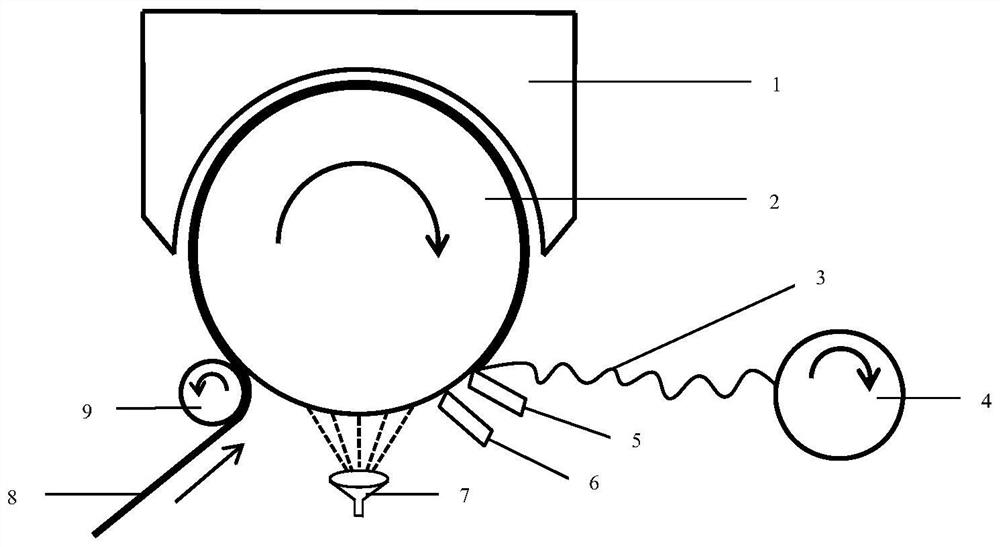
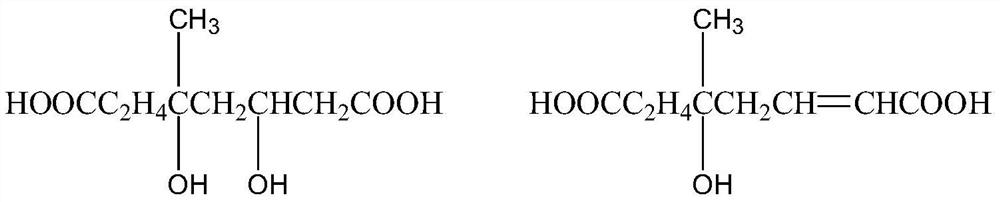Biomass-based water type cylinder adhesive and preparation method thereof
A technology of sticking agent and biomass, which is applied in the direction of coating, polyamide coating, etc., and can solve the problems of the sticking agent containing organic chlorine and poor wrinkling effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Step 1: Weigh 50.00g of levulinic acid, 31.03g of acrylic acid, and 50.00g of water into a 250mL three-necked flask, and stir and react at 140°C for 2h. After the reaction is finished, the temperature is lowered to room temperature to obtain a biomass-based dibasic acid.
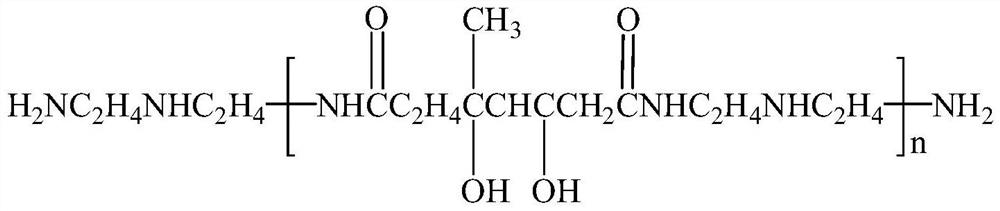
[0026] Step 2: Add 20.90 g of the prepared dibasic acid, 10.3 g of diethylenetriamine and 20.0 g of water into a 100 mL three-necked flask. The reaction was connected to a distillation device, and after reacting at 150°C for 4 hours, the generated water was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the distillation ended when there was no distillate. Finally, a yellow transparent water-based polyamide is obtained.
[0027] Step 3: Add 50.00 g of amino-terminated polyether and 6.15 g of dimer acid epoxy resin into a 250 mL three-necked flask, and add a catalyst in an amount of 0.5 wt.% of the total amount of dimer acid epoxy resin and amino-terminated polyether. The reaction was stirred at 140°C for ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Step 1: Weigh 50.00g of levulinic acid, 31.03g of acrylic acid, and 50.00g of water into a 250mL three-necked flask, and stir and react at 140°C for 2h. After the reaction is finished, the temperature is lowered to room temperature to obtain a biomass-based dibasic acid.
[0031] Step 2: Add 20.90 g of the prepared dibasic acid, 10.3 g of diethylenetriamine and 20.0 g of water into a 100 mL three-necked flask. The reaction was connected to a distillation device, and after reacting at 150°C for 4 hours, the generated water was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the distillation ended when there was no slip-out. Finally, a yellow transparent water-based polyamide is obtained.
[0032] Step 3: Add 50.00 g of amino-terminated polyether and 6.15 g of dimer acid epoxy resin into a 250 mL three-necked flask, and add a catalyst in an amount of 0.5 wt.% of the total amount of dimer acid epoxy resin and amino-terminated polyether. The reaction was stirred at 140°C for 4 ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Step 1: Weigh 50.00g of levulinic acid, 31.03g of acrylic acid, and 50.00g of water into a 250mL three-necked flask, and stir and react at 140°C for 2h. After the reaction is finished, the temperature is lowered to room temperature to obtain a biomass-based dibasic acid.
[0036] Step 2: Add 20.90 g of the prepared dibasic acid, 10.3 g of diethylenetriamine and 20.0 g of water into a 100 mL three-necked flask. The reaction was connected to a distillation device, and after reacting at 150°C for 4 hours, the generated water was distilled off under reduced pressure, and the distillation ended when there was no slip-out. Finally, a yellow transparent water-based polyamide is obtained.
[0037] Step 3: Add 50.00 g of amino-terminated polyether and 6.15 g of dimer acid epoxy resin into a 250 mL three-necked flask, and add a catalyst in an amount of 0.5 wt.% of the total amount of dimer acid epoxy resin and amino-terminated polyether. The reaction was stirred at 140°C for 4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com