A kind of magnesium alloy processing method for improving high temperature creep performance
A processing method and high-temperature creep technology, applied in the field of magnesium alloy processing, can solve the problems that the alloy's high-temperature creep performance has a very large influence, limit the application scene of the alloy, and easily become a crack source. Precise control and effect of suppressing the formation of precipitates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The magnesium alloy was prepared by water-cooled semi-continuous casting method, and the pure magnesium ingot (Mg 99.9%), pure aluminum ingot (Al 99.9%), pure zinc ingot (Zn 99.9%), Al-Mn master alloy and Mg-Y master alloy were smelted , the as-cast structure of the magnesium alloy is obtained by pouring. The mass percentage composition of the magnesium alloy is: Al: 8.5%, Zn: 0.90%, Mn: 0.3%, Y: 0.5%, and the rest is magnesium and impurity elements that cannot be removed.
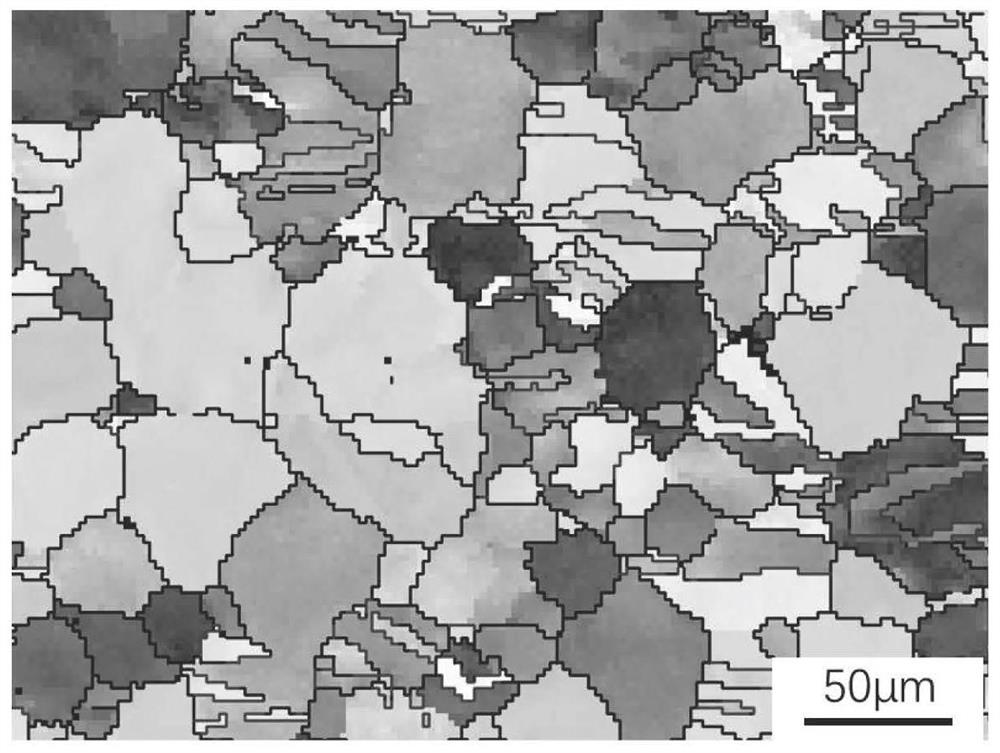
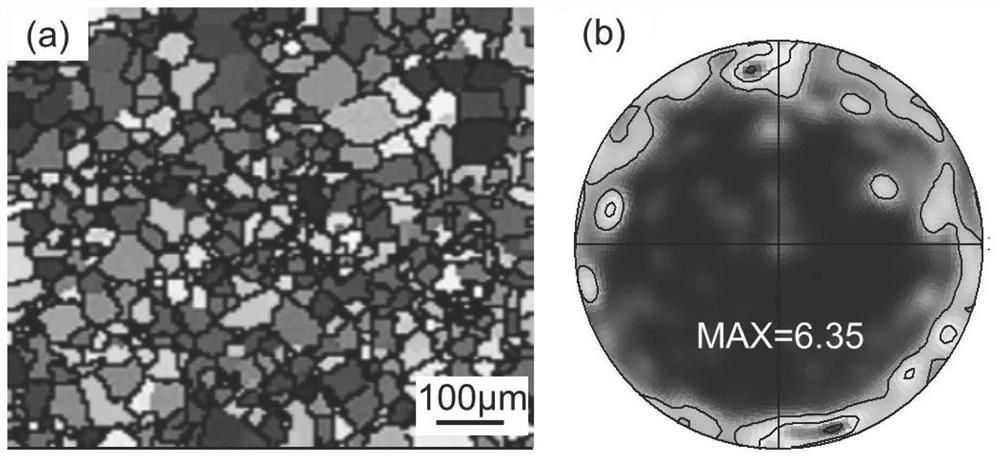
[0031] The as-cast structure was subjected to solution treatment at 380°C×12h; then the solid solution state was extruded at a temperature of 400°C, an extrusion ratio of 16:1, and an extrusion speed of 17 mm / s. The apparent quality of the magnesium alloy after extrusion is good, and the EBSD microstructure of the magnesium alloy after extrusion is as follows: figure 1 As shown, it can be seen that it has an obvious preferred orientation, and the texture strength of its 0001 base plane is 6.35; then...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The magnesium alloy was prepared by water-cooled semi-continuous casting method, and the pure magnesium ingot (Mg 99.9%), pure aluminum ingot (Al 99.9%), pure zinc ingot (Zn 99.9%), Al-Mn master alloy and Mg-Y master alloy were smelted , the as-cast structure of the magnesium alloy is obtained by pouring. The mass percentage composition of the magnesium alloy is: Al: 9.5%, Zn: 0.45%, Mn: 0.4%, Y: 0.8%, and the rest is magnesium and impurity elements that cannot be removed.
[0036]The as-cast structure was subjected to solution treatment at 400°C×8h; then the solid solution state was extruded at a temperature of 350°C, an extrusion ratio of 8:1, and an extrusion speed of 20 mm / s. The EBSD microstructure of the magnesium alloy after Image 6 As shown, it can be seen that it has an obvious preferred orientation, and the texture strength of its 0001 base plane is 7.44; then the extruded structure is compressed with a small amount of deformation, the compression direction i...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The magnesium alloy was prepared by water-cooled semi-continuous casting method, and the pure magnesium ingot (Mg 99.9%), pure aluminum ingot (Al 99.9%), pure zinc ingot (Zn 99.9%), Al-Mn master alloy and Mg-Y master alloy were smelted , the as-cast structure of the magnesium alloy was obtained by pouring. The mass percentage composition of the magnesium alloy is: Al: 9.1%, Zn: 0.61%, Mn: 0.15%, Y: 0.3%, and the rest is magnesium and impurity elements that cannot be removed.
[0040] The as-cast structure was subjected to solution treatment at 420°C×4h; then the solid solution state was extruded at a temperature of 450°C, an extrusion ratio of 25:1, and an extrusion speed of 15 mm / s. The EBSD microstructure of the magnesium alloy after Figure 8 As shown, the extruded microstructure has obvious preferred orientation, and the texture strength of its 0001 base plane is 6.82; then the extruded microstructure is compressed with a small amount of deformation, the compression...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strain rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| texture strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com