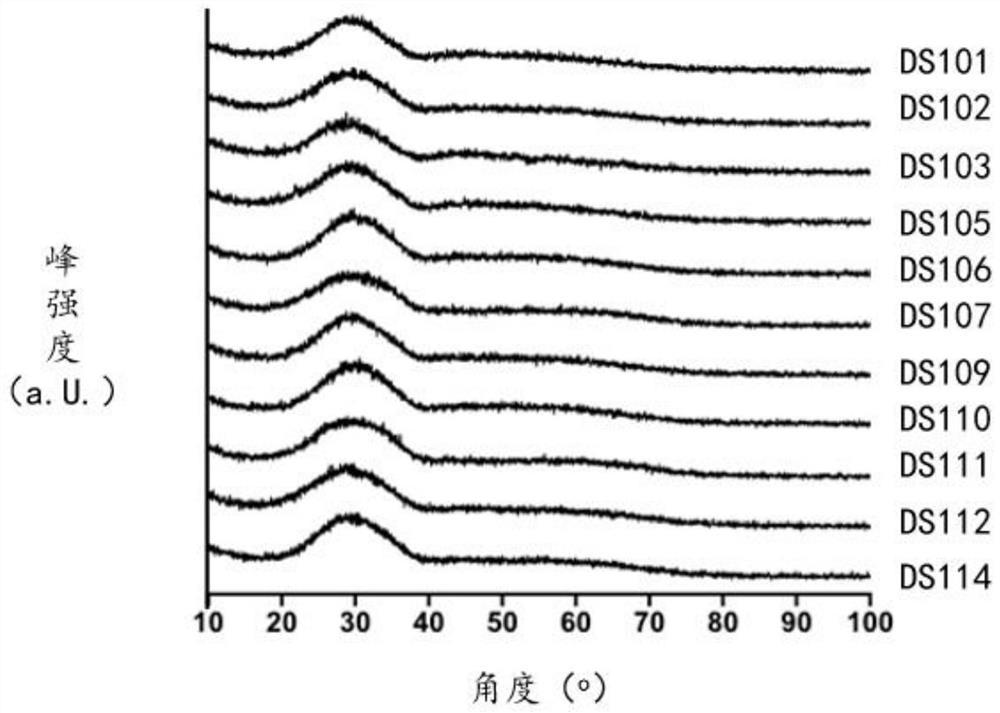
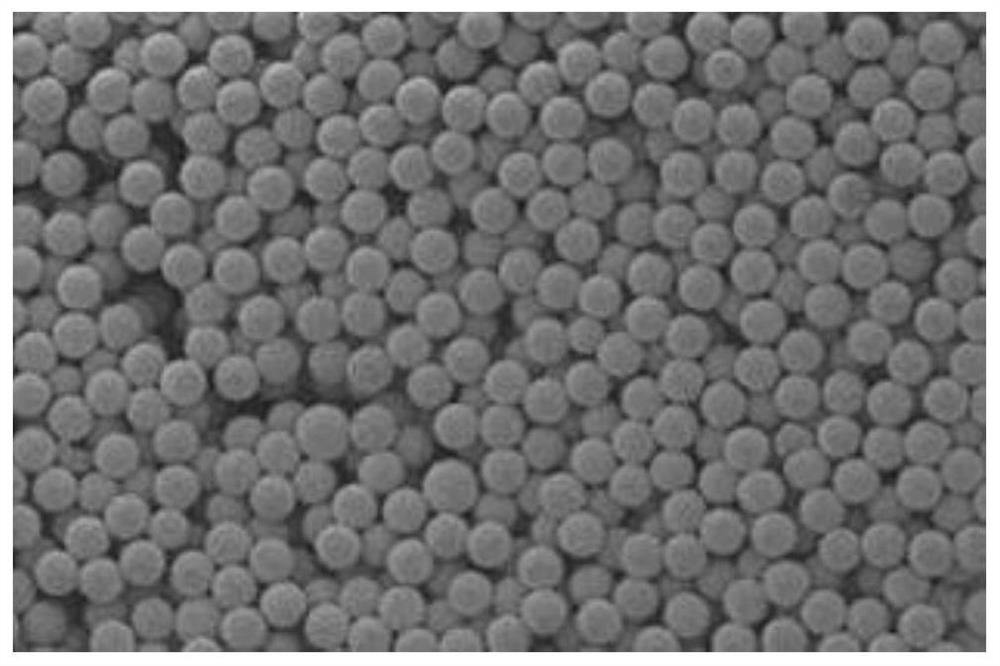
radioactive glass microspheres
A glass microsphere, radioactive technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of radiation dose limitation, unable to achieve tumor radical cure dose, etc., and achieve the effect of high radiation energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040]This embodiment provides a first radioactive glass microsphere group and a preparation method of each radioactive glass microsphere in the first radioactive glass microsphere group. The preparation method of each radioactive glass microsphere in the first radioactive glass microsphere group is as follows:
[0041] S11: Provide a well-mixed first inorganic mixture as a raw material, vacuum dry at 100° C. for 1-3 hours, and preheat to 1350° C.-1600° C. in a high-temperature box furnace to obtain a melt.
[0042] S12: Quenching the melt in water to obtain a frit, and then vacuum drying the frit at 100° C. for 24 hours to obtain a dry frit.
[0043] S13: Using a planetary ball mill to grind the dry frit into solid powder.
[0044] S14: Place the solid powder in a gas flame to re-melt to obtain a spheroidized melt.
[0045] S15: sequentially cooling and screening the spheroidized melt to obtain radioactive glass microspheres with an average particle size of 15-200 microns. ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a second radioactive glass microsphere group, and the preparation method of each radioactive glass microsphere in the second radioactive glass microsphere group is the same as that of the first radioactive glass microsphere group in Example 1. The difference in the preparation method of each radioactive glass microsphere is that the raw material for preparing the radioactive glass microsphere is the second inorganic mixture.
[0087] Each radioactive glass microsphere in the second inorganic mixture and the second radioactive glass microsphere group is composed of a molar percentage of 13-30% Y 2 O 3 , 40-60 mol% SiO 2 , 10-30 mol% MnO and 5-15 mol% ZrO 2 composition.
[0088] Table 6 of Example 2 of the present invention provides the molar percentage content of each component of 15 kinds of radioactive glass microspheres with glass sample numbers S201 to S215.
[0089] Table 6
[0090]
[0091] In Example 2 of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides a third group of radioactive glass microspheres. The difference in the preparation method of each radioactive glass microsphere is that the raw material for preparing the radioactive glass microsphere is the third inorganic mixture.
[0098] Each radioactive glass microsphere in the third inorganic mixture and the third radioactive glass microsphere group is composed of a molar percentage of 13-30% Y 2 O 3 , 40-60 mol% SiO 2 , 10-30 mol% MnO and 5-15 mol% TaO 2 composition.
[0099] Table 8 of Example 3 of the present invention provides the molar percentage of each component of 15 kinds of radioactive glass microspheres with glass sample numbers S301 to S315.
[0100] Table 8
[0101]
[0102] In Example 3 of the present invention, the densities ρ of the 15 kinds of radioactive glass microspheres recorded in Table 8 were investigated according to the ASTM B923 test standard, and the axial CT scan was loosely placed ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com