Methods for treating oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD)
A technology for malnutrition and oculopharyngeal muscles, applied in gene therapy, biochemical equipment and methods, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems such as dysphagia, death, and progressive degeneration of the pharyngeal muscle system that cannot be corrected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0516] Example 1 - Design of shmiR targeting PABPN1
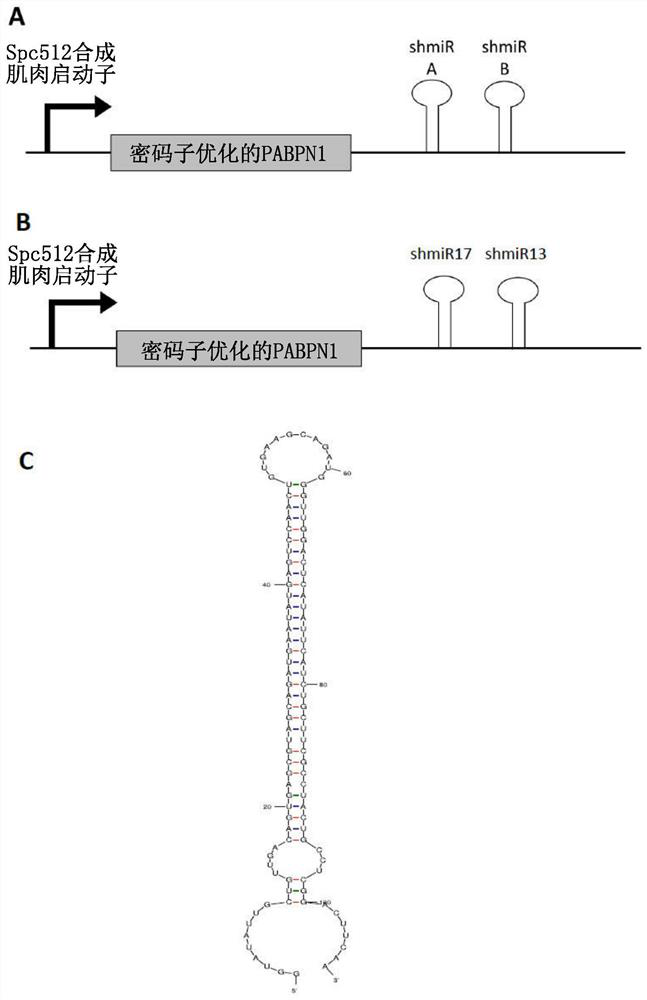
[0517] Sequences representing potential targets for siRNA construct design were identified from PABPN1 mRNA sequences using publicly available siRNA design algorithms (including Ambion, Promega, Invitrogen, Origene, and MWG): the selected sequences were in human, non-human Conserved in mammalian, bovine and mouse species. Sequences encoding candidate siRNAs were incorporated into the pre-miR30a scaffold to generate sequences encoding short hairpin microRNAs (shmiRs) including 5' flanking regions (SEQ ID NO: 41), siRNA sense strand sequence (effector complement), stem / loop junction sequence (SEQ ID NO: 40), siRNA antisense strand (effector sequence) and 3' flanking region (SEQ ID NO: 42). The predicted secondary structures of representative shmiRs are shown in figure 1 C. The target regions of the PABPN1 mRNA transcripts of the designed shmiRs are shown in Table 1, and the corresponding shmiR effector sequences (antisense...
Embodiment 2
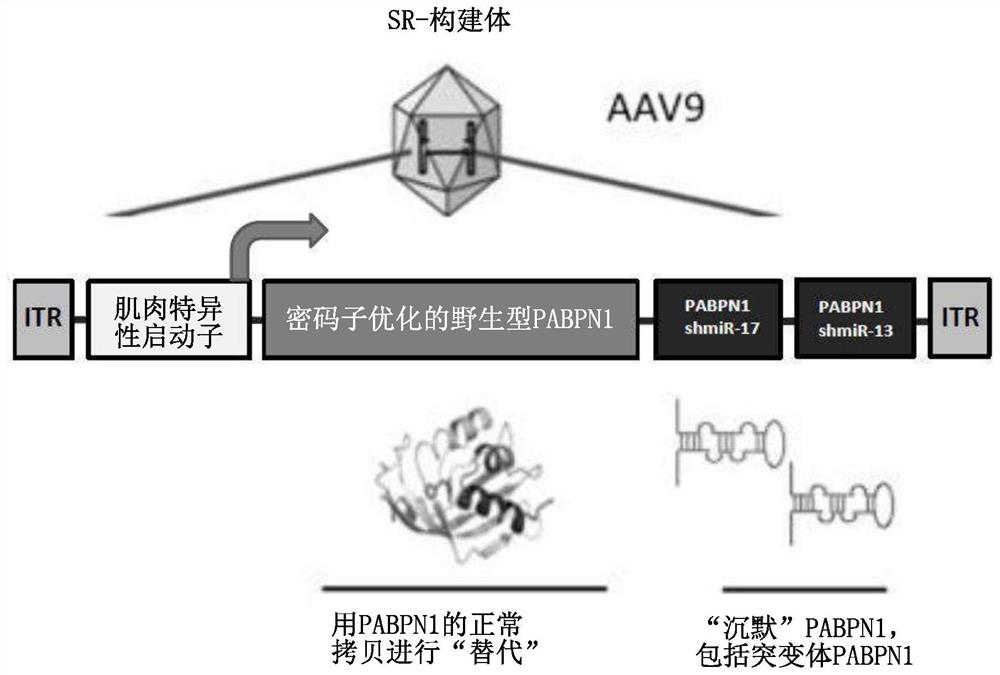
[0518] Example 2 - Generation of a single "silencing and replacement construct" for simultaneous gene silencing of endogenous PABPN1 and replacement with codon-optimized PABPN1.
[0519] A single-stranded adeno-associated virus type 2 (ssAAV2) plasmid expressing shmiR17 and shmiR13 (eg, as described in Tables 3 and 4) and the optPABPN1 sequence was created.
[0520] Silencing and replacement constructs (hereinafter referred to as "SR-constructs") were obtained by subcloning the DNA sequences encoding shmiR17 and shmiR13 (as in Table 4) into optPABPN1 in the pAAV2 vector backbone (pAAV-shmiR viral plasmid) produced in the 3' untranslated region of the transcript. Expression of optPABPN1 and both shmiRs in a single transcript is driven by the muscle-specific promoter Spc512. figure 1 (A), figure 1 (B) and figure 2 A schematic of the SR construct is provided in .
[0521] A recombinant pseudotyped AAV vector stock is then generated. Briefly, HEK293T cells were cultured in cel...
Embodiment 3
[0522] Example 3 - In vivo studies using a single vector "silence and replace" approach.
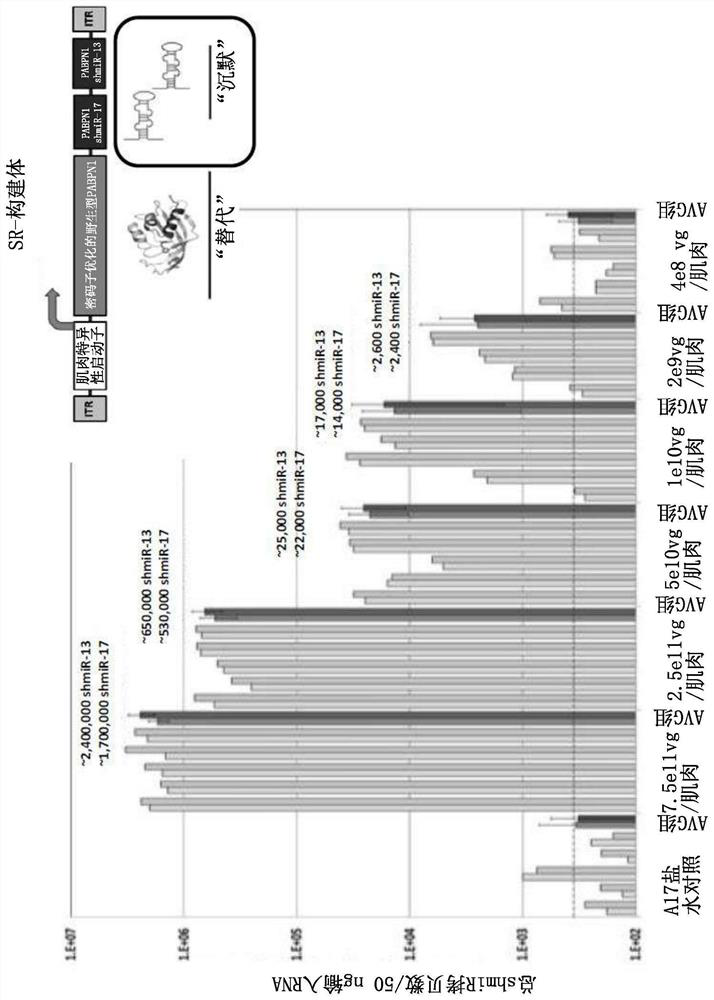
[0523] To test the in vivo efficacy of the SR-constructs described in Example 2 in an OPMD-associated disease model, the SR-constructs were administered alone in a range of doses by intramuscular injection into the tibiae of 10-12 week-old A17 mice in the anterior muscle (TA). The doses administered were 7.5x10 per muscle 11 , 2.5x10 11 , 5x10 10 , 1x10 10 , 2x10 9 and 4x10 8 A vector genome (vg). Age-matched A17 mice were injected with saline as untreated group. Mice were sacrificed 14 or 20 weeks after treatment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com