Method for extracting diphenol from wastewater
A technology for dihydric phenol and wastewater, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, and water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of low dephenolization efficiency, harsh solvent recovery conditions, and high solvent prices.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
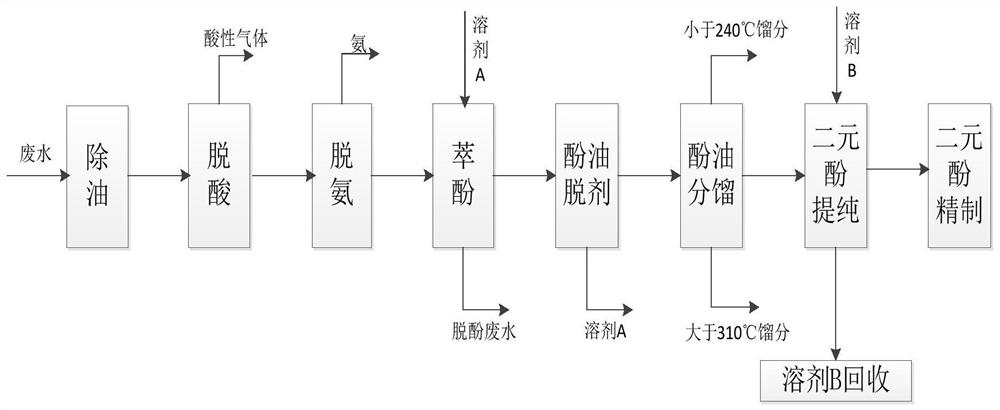
[0046] The present embodiment provides a method for extracting dihydric phenols from waste water, comprising the steps of:
[0047] Wastewater deoiling: Using the difference in density and polarity, most of the oil in the coal chemical wastewater is removed in the grease trap.
[0048] Wastewater deacidification: The acid gas in the deoiled wastewater is removed by heating and stripping.
[0049] Wastewater deammonization: The ammonia in the acid removal wastewater is removed by stripping and the ammonia is cooled and recovered.
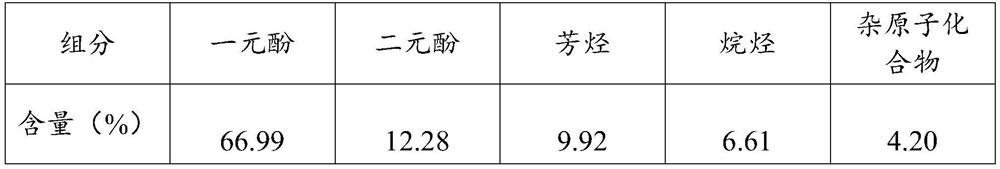
[0050] Wastewater phenol extraction: use solvent A to extract the phenolic substances in the deamination wastewater, and the obtained dephenolization wastewater is sent to subsequent biochemical treatment. Among them, the mass ratio of solvent A to deamination wastewater is 1:10, and the extraction temperature is 50°C. Solvent A is dimethyl carbonate.
[0051] Removal of phenol-containing solvents: Removal of solvent A by distillation of phenol-co...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The present embodiment provides a method for extracting dihydric phenols from waste water, comprising the steps of:
[0065] Wastewater deoiling: Using the difference in density and polarity, most of the oil in the coal chemical wastewater is removed in the grease trap.
[0066] Wastewater deacidification: The acid gas in the deoiled wastewater is removed by heating and stripping.
[0067] Wastewater deammonization: The ammonia in the acid removal wastewater is removed by stripping and the ammonia is cooled and recovered.
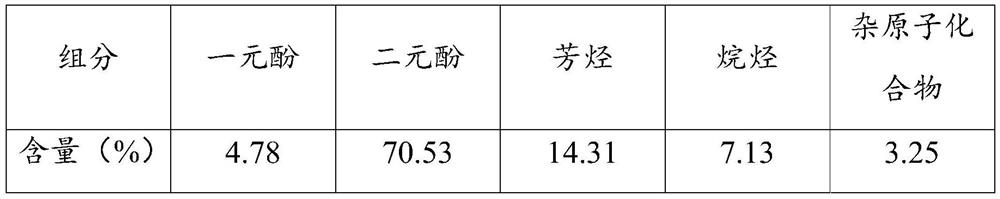
[0068] Wastewater phenol extraction: use solvent A to extract the phenolic substances in the deamination wastewater, and the obtained dephenolization wastewater is sent to subsequent biochemical treatment. Among them, the mass ratio of solvent A to deammonization wastewater is 1:5, and the extraction temperature is 30°C. Solvent A is dimethyl carbonate.
[0069] Removal of phenol-containing solvents: Removal of solvent A by distillation of phenol-...
Embodiment 3
[0081] The present embodiment provides a method for extracting dihydric phenols from waste water, comprising the steps of:
[0082] Wastewater deoiling: Using the difference in density and polarity, most of the oil in the coal chemical wastewater is removed in the grease trap.
[0083] Wastewater deacidification: The acid gas in the deoiled wastewater is removed by heating and stripping.
[0084] Wastewater deammonization: The ammonia in the acid removal wastewater is removed by stripping and the ammonia is cooled and recovered.
[0085] Wastewater phenol extraction: use solvent A to extract the phenolic substances in the deamination wastewater, and the obtained dephenolization wastewater is sent to subsequent biochemical treatment. Among them, the mass ratio of solvent A to deamination wastewater is 1:10, and the extraction temperature is 50°C. Solvent A was ethyl acetate.
[0086] Removal of phenol-containing solvents: Removal of solvent A by distillation of phenol-contai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com