Mixed-valence iron-based fluoride positive electrode material and preparation method thereof
A positive electrode material, fluoride technology, applied in the field of electrochemistry and material chemistry, can solve problems such as poor conductivity, achieve the effect of improving electronic conductivity, low operating labor intensity, and good flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
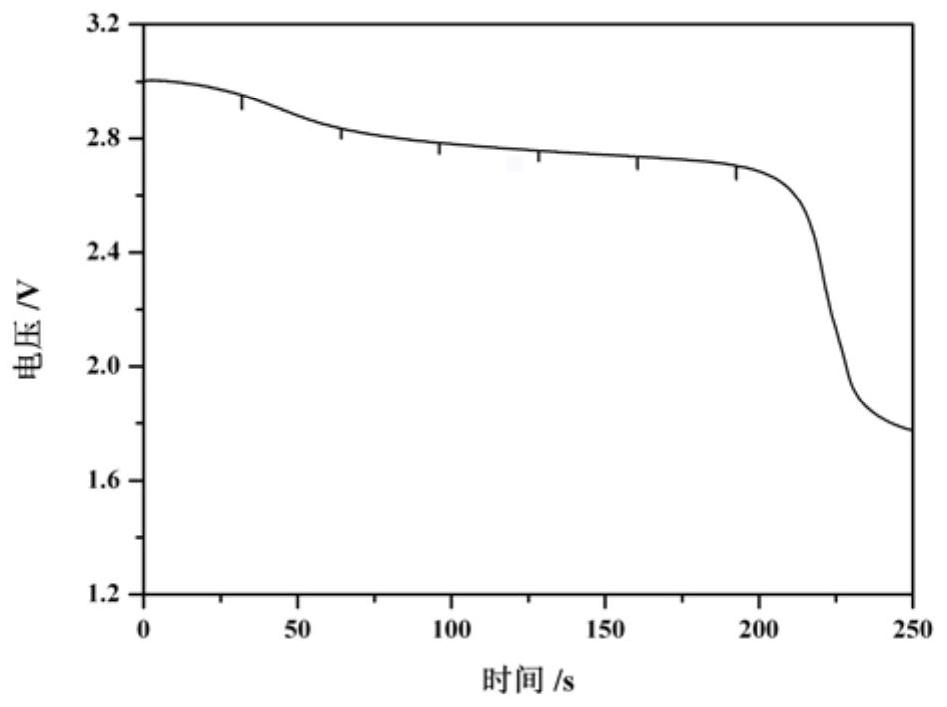
[0019] Weigh FeF 3 ·3H 2 O raw materials were placed in a high-temperature reaction furnace, heated to 200°C under the protection of argon, and then kept for 2 hours; heated again to 400°C, kept for 2 hours, and then naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain the precursor. Mix the precursor with oxalic acid at a mass ratio of 1:1.5, high-speed ball milling and ensure that the particle size D90≤10μm, place it in a high-temperature and high-pressure reaction furnace, and feed hydrogen-argon mixed gas (hydrogen concentration is 10%), After heating up to 420° C. and keeping it warm for 20 minutes, the hydrogen-argon gas mixture was stopped, and the argon gas was injected again to rapidly cool to room temperature to obtain the mixed valent iron-based fluoride positive electrode material. After the cathode material is assembled into a single battery with LiCl spacer powder and lithium-boron alloy, the discharge curve at 650 ° C is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the open circu...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Weigh FeF 3 ·3H 2 O raw materials were placed in a high-temperature reaction furnace, heated to 200°C under the protection of argon, and then kept for 2 hours; heated again to 400°C, kept for 2 hours, and then naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain the precursor. Mix the precursor with oxalic acid at a mass ratio of 1:2, and after high-speed ball milling to ensure that D90≤10 μm, place it in a high-temperature and high-pressure reaction furnace, feed hydrogen-argon mixed gas (hydrogen concentration is 10%), and heat up to After holding at 420°C for 30 minutes, stop feeding the hydrogen-argon gas mixture, and then feed the argon gas again to quickly cool to room temperature to obtain the mixed valence iron-based fluoride positive electrode material.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Weigh FeF 3 ·3H 2 O raw materials were placed in a high-temperature reaction furnace, heated to 200°C under the protection of argon, and then kept for 2 hours; heated again to 400°C, kept for 2 hours, and then naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain the precursor. Mix the precursor with oxalic acid at a mass ratio of 1:1, and after high-speed ball milling to ensure that D90≤10 μm, place it in a high-temperature and high-pressure reaction furnace, feed hydrogen-argon mixed gas (hydrogen concentration is 10%), and heat up to After holding at 420°C for 10 minutes, stop feeding the hydrogen-argon gas mixture, and then feed the argon gas again to rapidly cool to room temperature, and then obtain the mixed valence iron-based fluoride positive electrode material.
[0024] In summary, the present invention creatively proposes a mixed valence Fe x f 3 (1≤x≤1.2) The preparation method of the positive electrode material controls the content of ferrous iron in the positiv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com