Composite structure for airbag cover, and sewn product of composite structure
A composite structure and product technology, applied in synthetic resin layered products, layered products, vehicle safety arrangements, etc., can solve the problems of low flexibility and softness, small thickness, unfavorable touch, and achieve high breaking strength, easy Operation, the effect of reducing manufacturing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
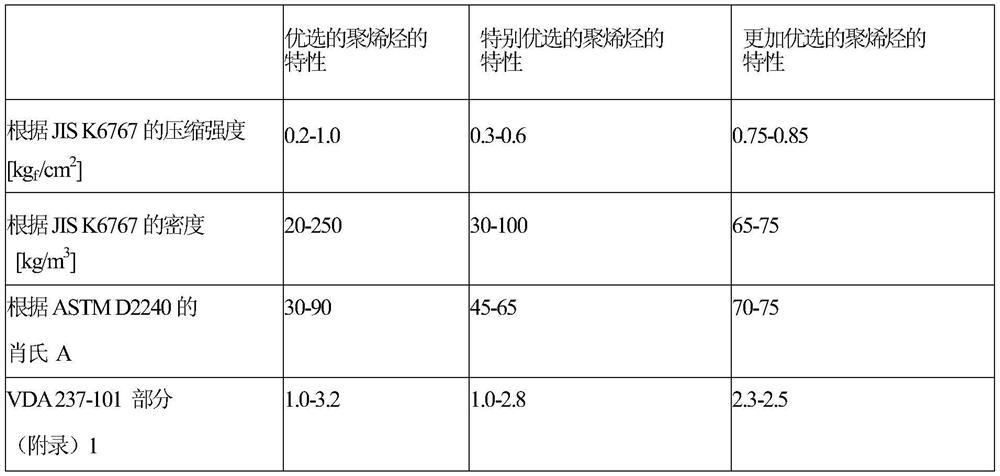
Method used
Image
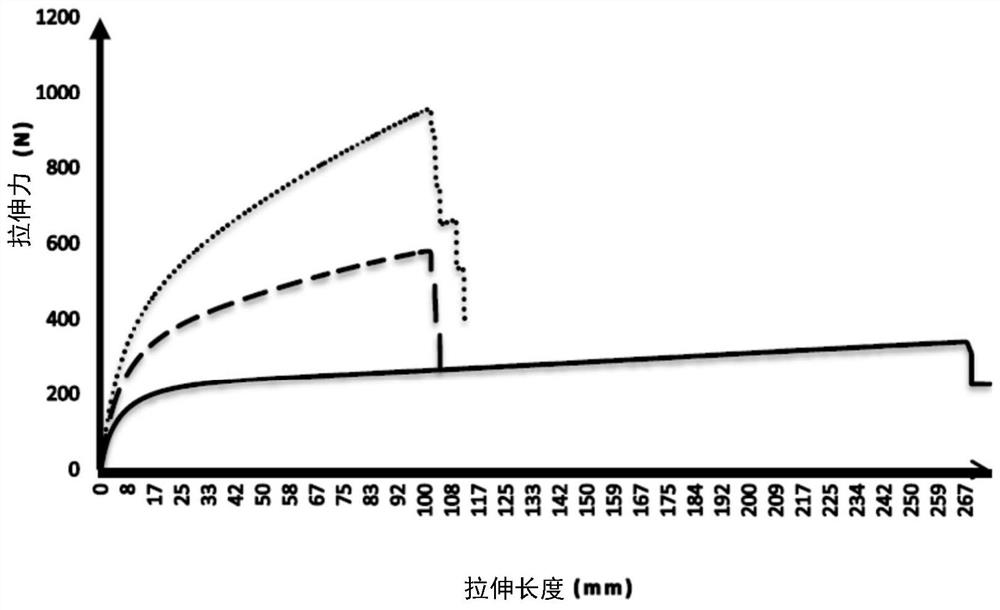
Examples
example 1
[0165] The artificial leather of example 1 has following structure:
[0166] Layer 0: lacquer based on silicone-containing aliphatic polyurethane, about 5 μm thick
[0167] Layer 1: Tight TPO layer (approximately 130 μm layer thickness)
[0168] Layer 2: Tight TPO layer (approximately 130 μm layer thickness)
[0169] Layer 3: Tight TPO layer (approximately 130 μm layer thickness)
[0170] Layer 4: Polypropylene foam (3500 to 4000 μm layer thickness; ground foam)
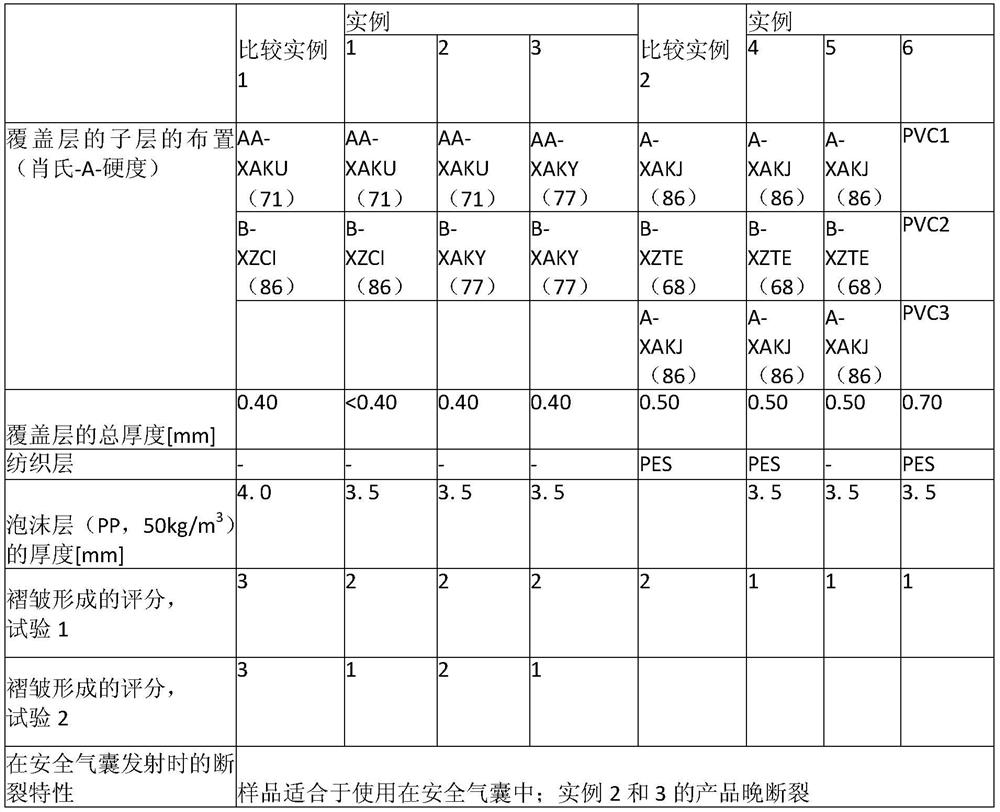
[0171] Layers 1 to 3 correspond to layers AA-B in Table 1.
[0172] Composite structures can be fabricated according to a method having the following steps:
[0173] (i) Lamination of TPO layer and thermal lamination to PP-foam
[0174] (ii) Paint the upper side and if necessary the back side
[0175] (iii) Embossing to form particles
[0176] (iv) Paint the back side if necessary
[0177] An alternative method includes the following steps:
[0178] (i) Pressed TPO layer
[0179] (ii) Paint the upper side
...
example 4
[0183] The artificial leather of example 4 has following structure:
[0184] Layer 0: lacquer based on silicone-containing aliphatic polyurethane, about 5 μm thick Layer 1: Tight TPO layer (layer thickness about 130 μm)
[0185] Layer 2: Tight TPO layer (approximately 130 μm layer thickness)
[0186] Layer 3: Tight TPO layer (approximately 130 μm layer thickness)
[0187] Middle layer: hot melt adhesive material, 40μm thick
[0188] Layer 4: 100% polyester textile, 400 to 600 μm thick
[0189] Middle layer: hot melt adhesive material, 40μm thick
[0190] Layer 5: Polypropylene foam (3500 to 4000 μm layer thickness, ground foam)
[0191] Layers 1 to 3 correspond to layers A-B-A in Table 1.
[0192] Composite structures can be fabricated according to a method having the following steps:
[0193] (i) Pressed TPO layer
[0194] (ii) Paint the upper side
[0195] (iii) Hot-melt bonding of TPO layer and polypropylene foam to polyester textile
[0196] (iv) embossing to form...
example 6
[0204] The artificial leather of example 6 has following structure:
[0205] Layer 0: lacquer based on silicone-containing aliphatic polyurethane, about 5 μm thick
[0206] Layer 1: Tight PVC layer (approximately 220 μm layer thickness) (PVC1)
[0207] Layer 2: PVC foam layer (approximately 430 μm layer thickness) (PVC2)
[0208] Layer 3: PVC-based tight adhesive material layer (approx. 40 μm layer thickness) (PVC3)
[0209] Layer 4: 100% polyester textile, 400 to 600 μm thick
[0210] Middle layer: hot melt adhesive material, 40μm thick
[0211] Layer 5: Polypropylene foam (3500 to 4000 μm layer thickness; ground foam)
[0212] PVC3 is used as the adhesive material layer.
[0213] Layers 1 to 3 correspond to layers PVC1 to PVC3 in Table 1.
[0214] Composite structures can be fabricated according to a method having the following steps:
[0215] (i) PVC layer coated and laminated with polyester textile
[0216] (ii) Paint the upper side
[0217] (iii) Embossing to for...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com