Porous polyolefin film and its preparation method
A polyolefin and composite polyolefin technology, applied in the field of porous membranes, can solve the problem of large pore size, etc., and achieve the effects of improved dispersion uniformity, improved dispersion and less pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] A preparation method of a porous polyolefin film provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0029] S1. The water-soluble organic porogen and the inorganic porogen are mixed uniformly in a mass ratio (40%:60%)~(60%:40%) to obtain a multi-level composite porogen. The organic porogen is in The viscosity at 200°C is 300-3000 centipoise; the water-soluble organic porogen and the inorganic porogen are first mixed, and the water-soluble organic porogen coats the surface of the inorganic porogen, and the water-soluble organic porogen can also be used. Acting as a dispersion modifier for inorganic porogens and polyolefins, it can improve the dispersibility of subsequent mixing with polyolefins.
[0030] S2. The multi-stage composite porogen obtained in step S1 and the polyolefin are melt-blended and extruded in a twin-screw extruder in a mass ratio of 2%: 98% to 30%: 70%, and molded to obtain a composite polymer Olefin flakes;
[0031] S3. The composite...
Embodiment 1
[0043] A preparation method of a porous polyolefin membrane, comprising the following steps:
[0044] S1. Polyethylene glycol with a molecular weight of 5000 g / mol and a viscosity of 300 centipoise (200° C.) and calcium carbonate (2500 mesh) are dried and mixed uniformly in a mass ratio of 50%:50% to obtain a multi-level composite porosity material; The water-soluble polyethylene glycol and calcium carbonate are mixed first, and the polyethylene glycol is coated on the surface of the calcium carbonate, thereby improving the dispersibility of the subsequent mixing with the polyolefin.
[0045] S2. The multi-stage composite porogen obtained in step S1 and polyethylene are melt-blended and extruded in a twin-screw extruder in a mass ratio of 15%:85% (the temperature of melt-blending is 160 ° C), and the flow Extension molding (the temperature of the casting molding is 245° C., and the casting speed is 10 m / min) to obtain a composite polyethylene sheet;
[0046] S3. The composite...
Embodiment 2-5
[0049] A preparation method of a porous polyolefin membrane, compared with Example 1, the difference is that in steps S1 and S2, the mass ratio of polyethylene glycol and calcium carbonate is m 1 :m 2 and the mass ratio m of the multi-stage composite porosity material to polyethylene 3 :m 4 As shown in Table 1, the others are substantially the same as those in Embodiment 1, and are not repeated here.
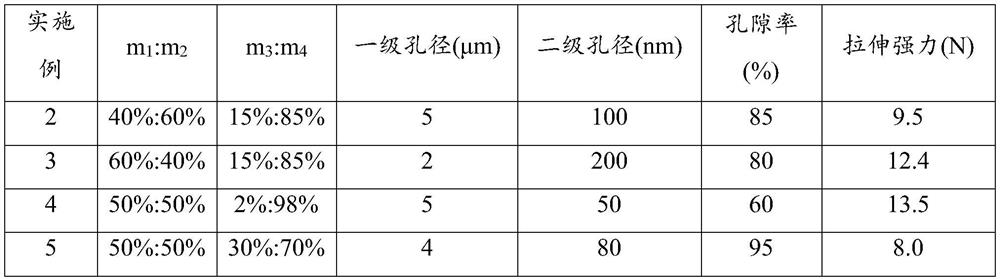
[0050] Table 1 Preparation conditions and performance test results of Examples 2-5
[0051]
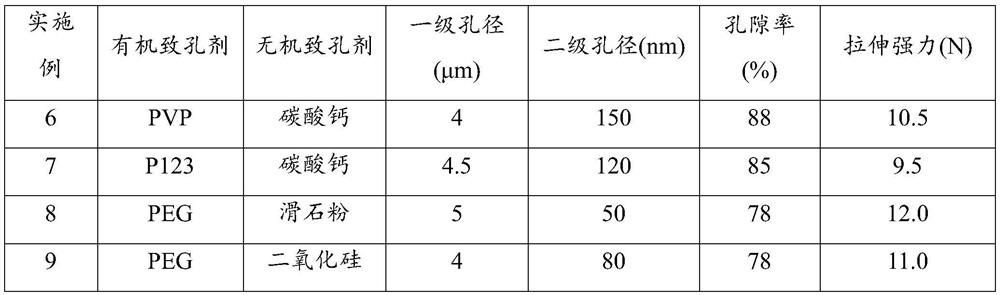
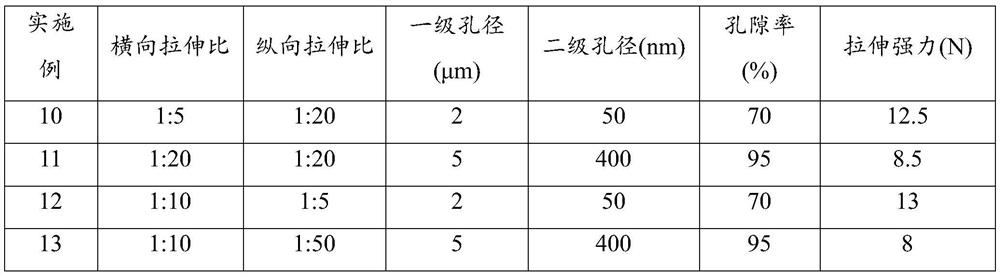
[0052] It can be seen from Table 1 that with the increase of the content of the porogen, the porosity of the porous membrane material increases, and the tensile strength of the membrane material decreases. In addition, with the increase of the organic porogen in the composite porogen, the secondary microporous structure of the porous film also increases accordingly.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| stretch ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com