Engineered fibroblast growth factor variants as receptor antagonists
A growth factor, human fibroblast technology, applied in the field of polypeptide variants, can solve problems such as lack of easy-to-adapt methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
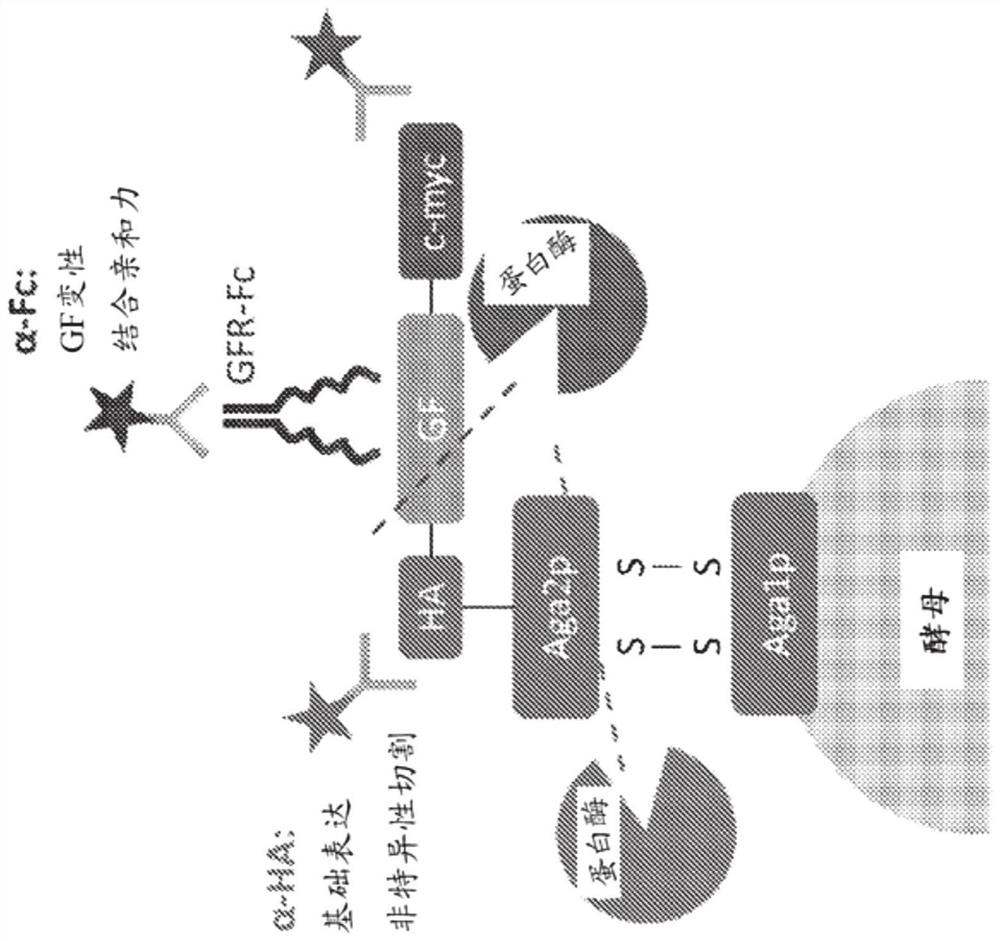
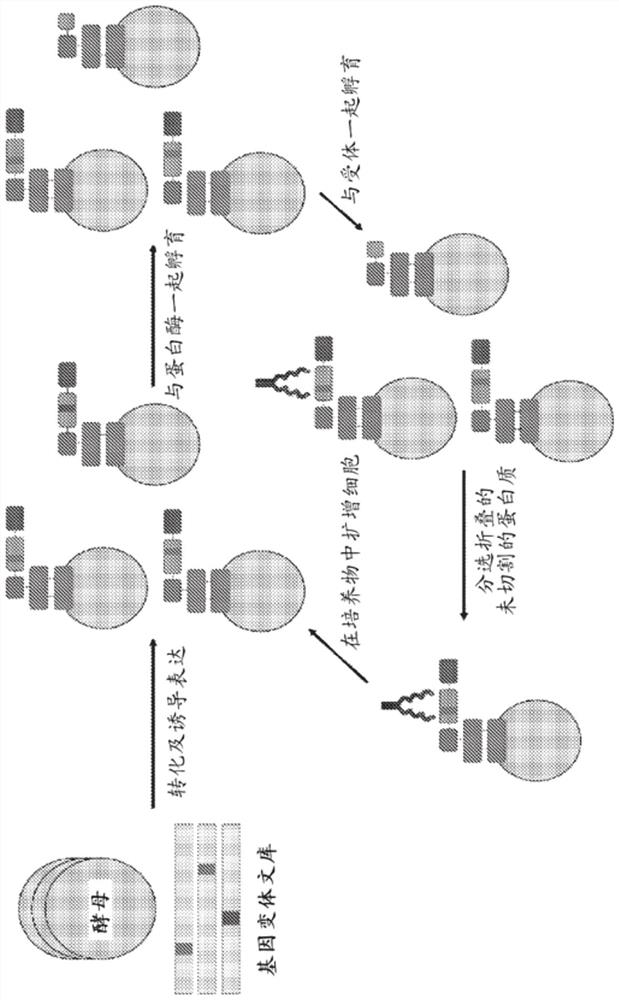
[0348] Example 1: High throughput screening method for engineering proteolytically stable growth factors
[0349] Summary
[0350] Growth factors are an important class of regulatory proteins with great potential for development as therapeutic molecules for regenerative medicine and cancer therapy. However, the activity and efficacy of growth factors as therapeutic molecules are greatly limited due to their poor thermostability and proteolytic stability. Although many methods have been developed to engineer growth factors with increased thermostability, there is a lack of attention and method development to develop engineered growth factors with increased proteolytic stability. Proteases such as plasmin, elastase, uPA, cathepsins and MMPs play key roles in extracellular matrix degradation and signal transduction, especially in wound healing and tumor formation. These proteases are also reported to degrade growth factors in general. In this work, a general method for enginee...
Embodiment 2
[0386] Example 2: Engineered Proteolytically Stabilized Fibroblast Growth Factor
[0387] Summary
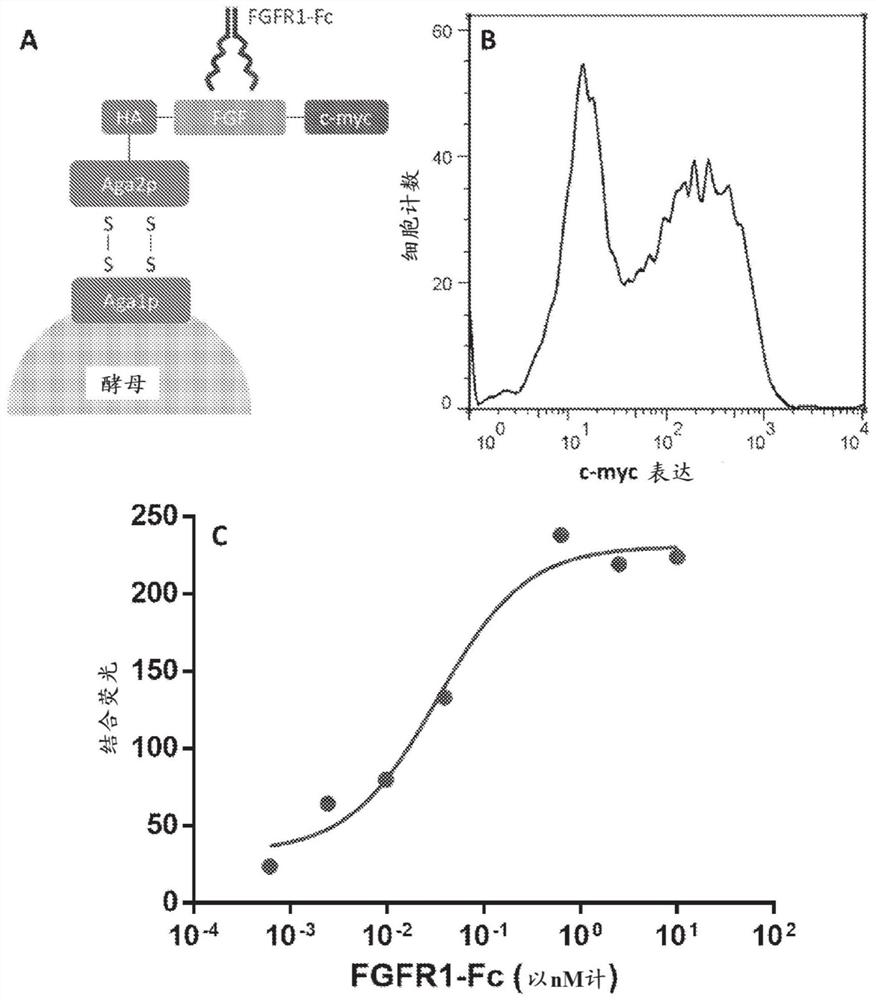
[0388] FGF1 plays an important role in cell differentiation and induction of angiogenesis during wound healing, tissue regeneration, tumor formation and other angiogenesis-dependent diseases. Therefore, FGF1-based agonists and antagonists may have important applications in cell culture and protein therapy. However, FGF1 has been reported to exhibit sensitivity to degradation when exposed to proteases in culture. Its poor proteolytic stability may hamper their activity and efficacy in cell culture or when developed as therapeutic molecules. In this example, FGF1 peptides were engineered for proteolytic stability using the yeast display-based screening method described in Example 1. A gating strategy for selection of proteolytically stable FGFs was explored and successfully identified characterization candidates.
[0389] introduction
[0390] Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) i...
Embodiment 3
[0429]Example 3: Characterization of Proteolytically Stabilized Fibroblast Growth Factor
[0430] Summary
[0431] Proteolytic stability can play an important role in enhancing the efficacy of labile growth factors such as FGF1. Studies have shown that FGF1 is rapidly degraded in culture, partly due to proteases seen in serum or expressed by cells. In Example 2, engineering of FGF1 for increased proteolytic stability is described. Screening of the FGF1 random mutagenesis library for FGF1 mutants exhibiting improved proteolytic stability on surface yeast. In this example, recombinant expression of soluble FGF1 and characterization of mutations identified by high-throughput screening to improve proteolytic stability in FGF1 are described. FGF1 and FGF2 were recombinantly expressed and purified in Escherichia coli expression system. The FGF1 BS4M1(D28N, L131R) and L131R mutants have been shown to be more proteolytically stable compared to wild-type FGF1, and the FGF1 L131R mu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com