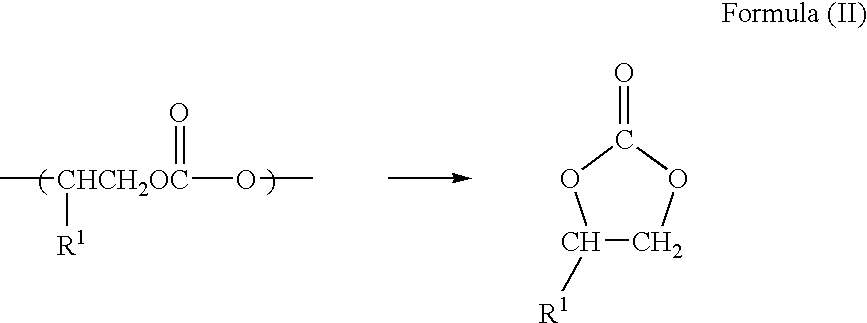
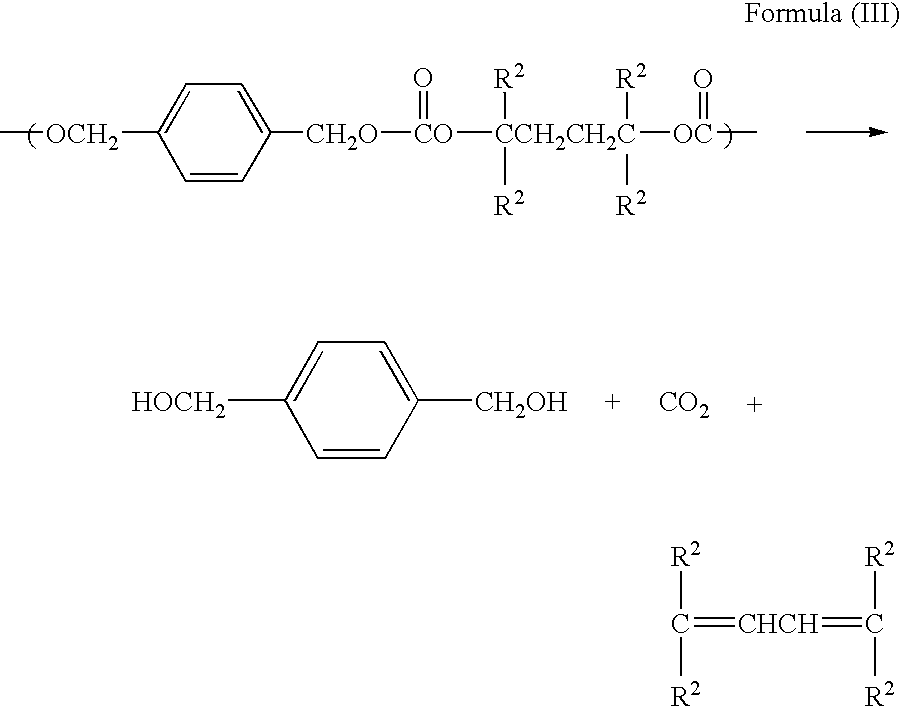
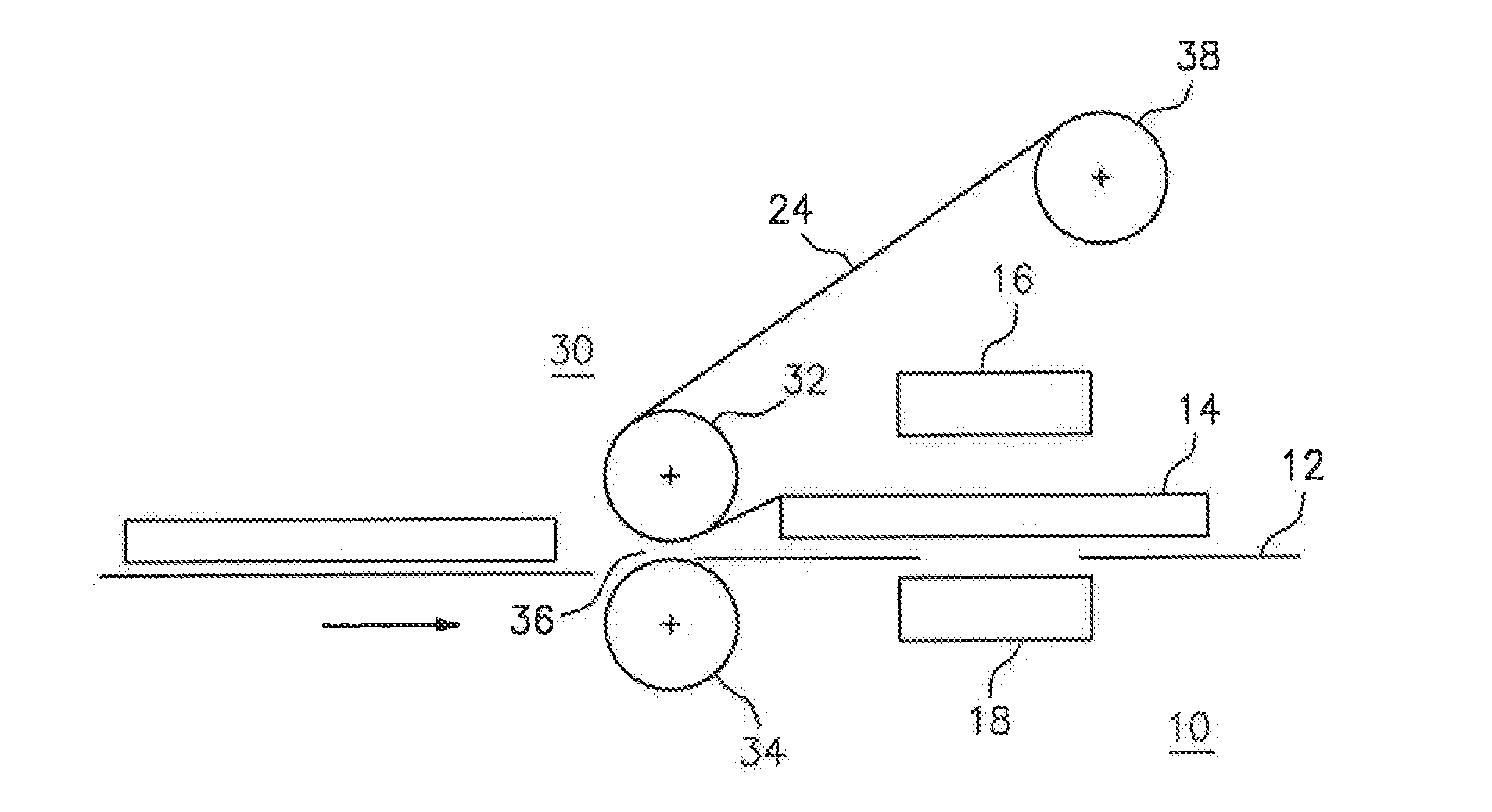
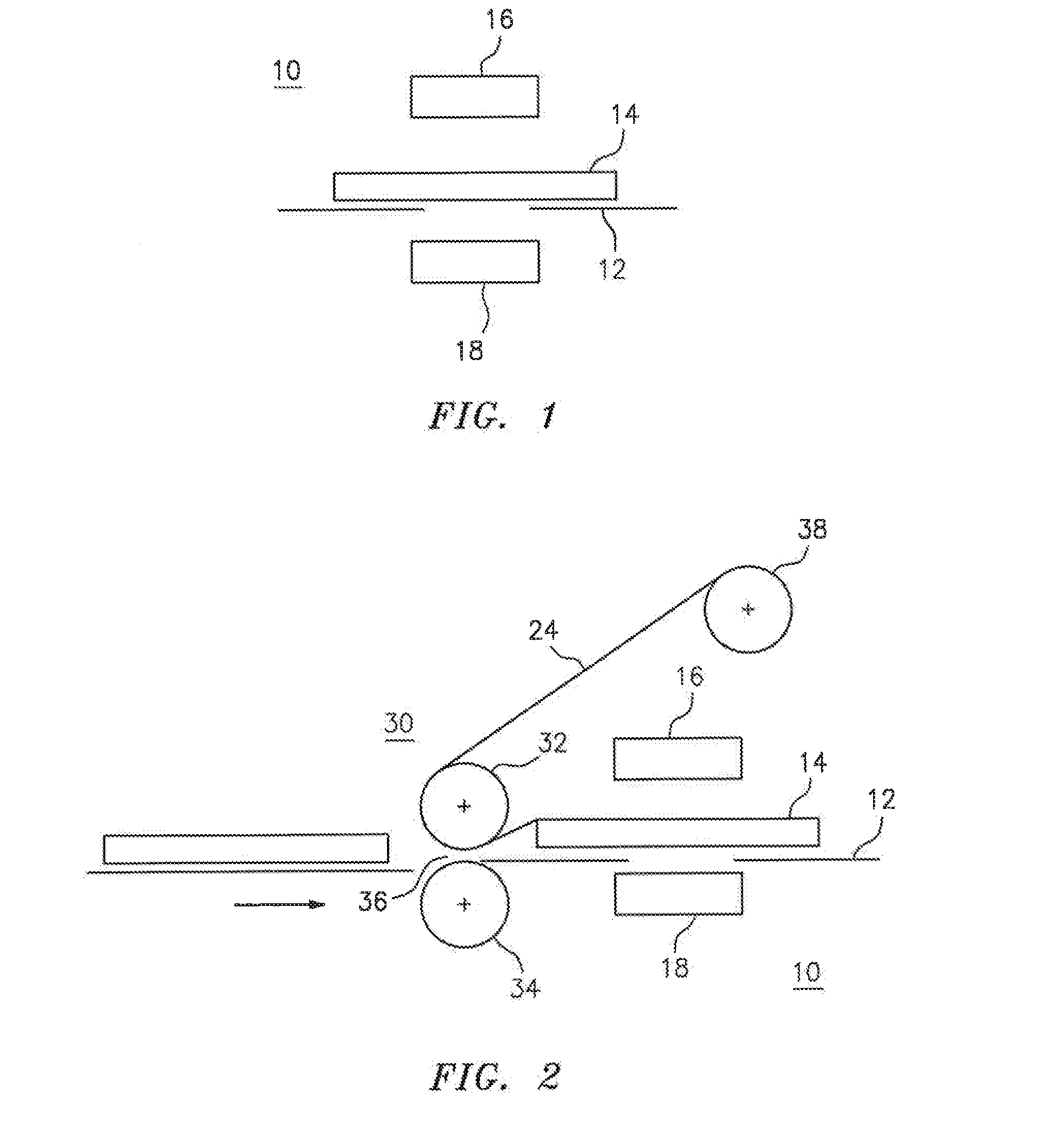
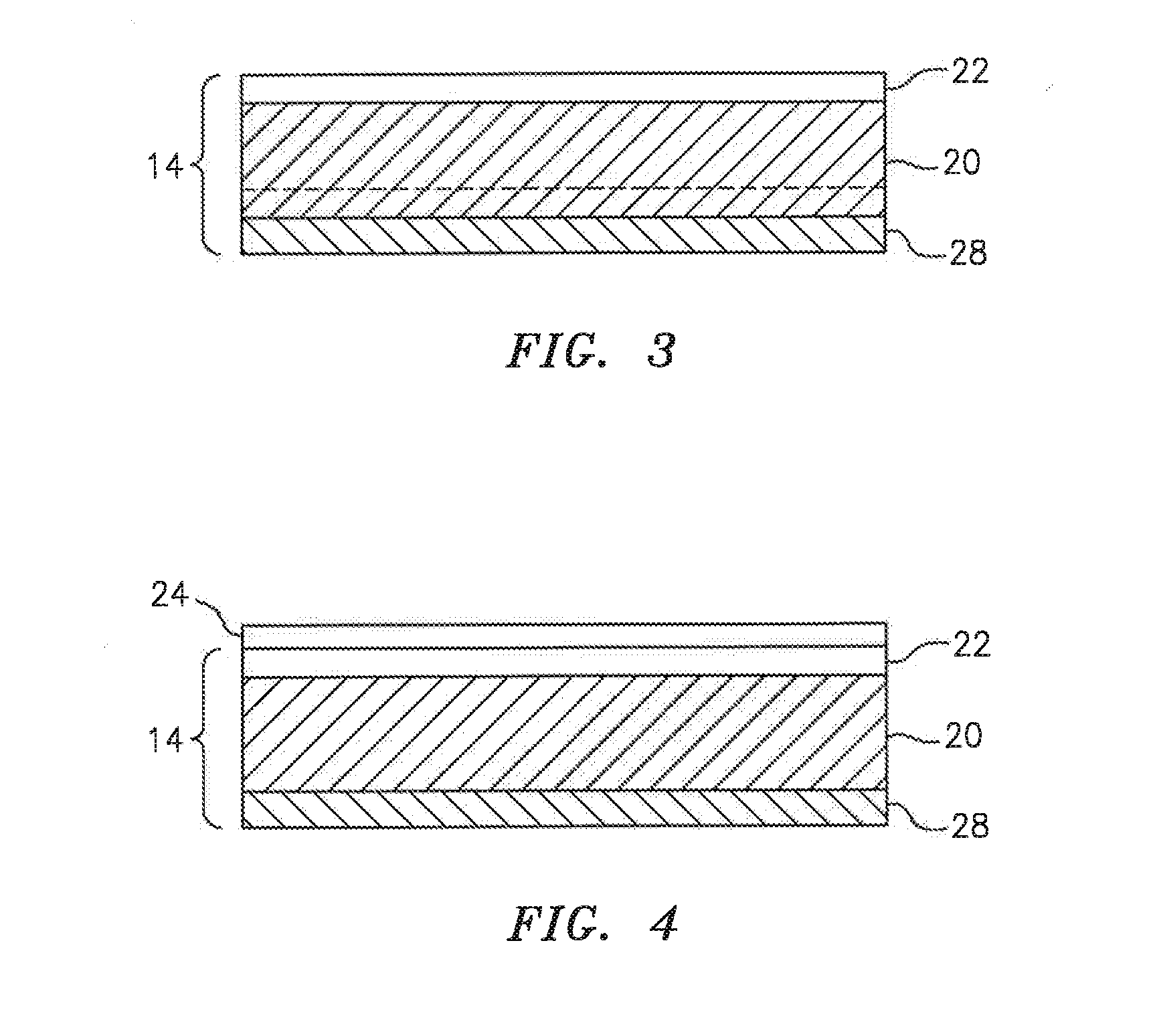
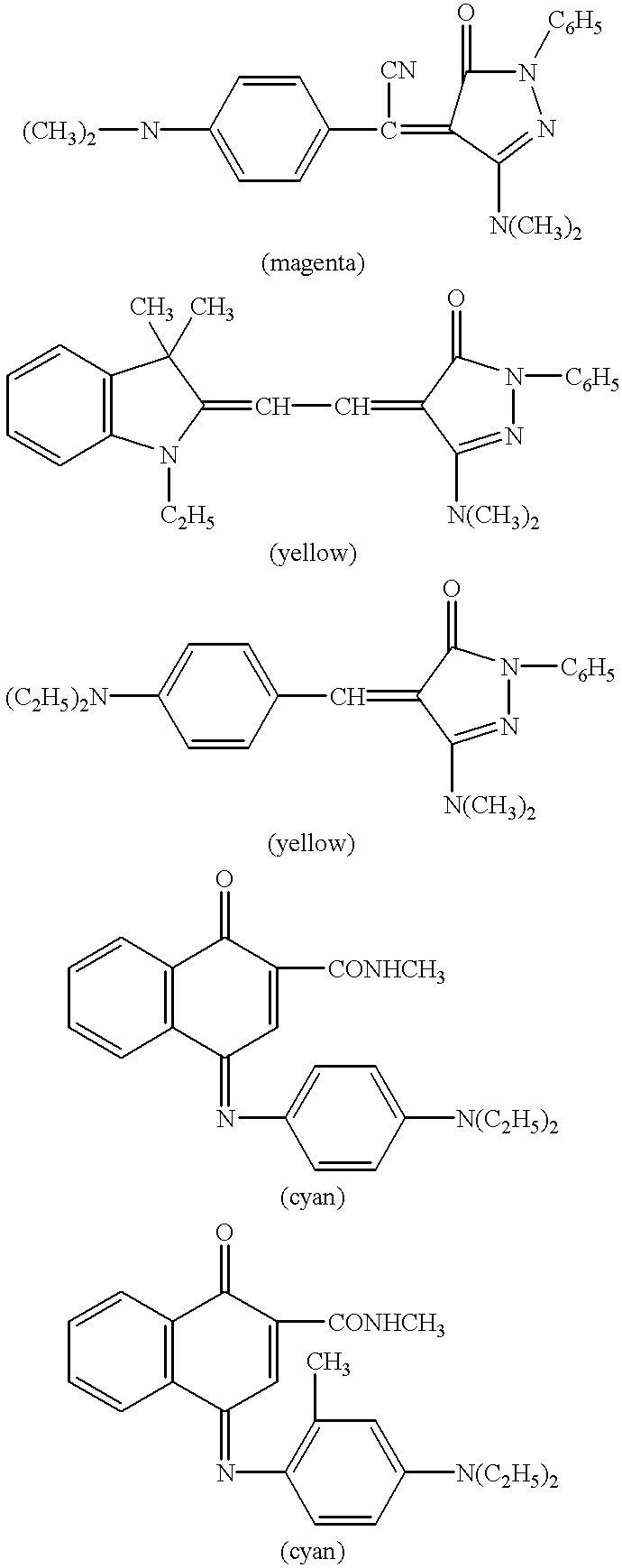
Ablatable elements for making flexographic printing plates
InactiveUS20080258344A1Reduce the environmentReduce health hazardsRadiation applicationsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymerLaser ablation
Flexographic printing plates and other relief images can be formed from a laser-ablatable element having a laser-ablatable layer that is at least 20 μm in thickness. The laser-ablatable layer includes a film-forming material that is a laser-laser-ablatable material or the film-forming material has dispersed therein a laser-ablatable material. The laser-ablatable material is a polymeric material that when heated to 300° C. at a rate of 10° C. / minute, loses at least 60% of its mass to form at least one predominant low molecular weight product. The element can be imaged by ablation at an energy of at least 1 J / cm2 to provide a relief image.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Excimer laser unit and relative control method for performing cornea ablation to reduce presbyopia
ActiveUS20060195074A1Mitigates presbyopiaLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsPhotoablationHyperopic astigmatism
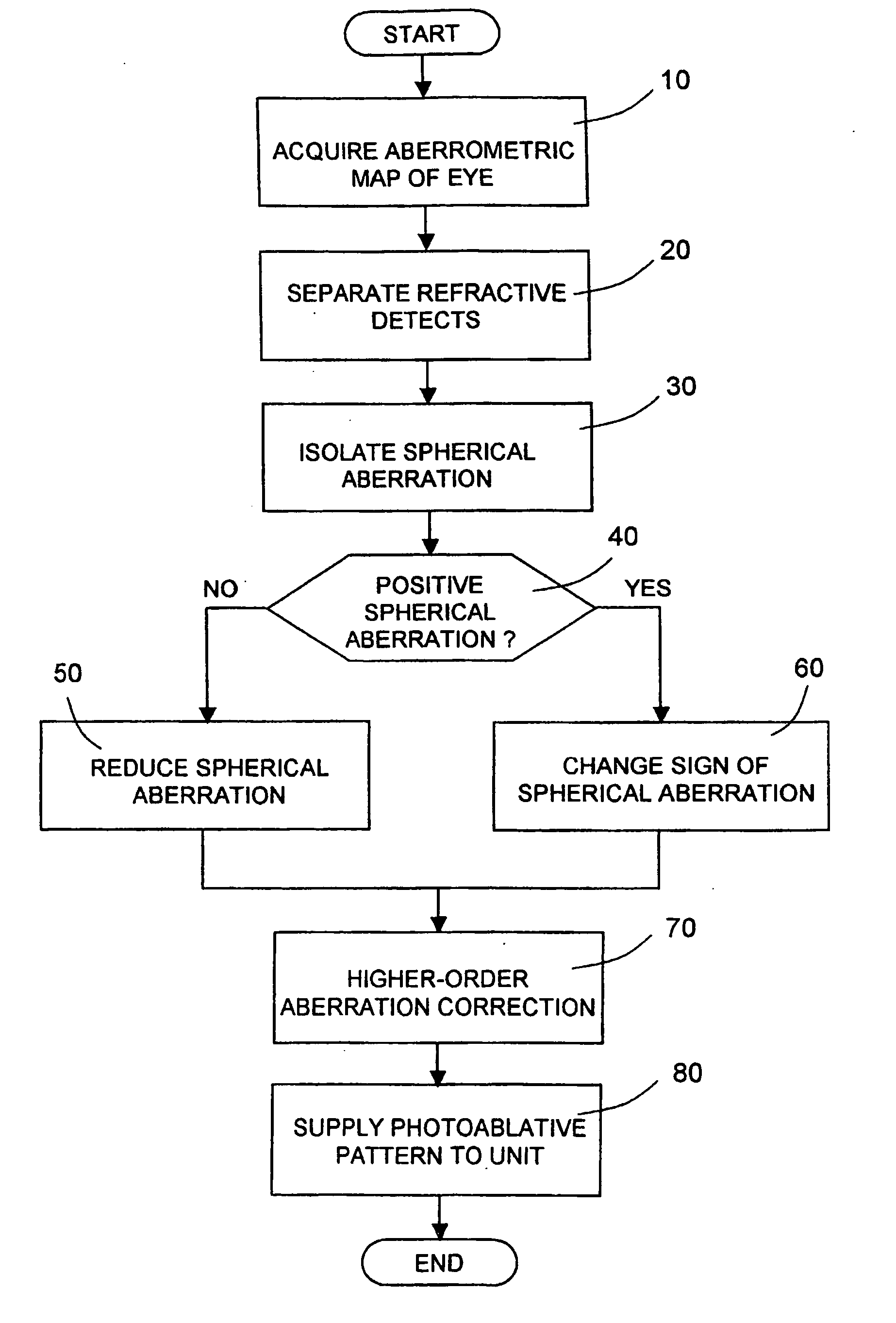
There are described an excimer laser unit and a method of controlling the unit to perform cornea ablation to reduce presbyopia, wherein the excimer laser unit is controlled to form on the cornea a photoablative pattern inducing a fourth-order ocular aberration, in particular a positive spherical aberration. More specifically, an aberrometric map of the eye is first acquired indicating the visual defects of the eye, which include second-order visual defects such as hypermetropia, astigmatism, and myopia, and higher-order visual defects such as spherical aberration; if the detected spherical aberration is negative, it is reduced by numerically increasing its absolute value to obtain an overcorrect photoablative inducing positive spherical aberration; conversely, if the detected spherical aberration is positive, its sign is changed and its absolute value increased numerically to obtain an overcorrect photoablative pattern inducing positive spherical aberration; and the photoablative pattern so generated is supplied to the excimer laser unit for implementation on the cornea.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
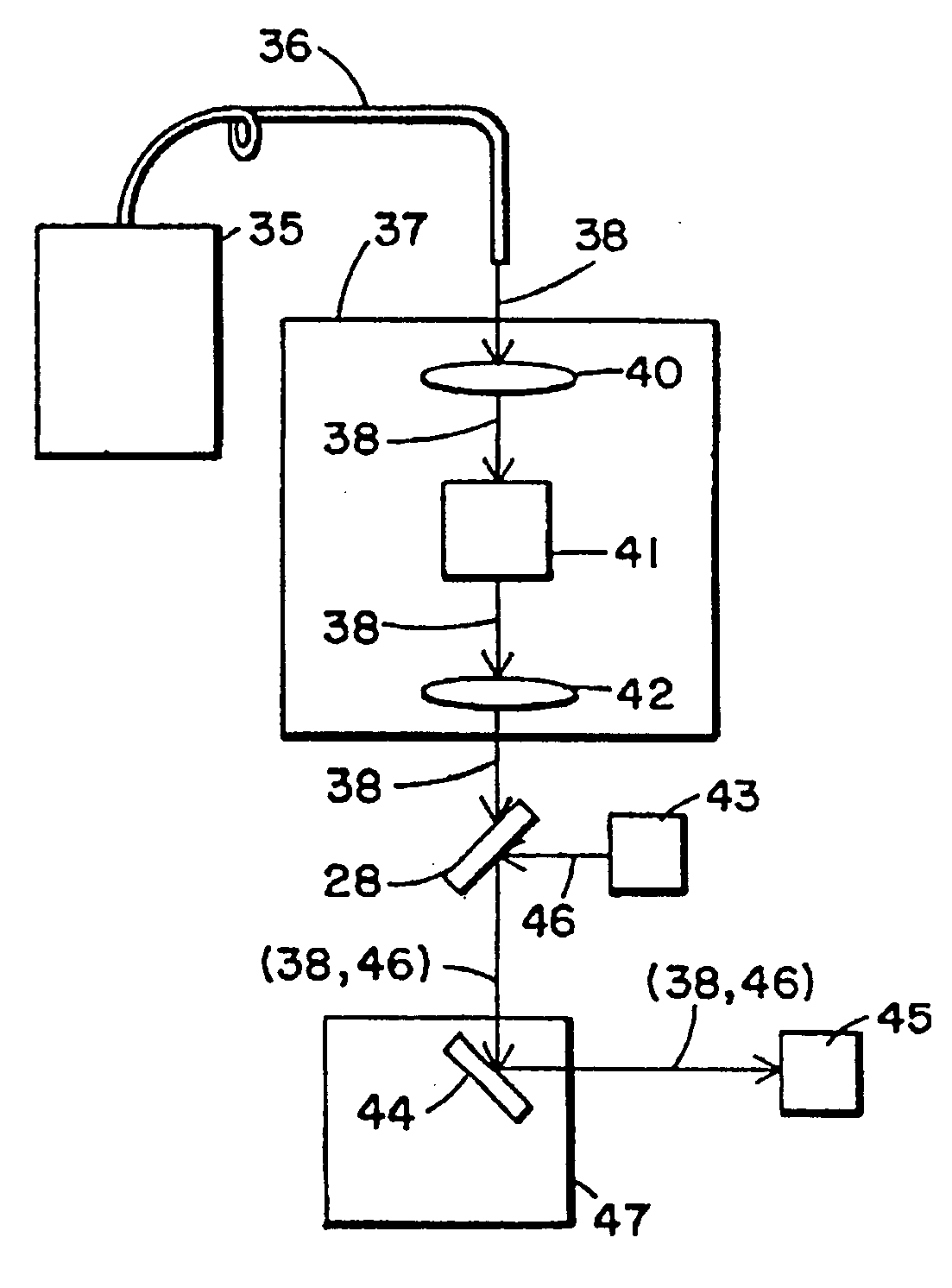
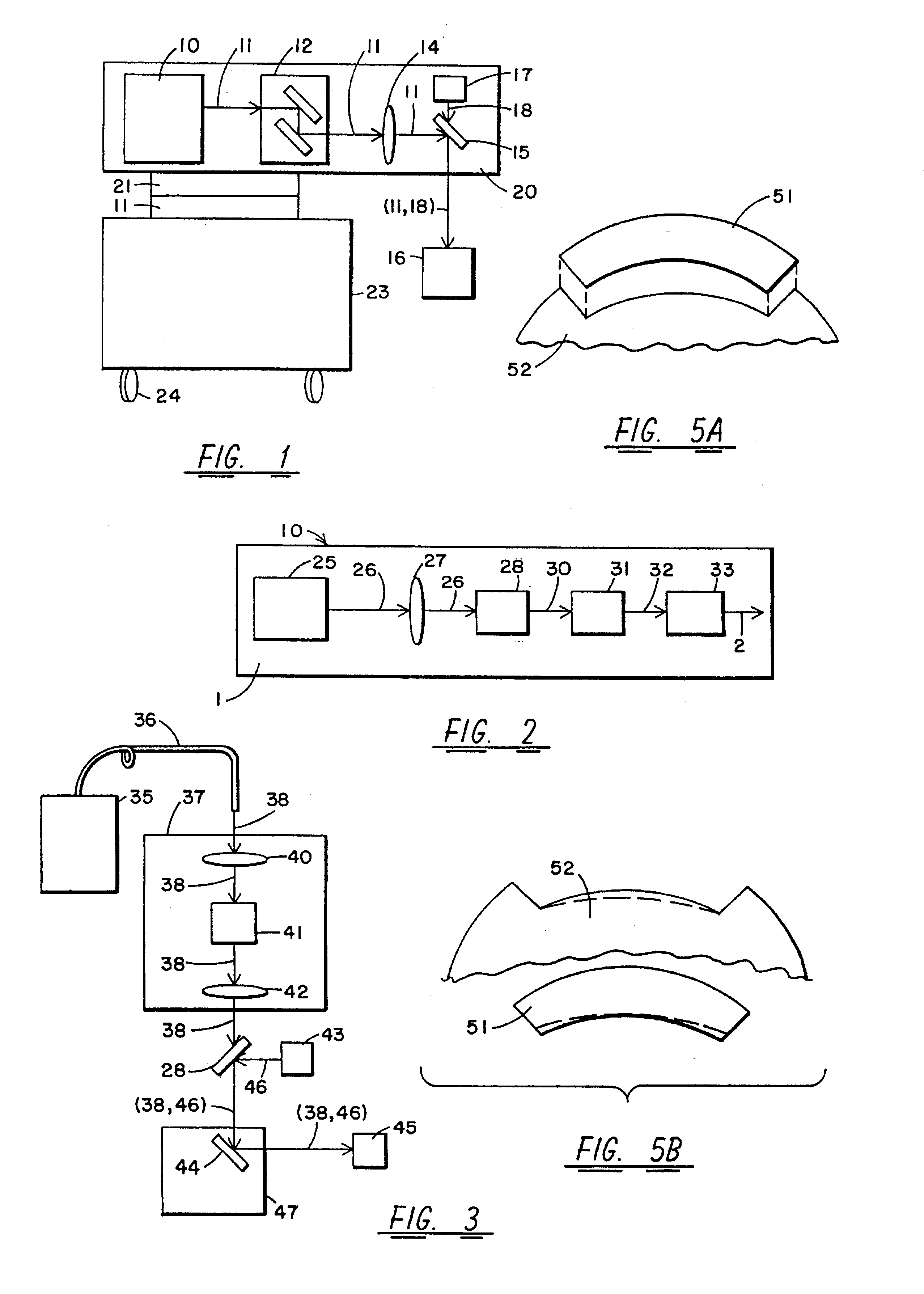
Method and Device for Cornea Reshaping by Intrastromal Tissue Removal
A method and device for flapless, intrastromal keratomileusis for the correction of myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism, i.e., for vision correction by corneal reshaping without creating a flap. Ultra-short laser pulses are used to create a temporary micro-channel extending to an end point located within the cornea. A second series of ultra-short laser pulses are then delivered to photo-ablate material in the vicinity of the micro-channel end-point. The photo-ablated material may exit through the micro-channel used to deliver the laser pulses, or via a separate micro-channel. With the micro-channel oriented substantially normal to the optical axis of the cornea, and by continuing to supply the ultra-short laser pulses in the appropriate number while moving the point of ablation along the micro-channel, the photo-ablation of the intrastromal tissue may continue in a controlled fashion and the cornea reshaped in a predetermined manner without creating a flap.
Owner:FEMTO VISION LTD
Artificial lens, in particular a contact or intraocular lens, for correcting presbyopia, possibly associated with other visual defects, and relative production method
InactiveUS20070279585A1High of long vision acuityDrawback can be obviatedSpectales/gogglesEye diagnosticsIntraocular lensVisual perception
An artificial lens (1) (contact lens or intraocular lens) for correcting presbyopia, possibly associated with other refractive defects, has at least one region (5) having a fourth-order spherical aberration in OSA notation greater than −1.5 μm and less than zero μm, and possibly associated with a basic vertex power for correcting refractive defects, and with higher-order aberrations for improving vision acuity. The lens is produced by ablating a surface of a base body of the lens by means of an appropriately controlled laser device, and according to a given photoablative pattern to induce the desired aberration.
Owner:STUDIO BOL DI GIUSEPPE BOLLINI +1
Method for manufacturing electrochromic devices
ActiveUS8168265B2Improve manufacturabilityLow costRadiation applicationsPretreated surfacesDevice materialPhysical chemistry
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
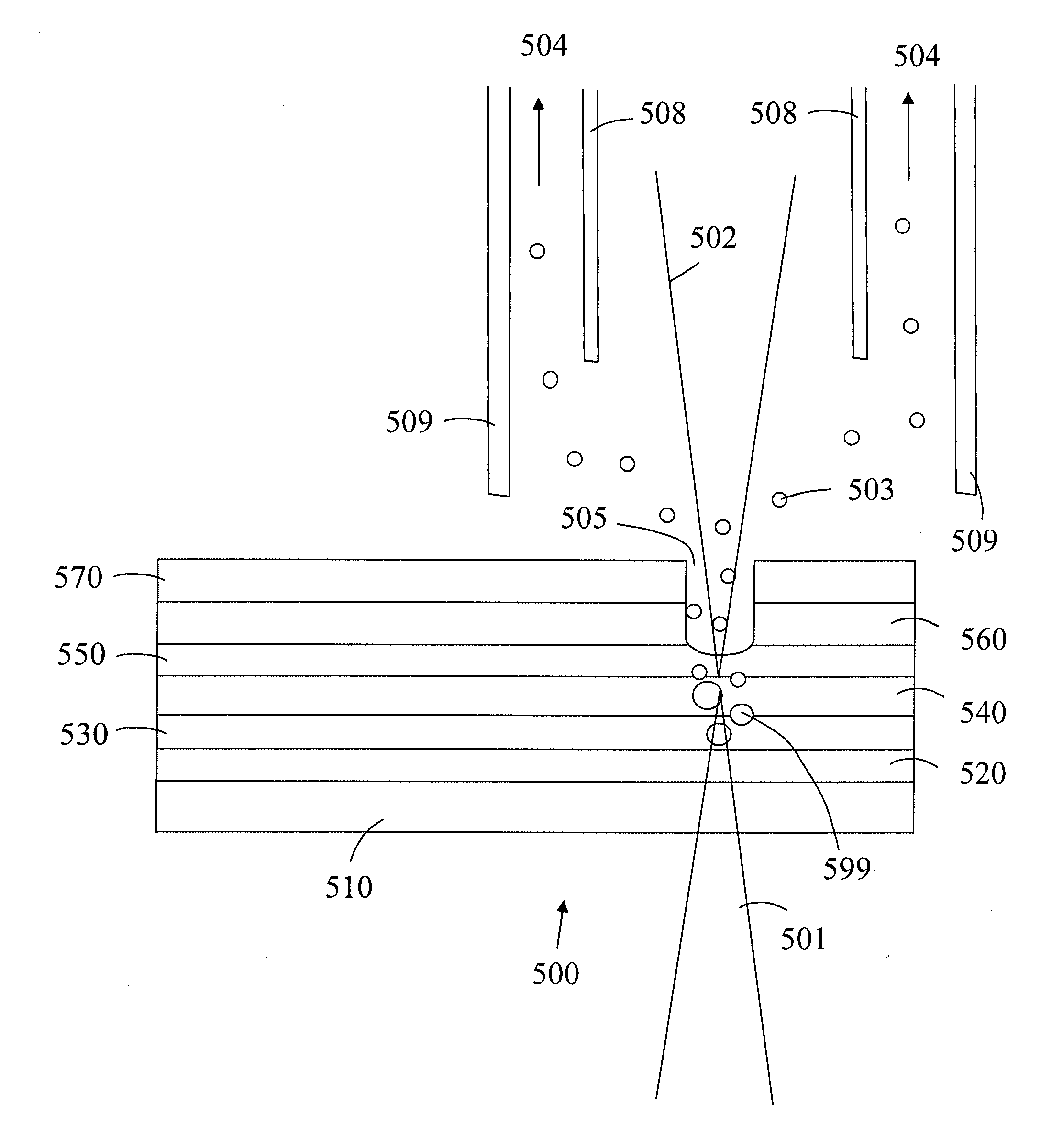
Integrated Membrane Lamination and UV Exposure System and Method of Using the Same
ActiveUS20130209939A1Reduce intensityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryPhoto ablation
A combined laminating and exposing apparatus for exposing a photosensitive printing blank to actinic radiation in a printing plate manufacturing system and a method of using the same are disclosed. The photosensitive printing blank comprises a backing layer, at least one photocurable layer disposed on the backing layer, and a laser ablatable mask layer disposed on the at least one photocurable layer, wherein the laser ablatable mask layer is laser ablated to create an in situ negative in the laser ablatable mask layer. The exposing apparatus comprises: (a) a laminating apparatus for laminating an oxygen barrier layer to a top of the laser ablated mask layer; (b) a conveyor; (c) a first exposing device for imagewise exposing the at least one photocurable layer to actinic radiation, and (d) a second exposing device for exposing the at least one photocurable layer to actinic radiation through the backing layer.
Owner:MACDERMID PRINTING SOLUTIONS
Laser thermal media with improved abrasion resistance
InactiveUS6259465B1Improved abrasionIncrease resistanceRecording apparatusAblative recordingNear infrared absorptionEngineering
A laser ablative recording element with a support having a certain Young's modulus and having thereon an image layer comprising an image dye or pigment dispersed in a polymeric binder, the image layer having a near infrared-absorbing material associated therewith to absorb at a given wavelength of the laser used to expose the element, the image dye or pigment absorbing in the region of from about 250 to about 700 nm, the element having a compliant layer between the support and the image layer, the compliant layer having a Young's modulus lower than that of the support, and the compliant layer having a thickness of between about 2 mum and about 200 mum.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method of direct Coulomb explosion in laser ablation of semiconductor structures
InactiveUS7759607B2Generate efficientlyReduce ablationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSemiconductor materialsMaterial removal
A new technique and Method of Direct Coulomb Explosion in Laser Ablation of Semiconductor Structures in semiconductor materials is disclosed. The Method of Direct Coulomb Explosion in Laser Ablation of Semiconductor Structures provides activation of the “Coulomb explosion” mechanism in a manner which does not invoke or require the conventional avalanche photoionization mechanism, but rather utilizes direct interband absorption to generate the Coulomb explosion threshold charge densities. This approach minimizes the laser intensity necessary for material removal and provides optimal machining quality. The technique generally comprises use of a femtosecond pulsed laser to rapidly evacuate electrons from a near surface region of a semiconductor or dielectric structure, and wherein the wavelength of the laser beam is chosen such that interband optical absorption dominates the carrier production throughout the laser pulse. The further application of a strong electric field to the semiconductor or dielectric structure provides enhancement of the absorption coefficient through a field induced redshift of the optical absorption. The use of this electric field controlled optical absorption is available in all semiconductor materials and allows precise control of the ablation rate. When used in conjunction with nanoscale semiconductor or dielectric structures, the application of a strong electric field provides for laser ablation on sub-micron lateral scales.
Owner:OPTICAL ANALYTICS
Method for Producing High-Quality Surfaces and a Product Having a High-Quality Surface
InactiveUS20090169871A1Fine and uniformSmall sizeElectric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringPhoto ablation
The invention relates to a laser ablation method for coating an object with one or more surfaces, so that the object to be coated, i.e. the substrate, is coated by ablating the target, so that the uniformity of the surface deposited on the object to be coated is ±100 nm. The surface of the coated object is advantageously free of micron size particles, and it is typically a nano technological surface where the size of separate particles is ±25 nm at most. The object also relates to products made by said method.
Owner:PICODEON OY
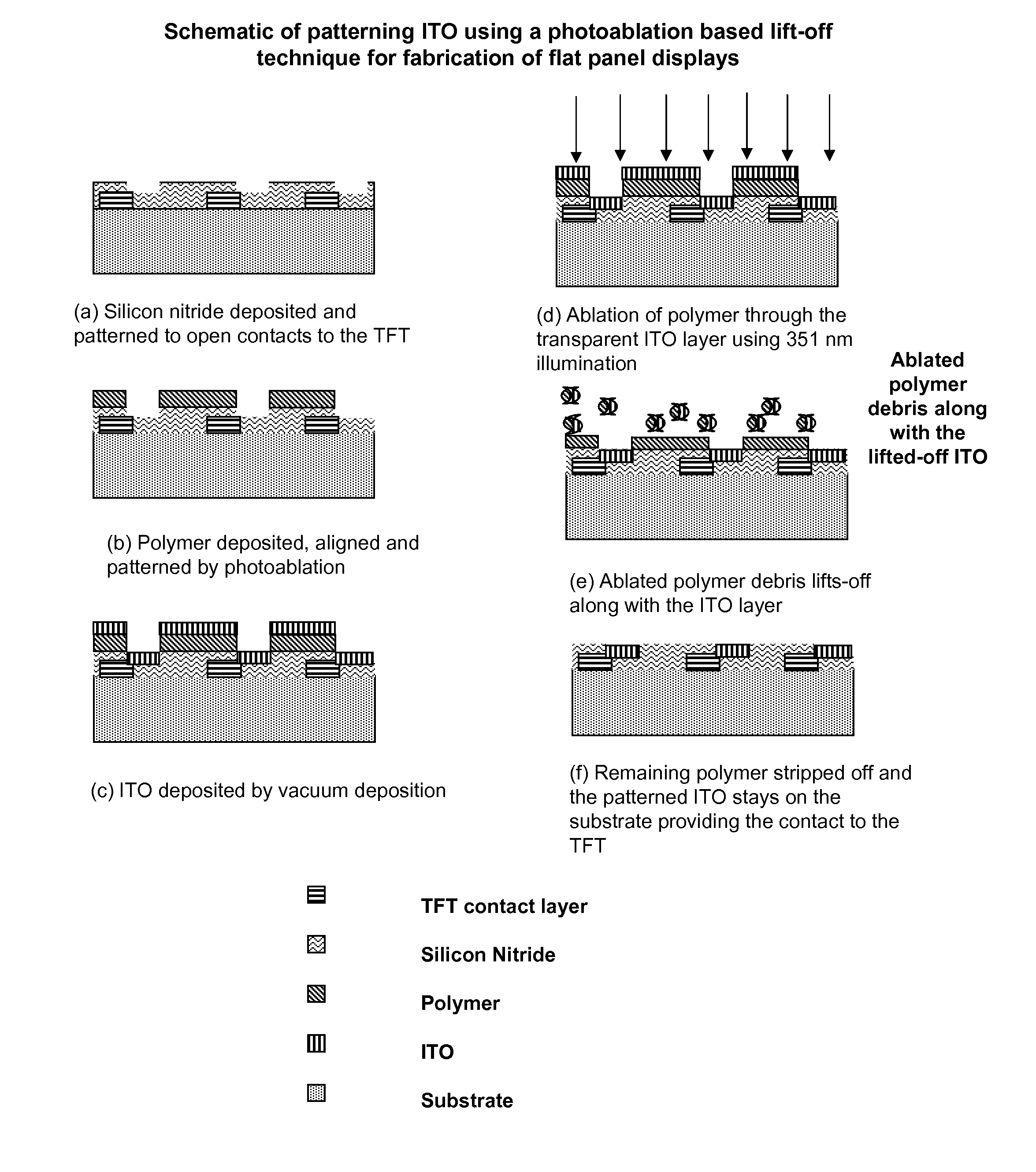
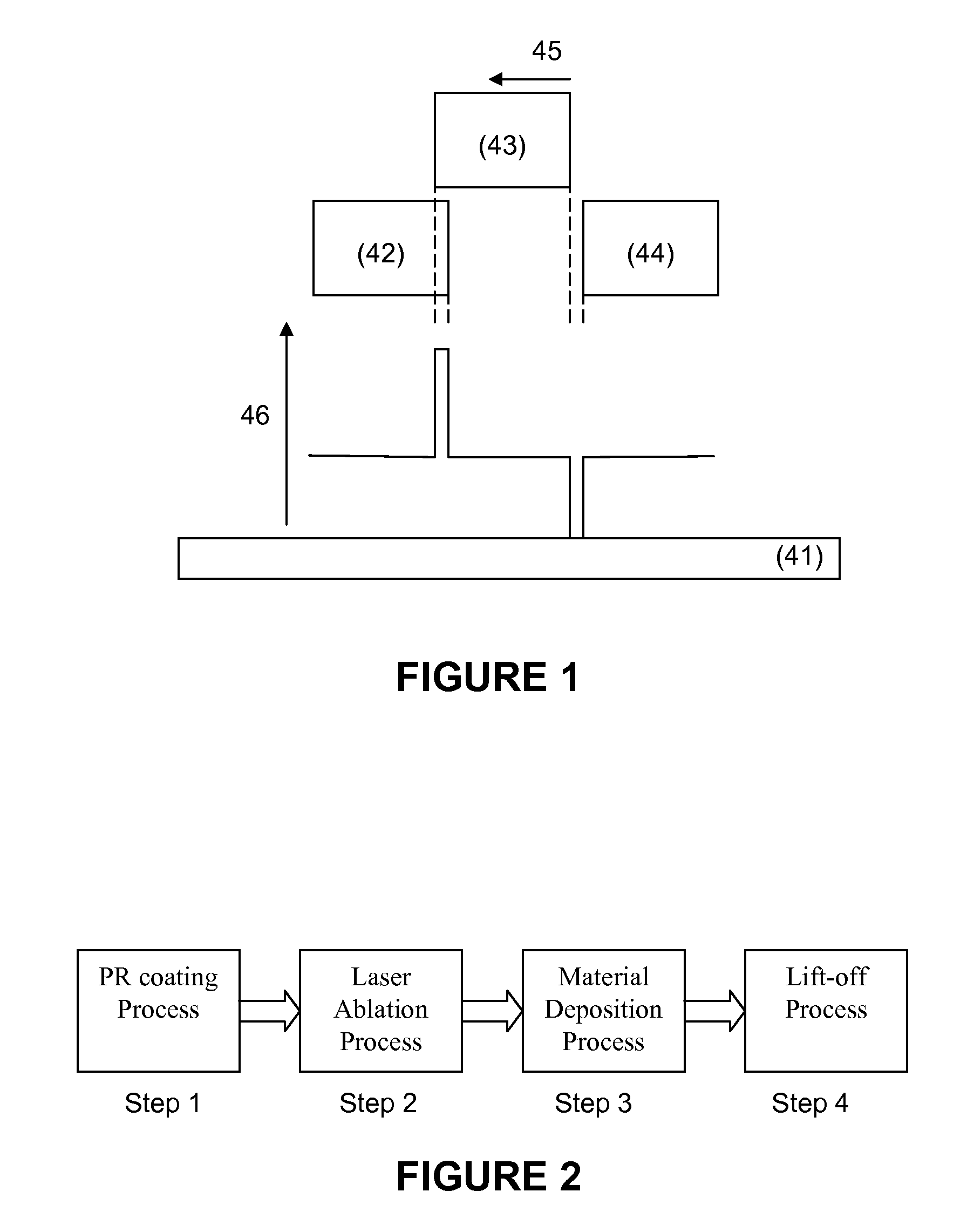
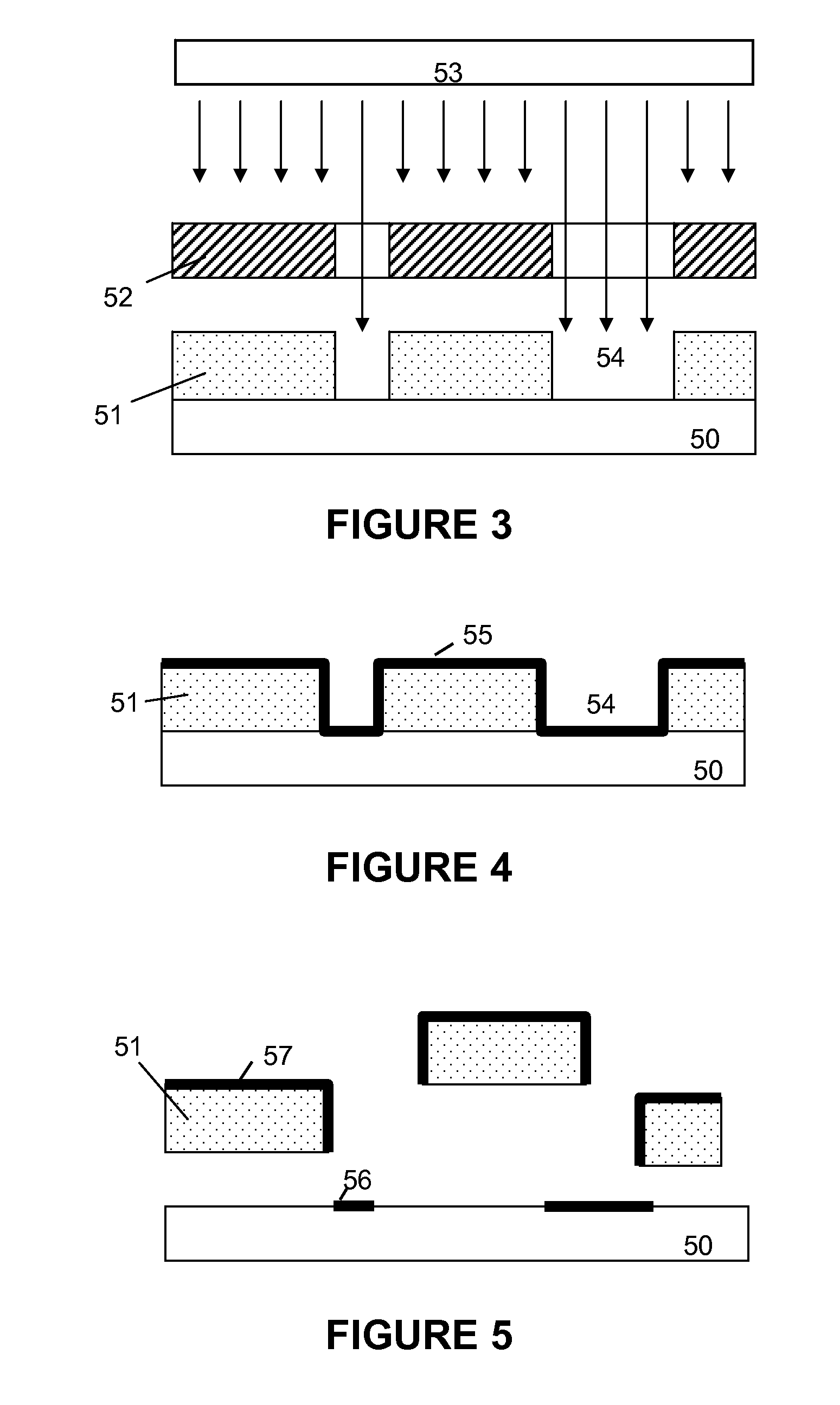
High throughput, low cost dual-mode patterning method for large area substrates
ActiveUS8420978B2Eliminate complex, costly and time consuming photolithographic patterningHigh resolutionRadiation applicationsSolid-state devicesSpatial OrientationsDual mode
A high-throughput, low cost, patterning platform is provided that is an alternative to conventional photolithography and direct laser ablation patterning techniques. The processing methods are useful for making patterns of microsized and / or nanosized structures having accurately selected physical dimensions and spatial orientation that comprise active and passive components of a range of microelectronic devices. Processing provided by the methods is compatible with large area substrates, such as device substrates for semiconductor integrated circuits, displays, and microelectronic device arrays and systems, and is useful for fabrication applications requiring patterning of layered materials, such as patterning thin film layers in thin film electronic devices.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
System and method for high precision isotope ratio destructive analysis
ActiveUS20110164248A1Precise proportionImprove spatial resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationRelative standard deviationSingle shot
A system and process are disclosed that provide high accuracy and high precision destructive analysis measurements for isotope ratio determination of relative isotope abundance distributions in liquids, solids, and particulate samples. The invention utilizes a collinear probe beam to interrogate a laser ablated plume. This invention provides enhanced single-shot detection sensitivity approaching the femtogram range, and isotope ratios that can be determined at approximately 1% or better precision and accuracy (relative standard deviation).
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Micropatterning of biological molecules using laser ablation
ActiveUS20090096133A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCombined usePhoto ablation
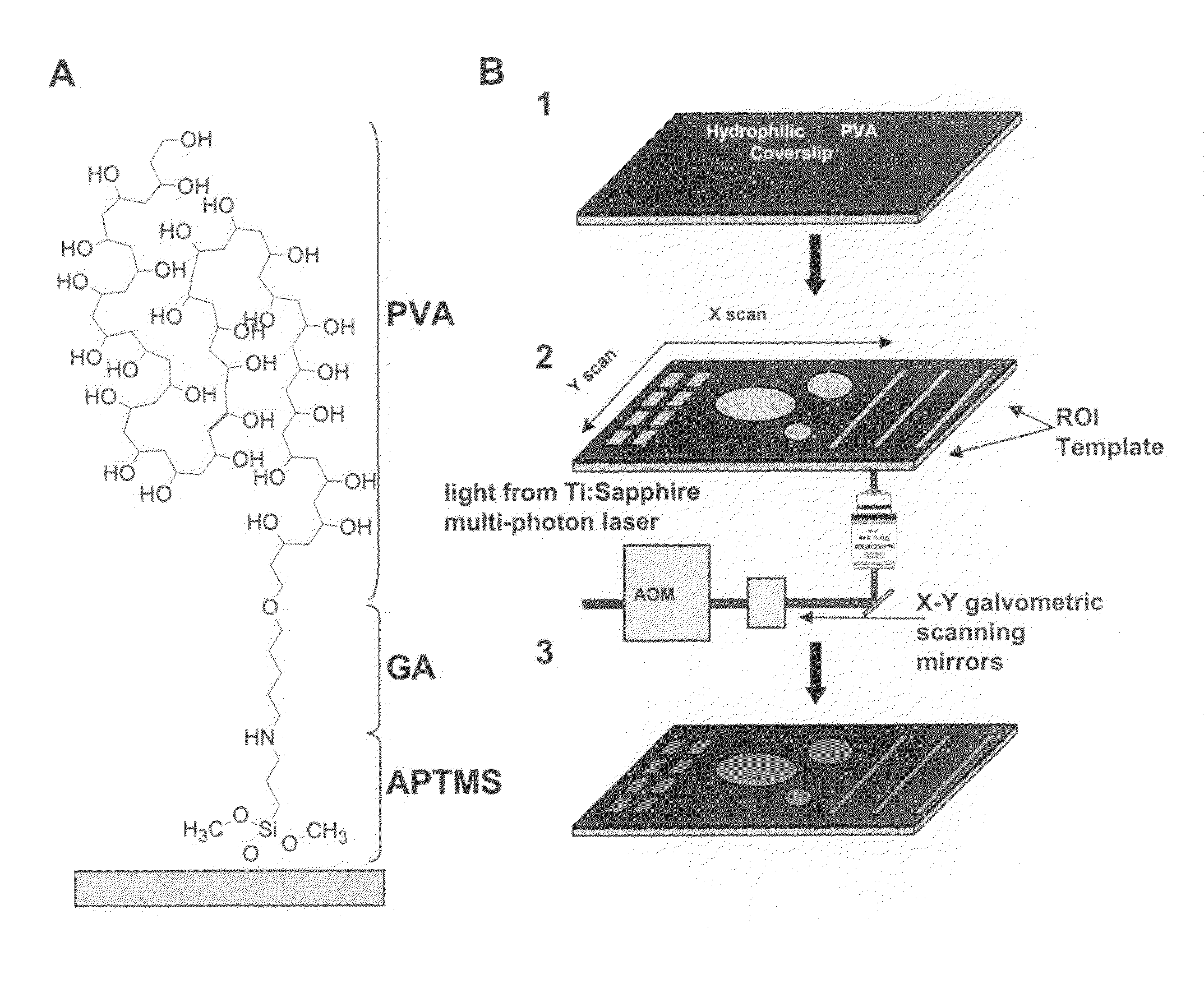
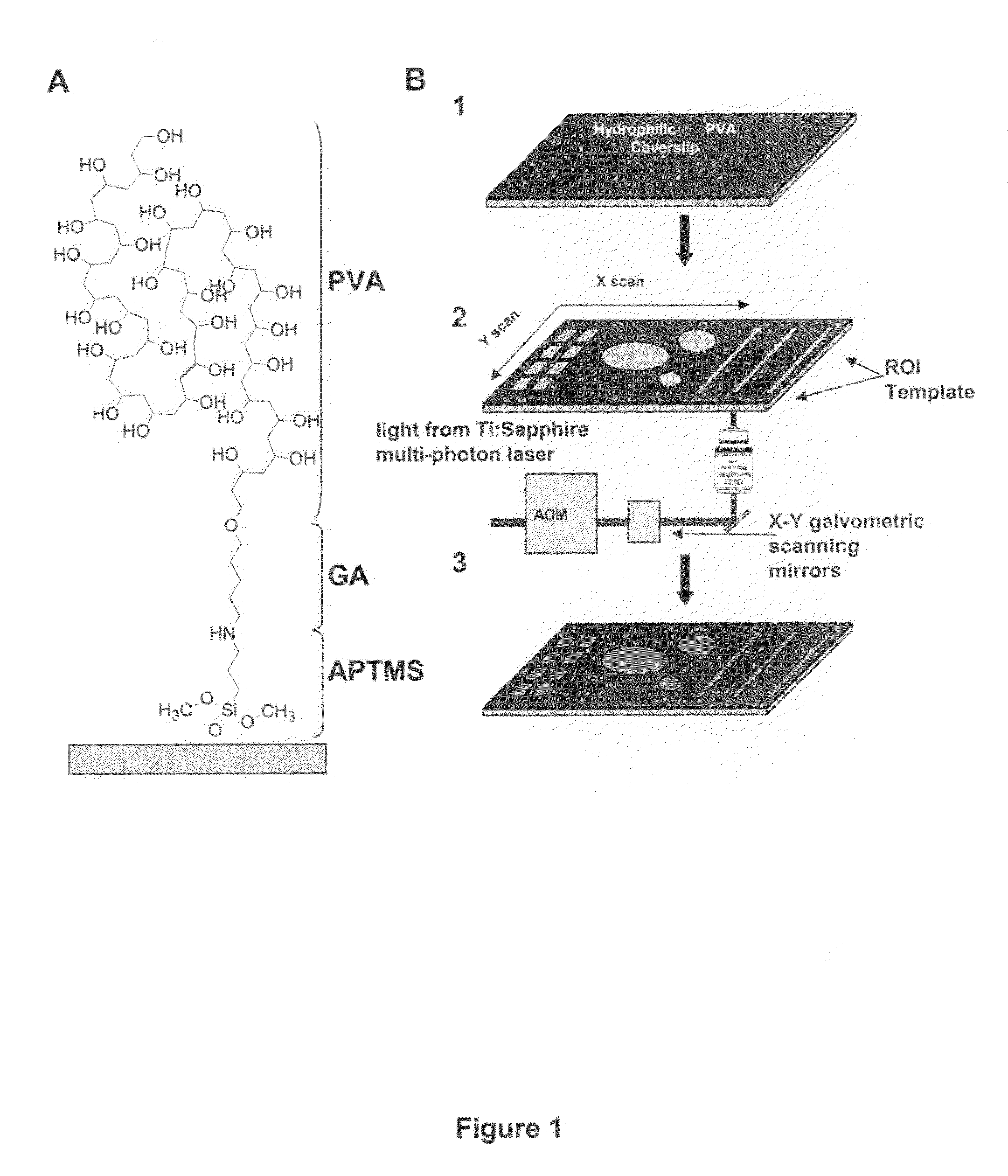
The present invention employs the natural hydrophilic properties of a macromolecular film such as a hydrogel and in combination with localized photo-ablation of monolayers created with the hydrogel using multi-photon laser excitation, provides a stampless, versatile method of micropattern fabrication.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF THE
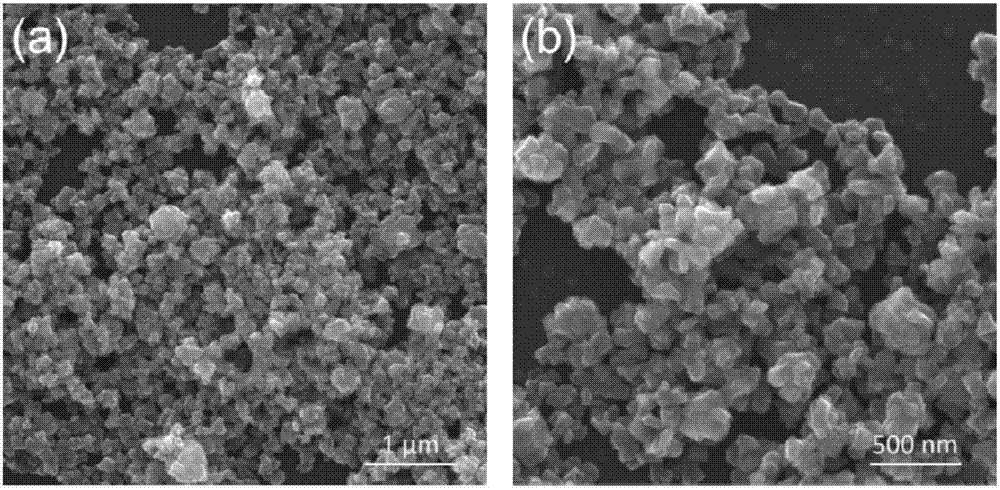
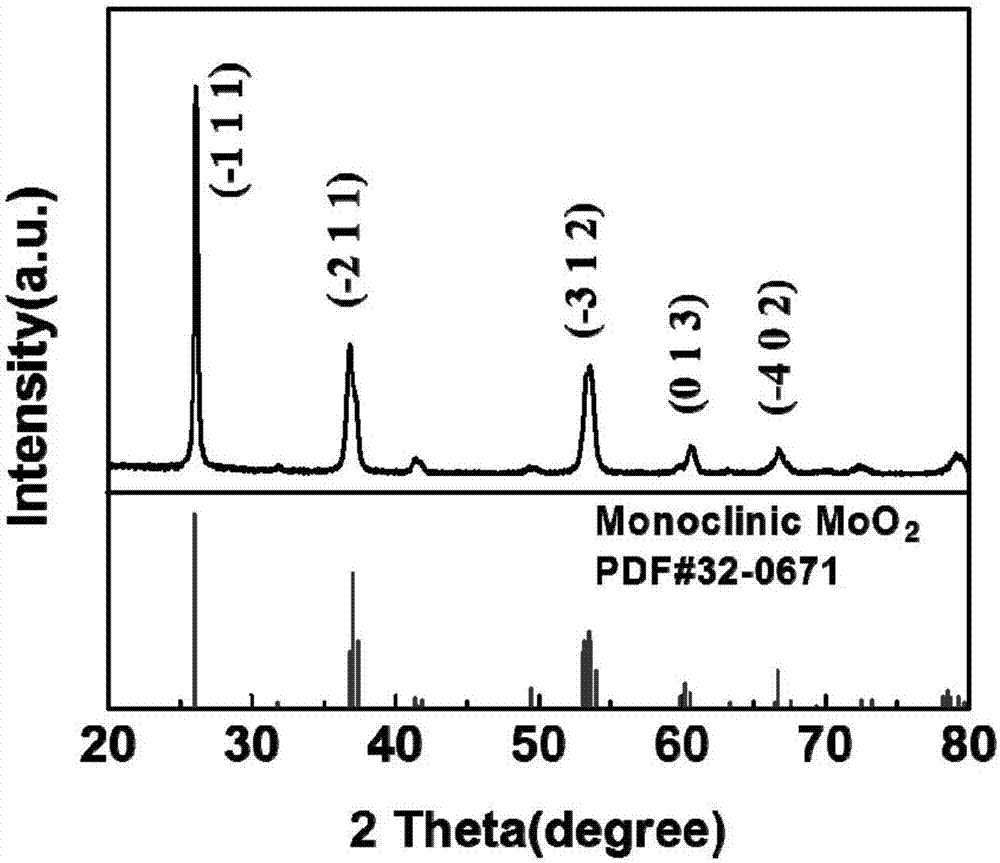
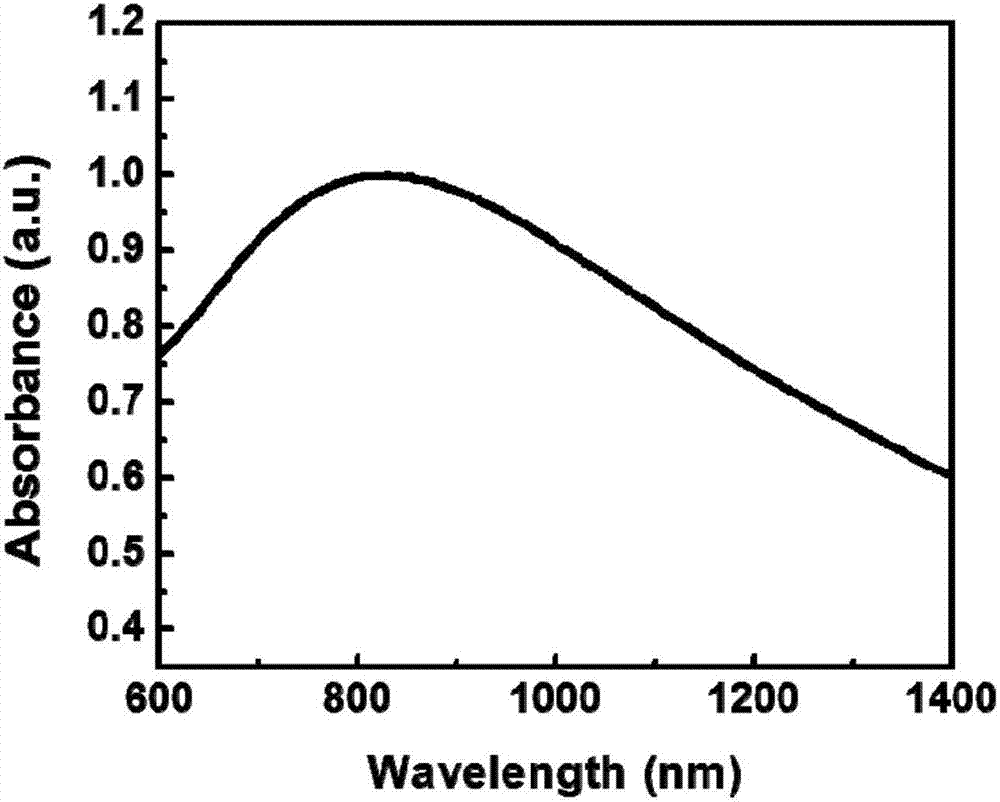
Molybdenum dioxide nano photothermal conversion material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106938857AHas surface plasmon resonance propertiesEfficient conversionMaterial nanotechnologyEnergy modified materialsThermal energyCancer cell
The invention discloses a molybdenum dioxide nano photothermal conversion material and a preparation method and application thereof. A high activity solvothermal precursor is obtained by laser ablation of high pure molybdenum in a mixed solution by combination of a liquid phase laser ablation technique and a solvothermal method; and molybdenum dioxide nano nanoparticles are synthesized by reaction under mild conditions by the solvothermal method. The prepared molybdenum dioxide nano nanoparticles have surface plasmon resonance properties, can produce strong light absorption in a near infrared band, can be used for effective conversion of absorbed light into heat so as to kill cancer cells under near infrared laser irradiation, have excellent photothermal stability and biological compatibility, and can be used for the preparation of a photothermal treatment reagent, the photothermal treatment reagent comprising the molybdenum dioxide nano photothermal conversion material is injected into a tumor site, tumor is irradiated by near infrared laser, the growth of the tumor can be effectively inhibited, and the molybdenum dioxide nano photothermal conversion material has wide application prospect in the field of tumor photothermal therapy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Capacitive touch panels
A novel method and apparatus for performing the method is disclosed the apparatus comprises a laser (17), at least one ink jet print head (14), means for holding a transparent substrate having a transparent conductive layer, means (22) for adjusting the relative positions of the laser and at least one ink jet print head to the transparent conducting layer (2) and a controller to control the laser and ink jet print head whereby in a first step to inkjet print one or more coarse metal borders (15) onto the deposited TCM layer and in a second step by means of a single laser ablation process, ablating tracks in both the metal border and underlying TCM layer to form a plurality of discrete electrical busbars (12) and optionally also to form electrodes in the remainder of the TCM layer.
Owner:盈天实业(深圳)有限公司
Laser ablation resistant copper foil
InactiveUS20050118448A1Flat surfaceInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementChromatisationEpoxyDielectric substrate
A copper foil for lamination to a dielectric substrate iscoated with a laser ablation inhibiting layer having an average surface roughness of less than 0.7 micron and an average nodule height of less than 0.75 micron that is effective to provide a lamination peel strength to FR-4 of at least 4.5 pounds per inch. The foil is typically laminated to a dielectric substrate, such as glass reinforced epoxy or polyimide and imaged into a plurality of circuit traces. Blind vias may be drilled through the dielectric terminating at an interface between the foil and the dielectric. The coated foil of the invention resists laser ablation, thereby resisting piercing of the foil by the laser during drilling.
Owner:OLIN CORP
Solid sample direct introduction device of microwave plasma torch spectrometer
ActiveCN104792768ARich varietyRapidly melts and evaporatesAnalysis by thermal excitationMetallic materialsElemental analysis
The invention provides a solid sample direct introduction device of a microwave plasma torch spectrometer. The solid sample direct introduction device mainly includes pulsed laser system, an imaging positioning system, a sample processing system, a position regulating system and an air path switching system. Through the adoption of the solid sample direct introduction device disclosed by the invention, the direct sampling analysis of solid samples comprising biological samples, metallic materials and the like can be realized, besides, the device is suitable for sampling regular sample surfaces and irregular sample surfaces, direct laser ablation sampling can atomize all the elements, and the device can be used for full elementary analysis of the microwave plasma torch spectrometer. The device can be applied to many existing fields of metallurgy, medical inspection, life science, agriculture, food safety detection, forestry, environmental monitoring, biological identification, medicolegal expertise and the like. The device disclosed by the invention is reasonable in design, and can be used for direct sample introduction for the solid samples, the pretreatment steps of the samples are decreased, requirements for the material state of the samples are lower, and the device satisfies user demands.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation method for nano-tungsten oxide electrochromic thin film
The present invention discloses a preparation method for a nano-tungsten oxide electrochromic thin film. The preparation method combines a liquid phase laser ablation method with an electrophoretic deposition method, and the preparation method comprises: firstly laser-ablating a tungsten source target material in a liquid phase environment by using a liquid phase laser ablation technique so as to obtain a colloid of highly active tungsten oxide nanoparticles; and then in the obtained colloid solution, preparing a nano tungsten oxide thin film on a transparent conductive glass substrate by virtue of electrophoretic deposition. The preparation method disclosed by the present invention is easy and convenient in operation, fast in manufacture process, mild in reaction conditions and easy to control, and the prepared nano WO3 electrochromic thin film responds quickly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of direct coulomb explosion in laser ablation of semiconductor structures
InactiveUS20070293057A1Generate efficientlyReduce ablationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSemiconductor materialsMaterial removal
A new technique and Method of Direct Coulomb Explosion in Laser Ablation of Semiconductor Structures in semiconductor materials is disclosed. The Method of Direct Coulomb Explosion in Laser Ablation of Semiconductor Structures provides activation of the “Coulomb explosion” mechanism in a manner which does not invoke or require the conventional avalanche photoionization mechanism, but rather utilizes direct interband absorption to generate the Coulomb explosion threshold charge densities. This approach minimizes the laser intensity necessary for material removal and provides optimal machining quality. The technique generally comprises use of a femtosecond pulsed laser to rapidly evacuate electrons from a near surface region of a semiconductor or dielectric structure, and wherein the wavelength of the laser beam is chosen such that interband optical absorption dominates the carrier production throughout the laser pulse. The further application of a strong electric field to the semiconductor or dielectric structure provides enhancement of the absorption coefficient through a field induced redshift of the optical absorption. The use of this electric field controlled optical absorption is available in all semiconductor materials and allows precise control of the ablation rate. When used in conjunction with nanoscale semiconductor or dielectric structures, the application of a strong electric field provides for laser ablation on sub-micron lateral scales.
Owner:OPTICAL ANALYTICS
Method for preparing multi-scale nano-composite structure through laser cleaning assisted laser ablation
ActiveCN111229719APrevent oxidationImprove absorbing performanceCleaning using liquidsLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoLight spot
The invention provides a method for preparing a multi-scale nano-composite structure through laser cleaning assisted laser ablation. The method comprises the steps of establishing a light path, wherein a femtosecond laser outputs light, the light passes through reflecting mirrors to go into a scanning galvanometer, is focused through a circular lens of the scanning galvanometer and then is irradiated on an objective stage, and the femtosecond laser and the scanning galvanometer are connected with a computer; setting laser ablation parameters of a silicon material and fixing a monocrystalline silicon wafer sample to the mobile objective stage; controlling the scanning galvanometer through the computer to move a laser spot crossed grid, and carrying out laser ablation on the surface of the monocrystalline silicon wafer sample to obtain the surface covered with a layer of flocculent oxide deposited grid nanostructure; replacing the circular lens of the scanning galvanometer with a cylindrical lens to obtain an elliptical light spot; and setting laser cleaning parameters of silicon oxide deposition, controlling the scanning galvanometer to move the laser spot grid, and carrying out laser cleaning on the surface of the latticed nanostructure to obtain the multi-scale nano-composite structure. The method provided by the invention is simple in operation, environment-friendly, economical and efficient.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
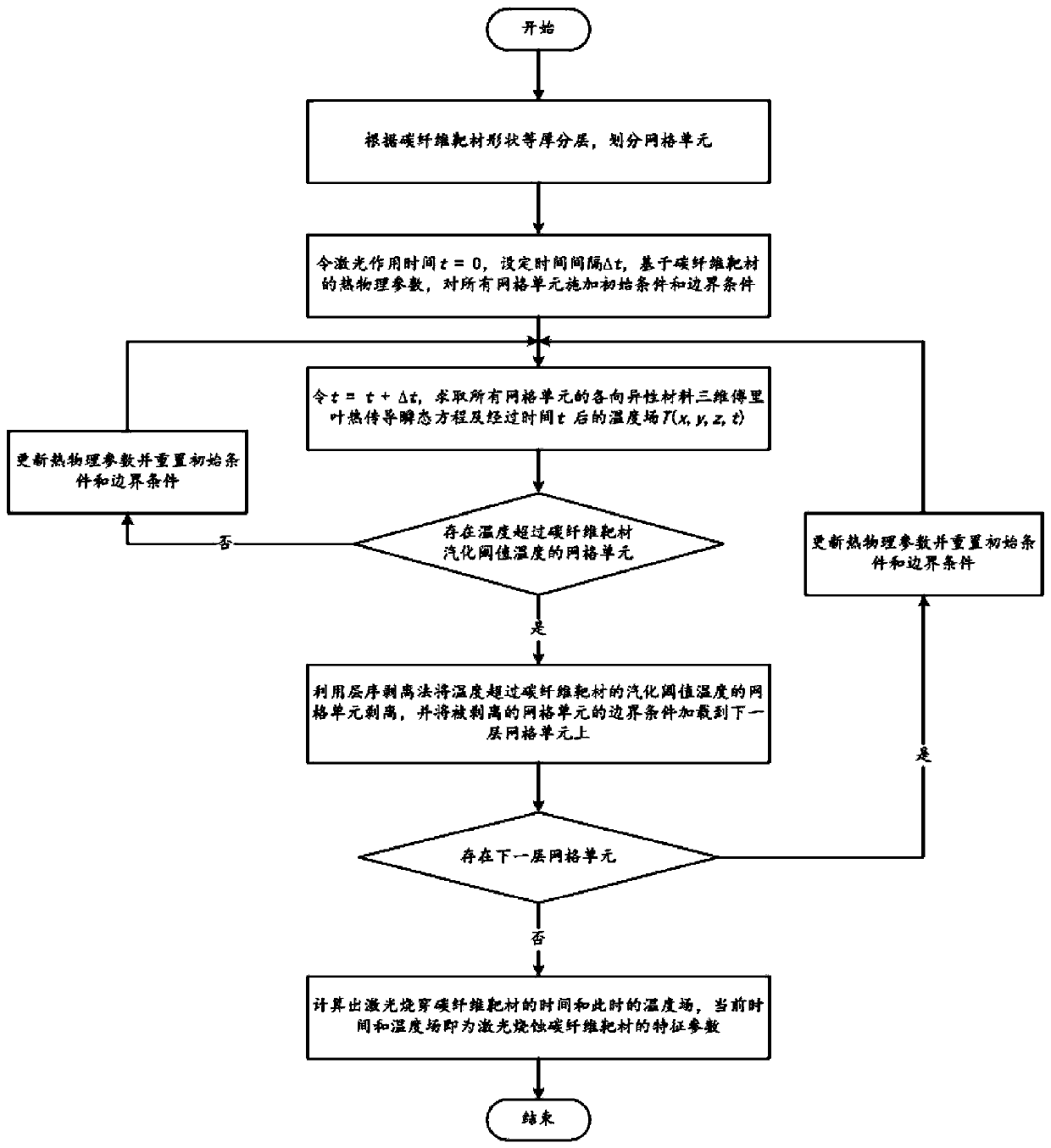
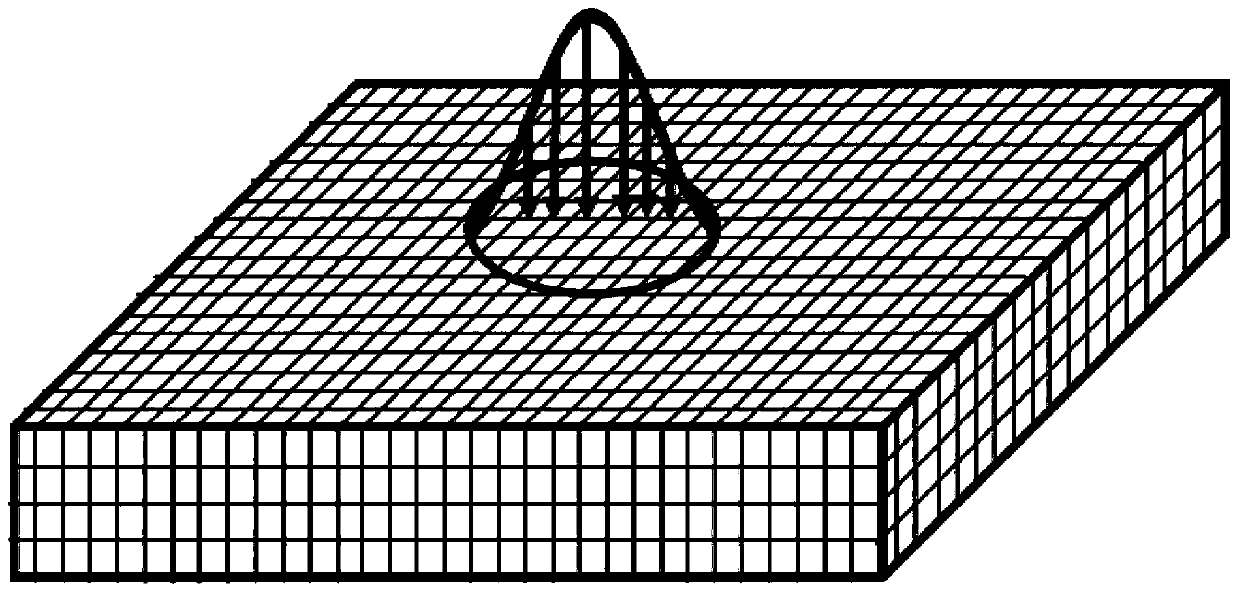
Method for calculating temperature field of laser ablation carbon fiber target material
The invention discloses a method for calculating a temperature field of a laser ablation carbon fiber target material, and relates to the field of laser damage effect research, and the method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out the equal-thickness layering according to the shape of the carbon fiber target material, and dividing grid units; 2, setting the laser action time t to be equalto 0, setting a time interval delta t, and applying an initial condition and a boundary condition to the unit according to the thermophysical parameters of the carbon fiber target material; 3, settingt= t + delta t, solving three-dimensional heat conduction transient equations of anisotropic materials of all units, and calculating a target material temperature field after time t; 4, if a grid unit with the temperature exceeding the vaporization threshold temperature of the carbon fiber target exists, vaporizing the unit according to a meta-order stripping method, loading the corresponding boundary condition to the next layer of unit, and then executing the step 5; 5, traversing the grid units: judging whether a next layer of unit exists, if yes, adjusting the thermophysical parameters ofthe target material, updating the boundary condition and the initial condition, and then executing the step 3; otherwise, determining a fact that the time and the temperature field are the characteristic parameters of the laser damaged carbon fiber target material.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for eliminating the structure and edge roughness produced during laser ablation of a material
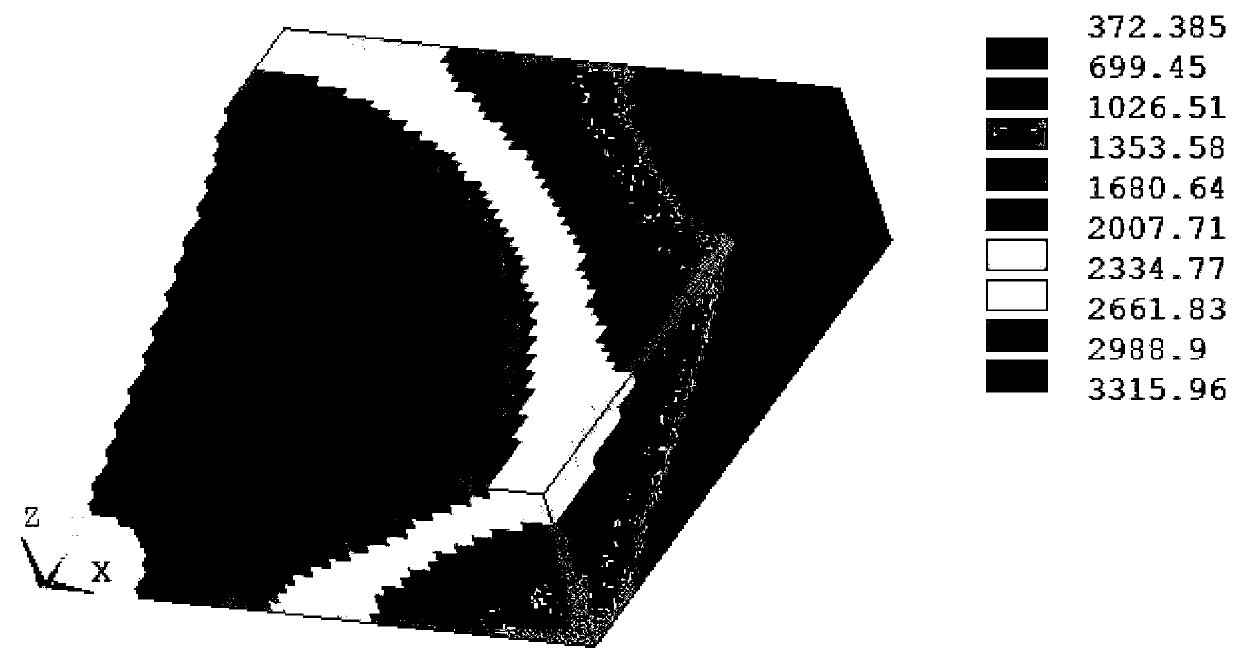
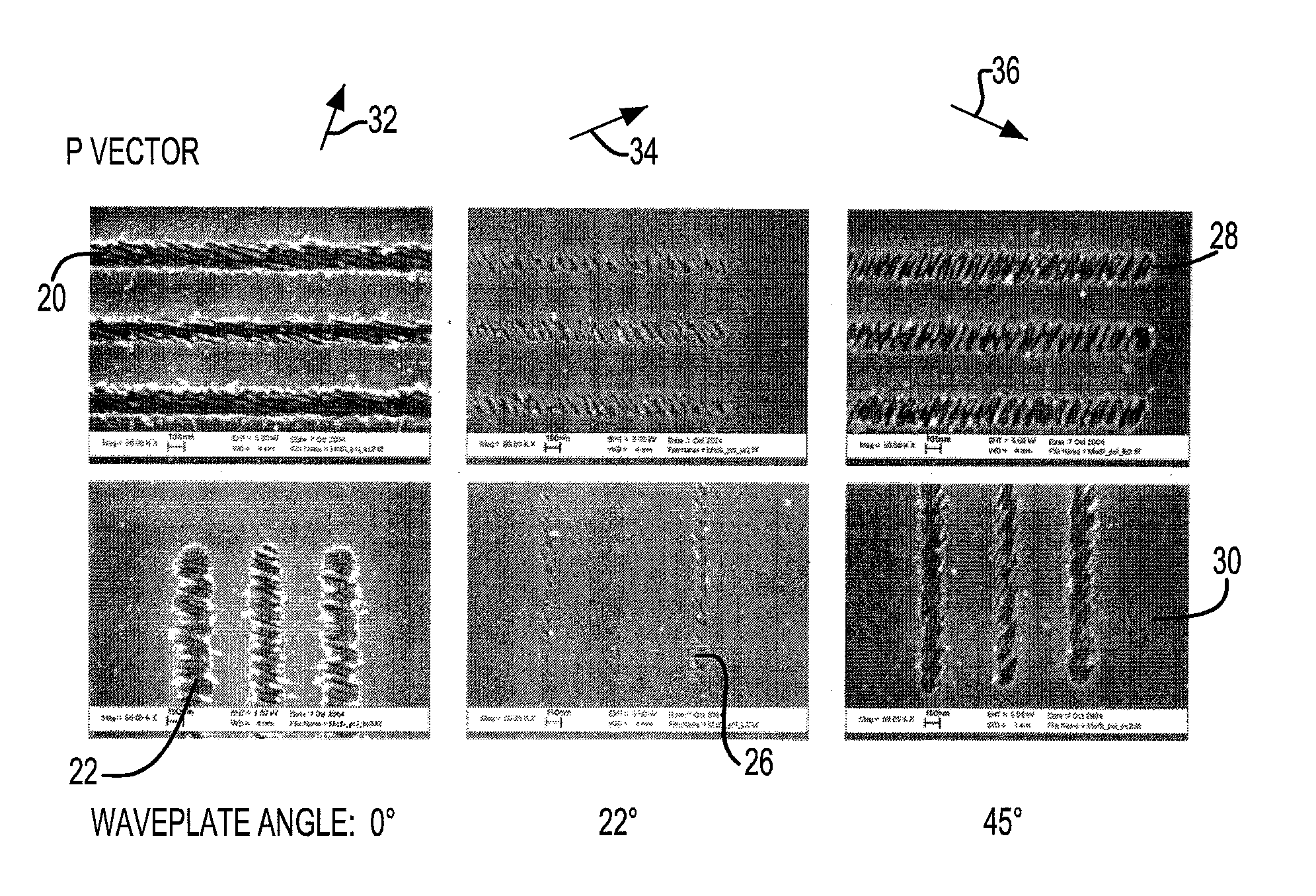
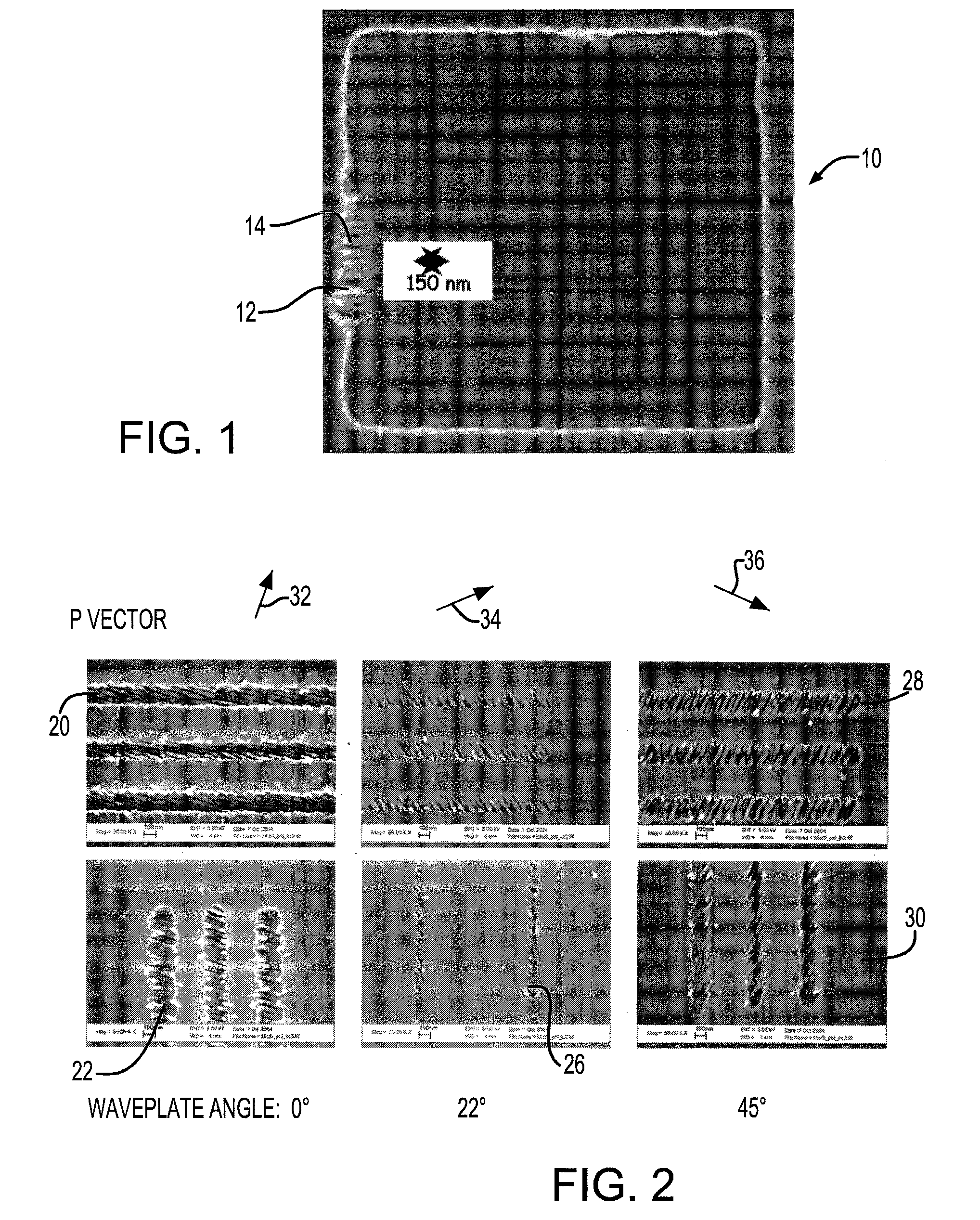
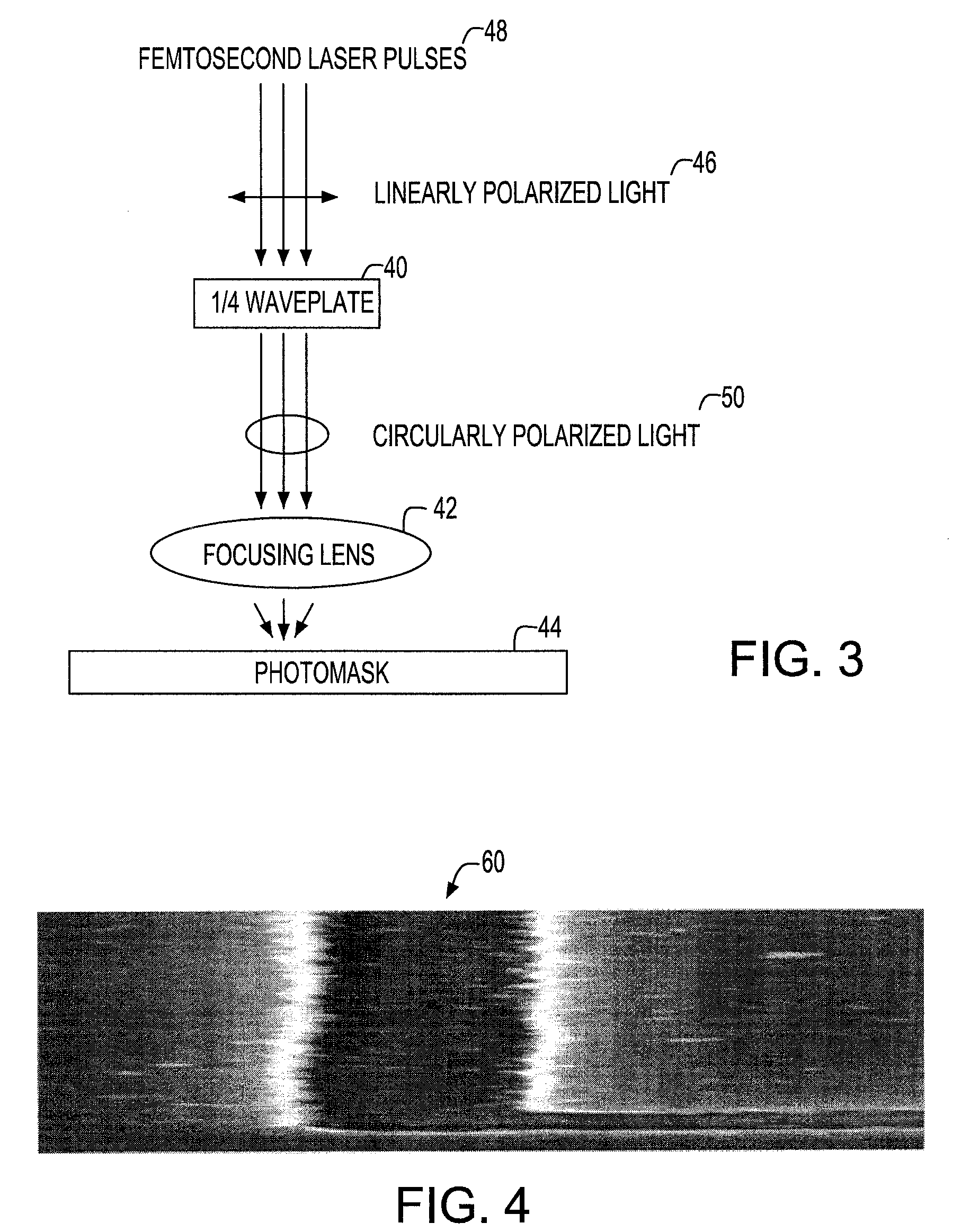
InactiveUS20080176147A1Remove roughnessEliminate structurePolarising elementsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentPhotomaskLaser beams
The present technology relates generally to laser ablation, and more particularly pertains to a system and method for eliminating structure and edge roughness, which is produced during the laser ablation of a material. Ablation of materials using a femtosecond laser beam produces a fine scale periodic structure in the ablated region. The structure consists of residual (i.e. unablated material) and is always perpendicular to the polarization direction of the laser beam. By changing the polarization direction during the ablation process, the structure is averaged over many directions and thus eliminated. This eliminates structure and edge roughness in a material caused by the laser ablation of the material. The method is employed to the repairing of photomasks so as to cause the optical quality thereof to be improved.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Preparation method of high-purity nano-structure ZnGa2O4 for deep ultraviolet extremely week light detection
ActiveCN107758726ANon-equilibriumHigh-purity nanostructureGallium/indium/thallium compoundsNanotechnologyLiquid mediumLow voltage
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-purity nano-structure ZnGa2O4 for deep ultraviolet extremely week light detection. The ZnGa2O4 has the band-gap width of 4.4 to 4.7 eV, has excellent thermal and chemical stability and high electronic migration rate, can bear high-current impact and can be applied to a deep ultraviolet photoelectric detector, a light-emitting diode and low-voltage light emission. A high-activity solvent hot precursor is obtained by a liquid phase laser ablation and solvent thermal method combined mode and by performing laser ablation on high-purity zinc target and gallium oxide target in a liquid medium, and the high-purity nano-structure ZnGa2O4 is synthesized by a solvothermal method. compared with the existing preparation method of the ZnGa2O4 nanometer material, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of high-purity product, single-phase structure, high crystallinity, uniform size, controllable shape, simplicity in preparation, mild experimental environment, short reaction time and the like; the prepared ZnGa2O4 nanometer material can be used for being assembled into the deep ultraviolet photoelectric detector and can realizehigh-sensitivity, quick-response and high-pressure-resistant detection on extremely weak light.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
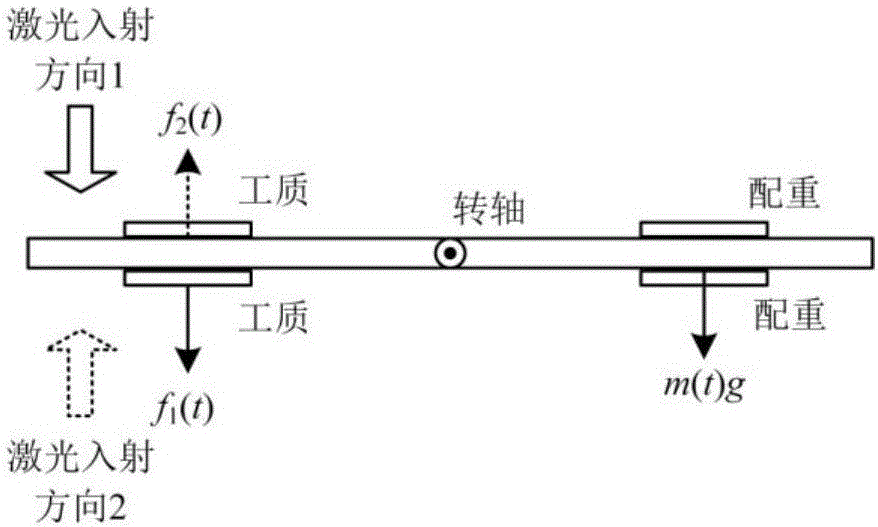
Method for directly measuring specific impulse of laser ablation micro-propulsion
ActiveCN106644395AImprove versatilityAvoid frequent disassemblyOptical apparatus testingPeak valueMeasurement precision
The invention discloses a method for measuring the impulse generated by a single-pulse laser ablation working medium and the corresponding ablation weight, and achieves the purpose of directly measuring the specific impulse. The method comprises the steps: obtaining the corresponding impulse and ablation weight in a mode that the weight isotropic and anisotropic effects aroused by the pulse generated by the single-pulse laser ablation working medium and the ablation weight are respectively carried out once based on a vertical motion torsional pendulum model; obtaining the impulse according to the maximum peak value of each torsional pendulum rotation angle and a rotation angle measurement value before the maximum peak value, and obtaining the ablation weight of the working medium according to a stable rotation angle mean value of the torsional pendulum rotation angles. The method can shorten the test cycle, avoids the frequent disassembly and assembly of the working medium, protects the working medium from being polluted, guarantees the measurement authenticity, and improves the specific impulse measurement precision.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
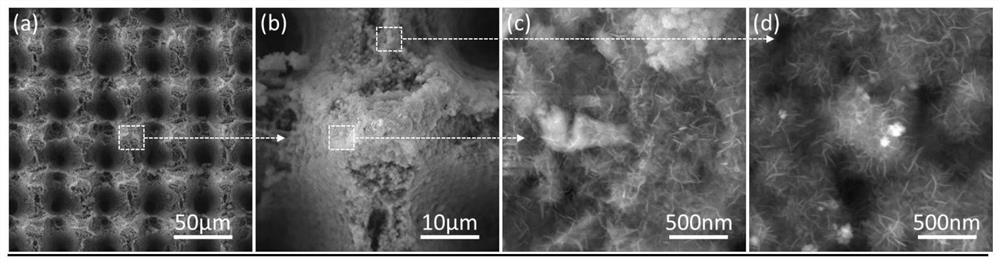
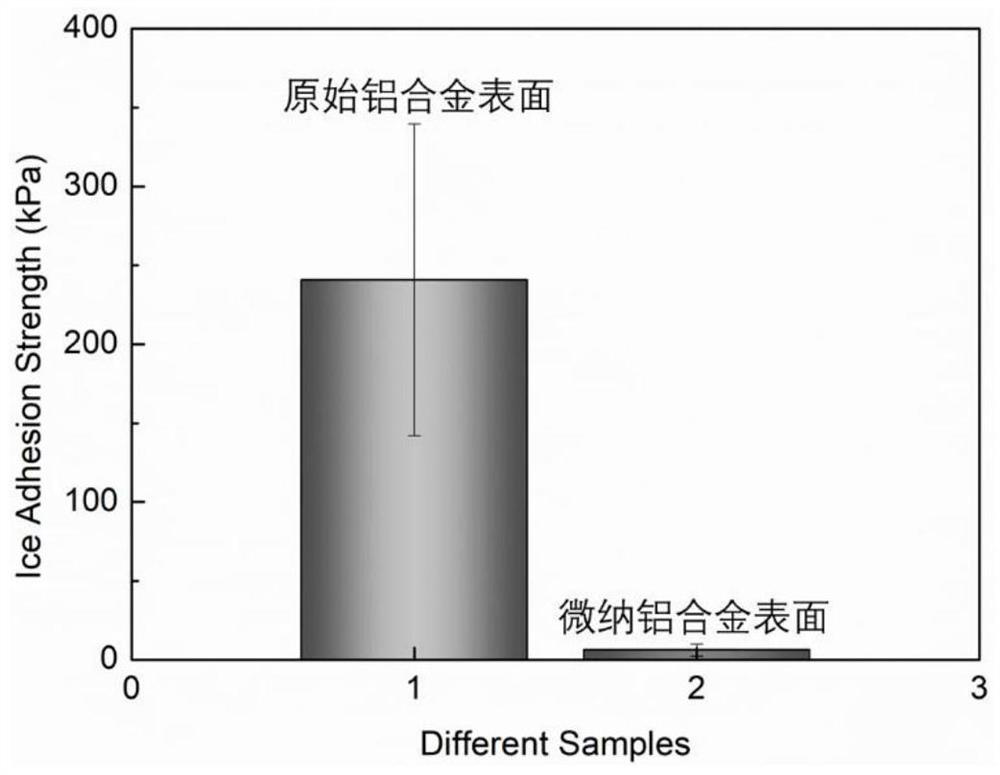
Super-hydrophobic anti-icing aviation aluminum alloy surface and production method
A super-hydrophobic anti-icing aviation aluminum alloy surface with ultralow ice adhesion is composed of a multi-stage micro-nano structure, the micro-nano structure is based on a three-dimensional micron cone structure periodically distributed on the surface of an aluminum alloy base material, and densely-growing nanosheets and nano flower clusters composed of the nanosheets are distributed on the surface of a micron cone; and one or two of submicron spheres and submicron flowers are dispersed and distributed on the surface of the micron cone or between the micron cones. The invention furtherdiscloses a production method of the surface, the surface is formed by combining ultrafast laser ablation and a wet chemical method and then carrying out low-free-energy surface chemical modification, and large-area efficient production can be achieved. The aviation aluminum alloy anti-icing surface has extremely low ice adhesion, adhesion strength between ice and the surface can be as low as 6 kPa, and the ice can automatically fall off under the action of self gravity or slight vibration. The surface structure can be widely applied to anti-icing fields of aviation key components, ships, ground transportation tools, refrigerators, air conditioners and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Ultrafast continuous three-dimensional imaging system and method for ultrashort pulse laser ablated object
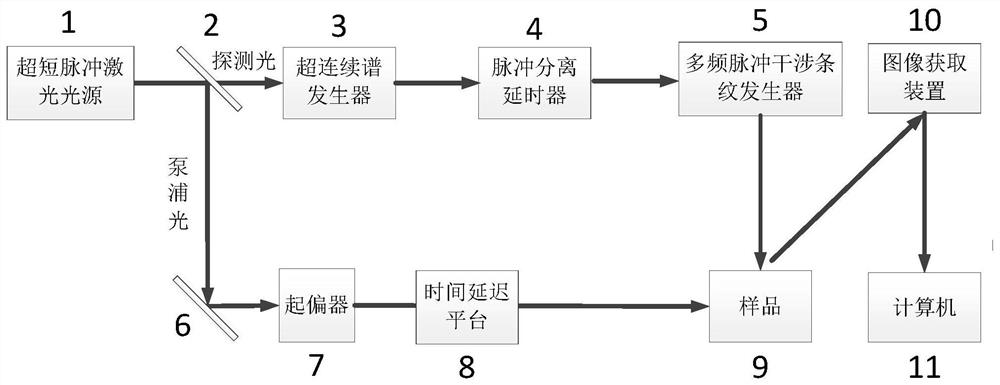
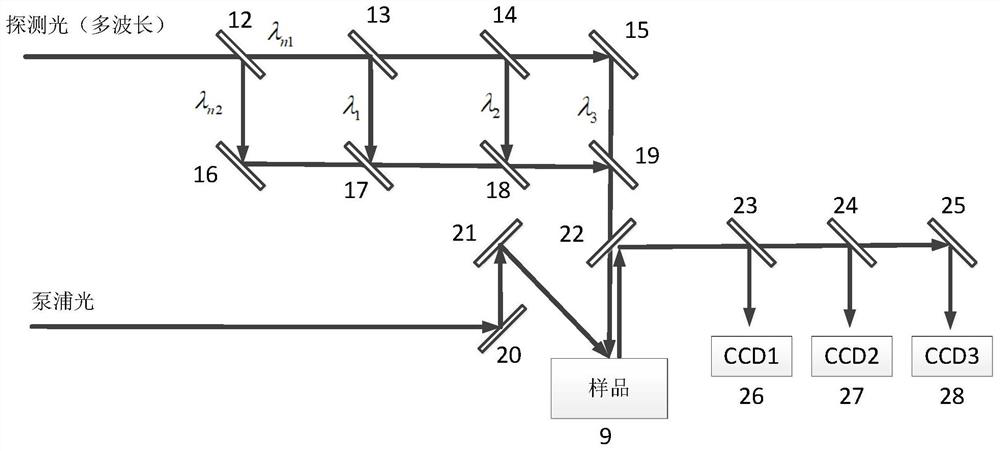
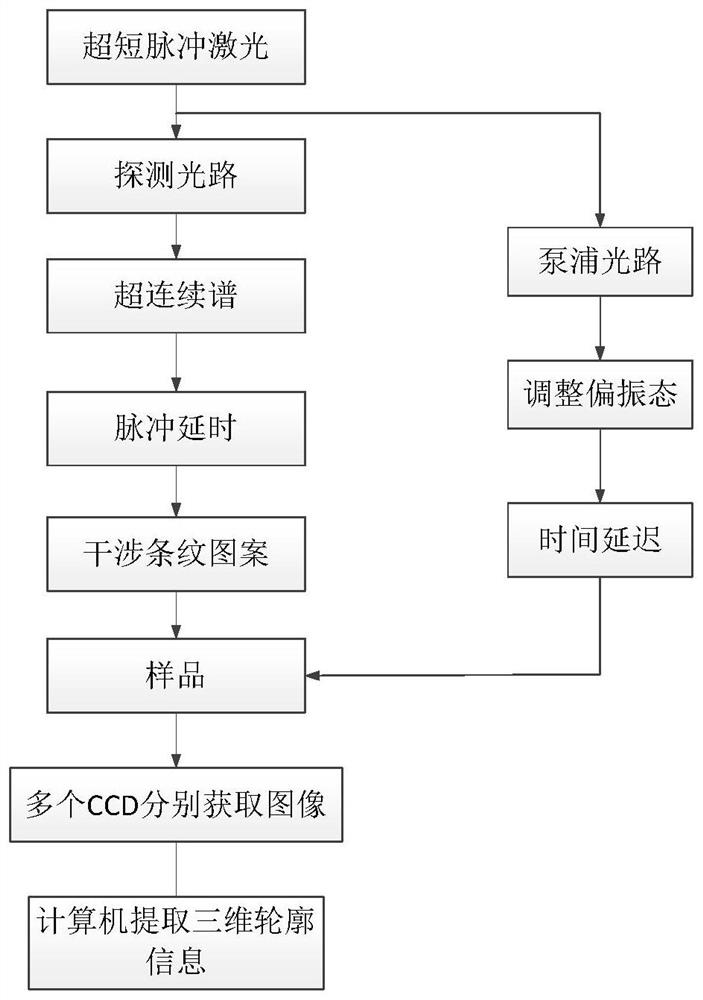
ActiveCN112894149AEnhanced Continuous ObservabilityUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splittingPicosecond
The invention relates to an ultrafast continuous three-dimensional imaging system and method for an ultrashort pulse laser ablated object, and belongs to the field of ultrafast imaging. According to the invention, the acquisition and restoration of three-dimensional contour information of an object surface with ultrahigh time resolution can be realized. The system specifically comprises an ultrashort pulse laser light source, a super-continuum spectrum generator, a pulse separation delayer, a multi-frequency pulse interference fringe generator, a polarizer, a time delay platform, a sample, an image acquisition device, a computer, a beam splitting-beam combining mirror, a reflecting mirror, and an image three-dimensional contour extraction method. According to the invention, ultrafast continuous three-dimensional observation in the process of ablating an object material by ultrashort pulse laser can be realized, the time resolution reaches femtosecond-picosecond magnitude, the surface three-dimensional shape of an object in the processing process can be presented, the continuous observability in the experiment process is enhanced, and an important auxiliary effect is provided for the mechanism research of ablating the processed object by the ultrashort pulse laser.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for preparing bulk molybdenum disulfide surface Raman-enhanced substrate through femtosecond lasers
ActiveCN110026684ASimple preparation processFast preparation processLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoLaser processing
The invention relates to a method for preparing a bulk molybdenum disulfide surface Raman-enhanced substrate through femtosecond lasers, and belongs to the field of application of functional surfaces.According to the method, bulk molybdenum disulfide which is cheap and easy to obtain is used as a sample, so that it is ensured that the lasers can perpendicularly enter the surface of the horizontally-placed sample; a laser device is set to a single-pulse trigger mode; a laser ablation area can be adjusted by adjusting the focal length of a plano-convex lens; and the shape of the laser ablationarea can be achieved by adjusting the angle between the sample and the incident lasers. According to the method, a micro-nano composite structure is ablated on the surface of the bulk molybdenum disulfide by means of the non-equilibrium characteristic of femtosecond laser processing, the material property of the molybdenum disulfide is modified, and thus, the molybdenum disulfide can be used as anefficient surface Raman-enhanced substrate. The method has the advantages that the preparation process is simple and rapid, the sample is cheap and easy to obtain, and the performance is stable and efficient; and an economical, simple, controllable and efficient preparation method is provided for preparing the surface Raman-enhanced substrate, and industrialization is facilitated.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
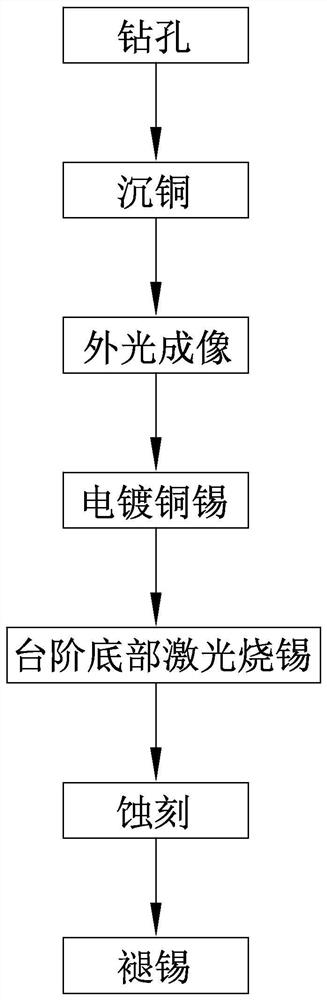
Manufacturing process of printed circuit board with steps and printed circuit board
InactiveCN111770638AConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalNon-metallic protective coating applicationMetallurgyHemt circuits
The invention discloses a manufacturing process of a printed circuit board with a step, which comprises the following steps: external light imaging: manufacturing a circuit pattern on a copper-clad plate in a dry film pasting mode, designing a dry film removal effect at the step position, and exposing copper on the side wall and the bottom of the step; electroplating copper and tin: sequentially electroplating a copper layer and a tin layer on the circuit pattern area on the copper-clad plate; step bottom laser tin burning: exposing the electrocoppering layer at the bottom of the step by meansof laser ablation of the tin layer; etching: after the dry film on the copper-clad plate is removed, etching off the exposed copper layer on the copper-clad plate to obtain the copper-clad plate of which the circuit pattern is covered by the tin layer; and tin removing: removing the tin layer on the copper-clad plate to obtain the printed circuit board with the outer layer circuit. According to the technological method, the technological process is shortened, and the manufacturing speed is increased. The invention further discloses a printed circuit board manufactured by adopting the manufacturing process. The printed circuit board is provided with a step mechanism.
Owner:珠海杰赛科技有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com