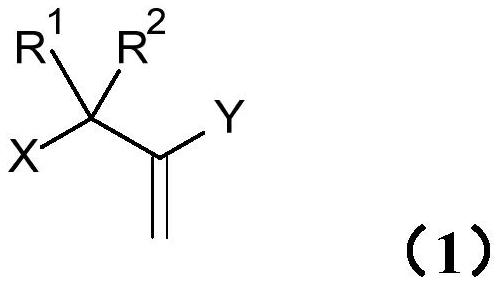
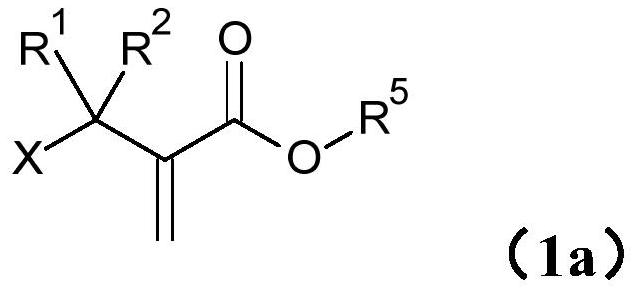
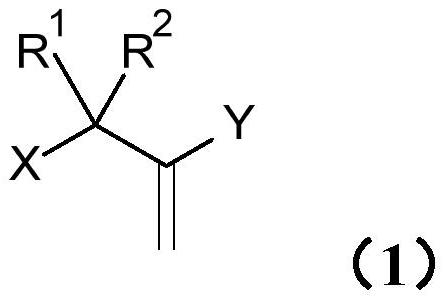
Process for producing aqueous polymer dispersion
A technology of water-based polymers and dispersions, applied in the direction of coating, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory application performance of polymer dispersions, and achieve the effects of superior performance, reduced leaching behavior, and low film-forming temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0316] Example 1 (E1)
[0317] 527.0 g of deionized water and 8.3 g of a 15% strength by weight aqueous solution of sodium lauryl sulfate were charged at 20 to 25° C. (room temperature) into a polymerization vessel equipped with a metering device and temperature regulation, and the mixture was stirred under a gentle nitrogen flow. The initial charge was heated to 95°C. When this temperature had been reached, 8.9 g of a 7% strength by weight aqueous solution of sodium peroxodisulfate were added and the batch was stirred for five minutes. Subsequently, 10.9 g of an aqueous sodium peroxodisulfate solution with a strength of 7% by weight were metered in parallel to feed stream 1 at a constant flow rate over the course of 40 minutes, maintaining the temperature. After the end of the two feed streams, a small sample was taken from the vessel to measure the molecular weight distribution of the polymer produced, and then the polymerization mixture was reacted at 95°C for a further 10...
Embodiment 2
[0332] Example 2 (E2)
[0333] Example 2 was prepared in the same manner as Example 1, except that in feed stream 1, 8.7 g of ethyl 2-(bromomethyl)acrylate was used instead of 11.7 g.
[0334] The obtained aqueous polymer dispersion had a solids content of 39.9% by weight. The polymer taken at the end of feed stream 1 had a number average molecular weight of 3500 Da, a weight average molecular weight of 6900 Da, and a peak maximum at 7100 Da. The number average molecular weight of the final polymer dispersion is 11600Da, the weight average molecular weight is 24600Da, and the maximum peak is at 20900Da.
Embodiment 3
[0335] Example 3 (E3)
[0336] Example 3 was prepared in the same way as Example 1 except that in feed stream 1, 124.0 g deionized water was used instead of 130.2 g and 5.8 g 2-(bromomethyl)acrylic acid was used Ethyl ester instead of 11.7g.
[0337] The obtained aqueous polymer dispersion had a solids content of 39.9% by weight. The polymer taken at the end of feed stream 1 had a number average molecular weight of 5600 Da, a weight average molecular weight of 11900 Da, and a peak maximum at 10600 Da. The number average molecular weight of the final polymer dispersion is 16200 Da, the weight average molecular weight is 29900 Da, and the maximum peak is at 27500 Da.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com