Costimulatory signal domain of chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
A chimeric antigen receptor and co-stimulatory signal technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering and biological immunotherapy, can solve the problems of increased cytokine secretion, uneven curative effect, limited anti-tumor activity, etc., and achieve the effect of high lethality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1 Obtaining the CAR gene whose full-length antigen is HER2 by PCR
[0052] (1) The first step, gene synthesis: synthesize the full-length RD-1(TM+cytoplasmic)-CD3ζ fragment.
[0053] (2) In the second step, primers were synthesized, and the (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge)-(RD-1TM+Cytoplasmic)-(CD3ζ) fusion fragment was obtained by overlapping PCR method, which specifically included the following two steps:
[0054] (2.1) Use primers F1 and R1 to amplify (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge); use F2 and R2 to amplify (RD-1TM+Cytoplasmic)-(CD3ζ).
[0055] (2.2) Using (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge) and (RD-1TM+Cytoplasmic)-(CD3ζ) as templates and F1 and R2 as primers, the full-length CAR gene was obtained by PCR.
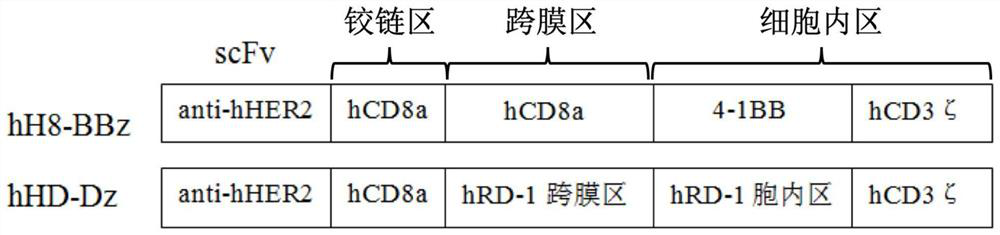
[0056] The amino acid sequence of the synthesized (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge)-(RD-1TM+Cytoplasmic)-(CD3ζ) is SEQ NO 5.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2 Construction of recombinant plasmid vector of CAR whose antigen is HER2
[0058] (1) The first step, gene synthesis: synthesize the full-length RD-1(TM+cytoplasmic)-CD3ζ fragment.
[0059] (2) The second step is to design primers and use the overlapping PCR method to obtain (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge)-(RD-1TM+Cytoplasmic)-(CD3ζ) fusion fragment, which specifically includes the following two steps:
[0060] (2.1) Use primers F1 and R1 to amplify (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge); use F2 and R2 to amplify (RD-1TM+Cytoplasmic)-(CD3ζ);
[0061] (2.2) Using (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge) and (RD-1TM+Cytoplasmic)-(CD3ζ) as templates and F1 and R2 as primers, the full-length CAR gene was obtained by PCR.
[0062] (3) Using Mlu I and Spe I as restriction sites, connect the CAR gene synthesized through the above steps and the PCLK vector to obtain the CAR-PCLK plasmid vector.
Embodiment 3
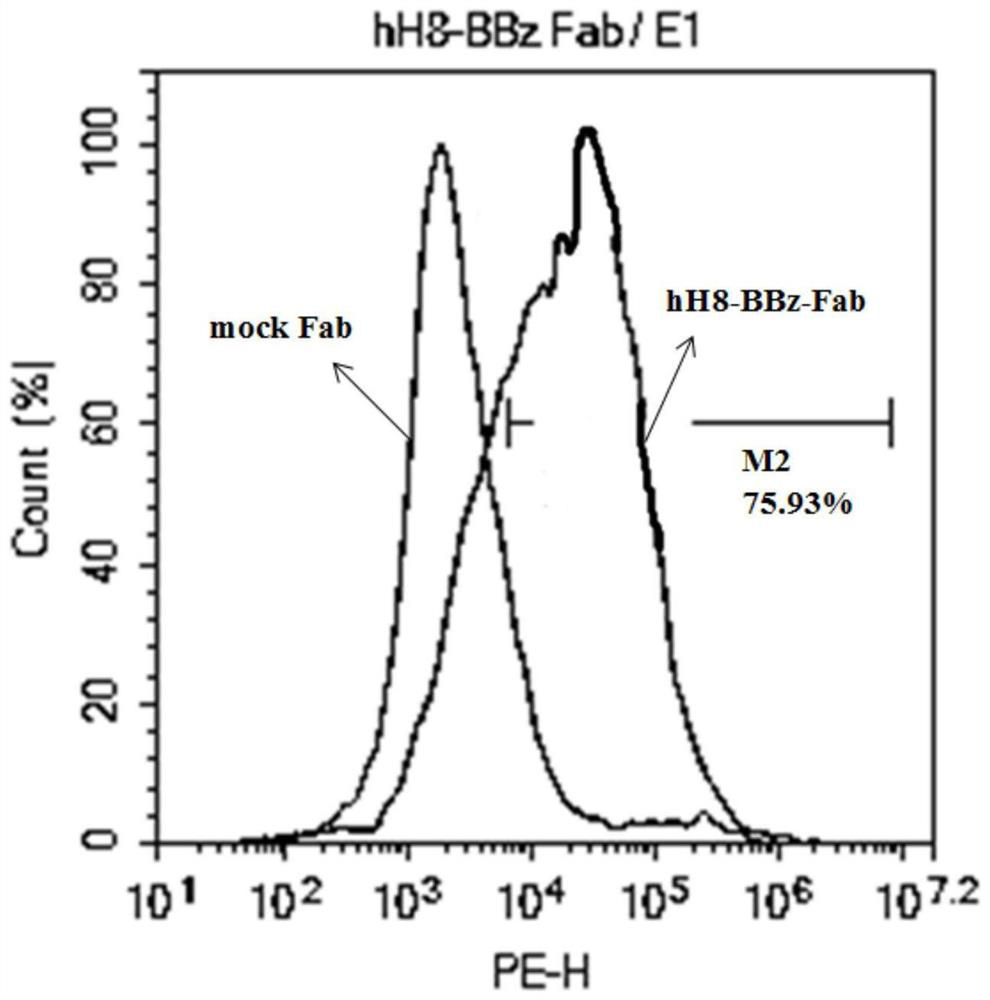
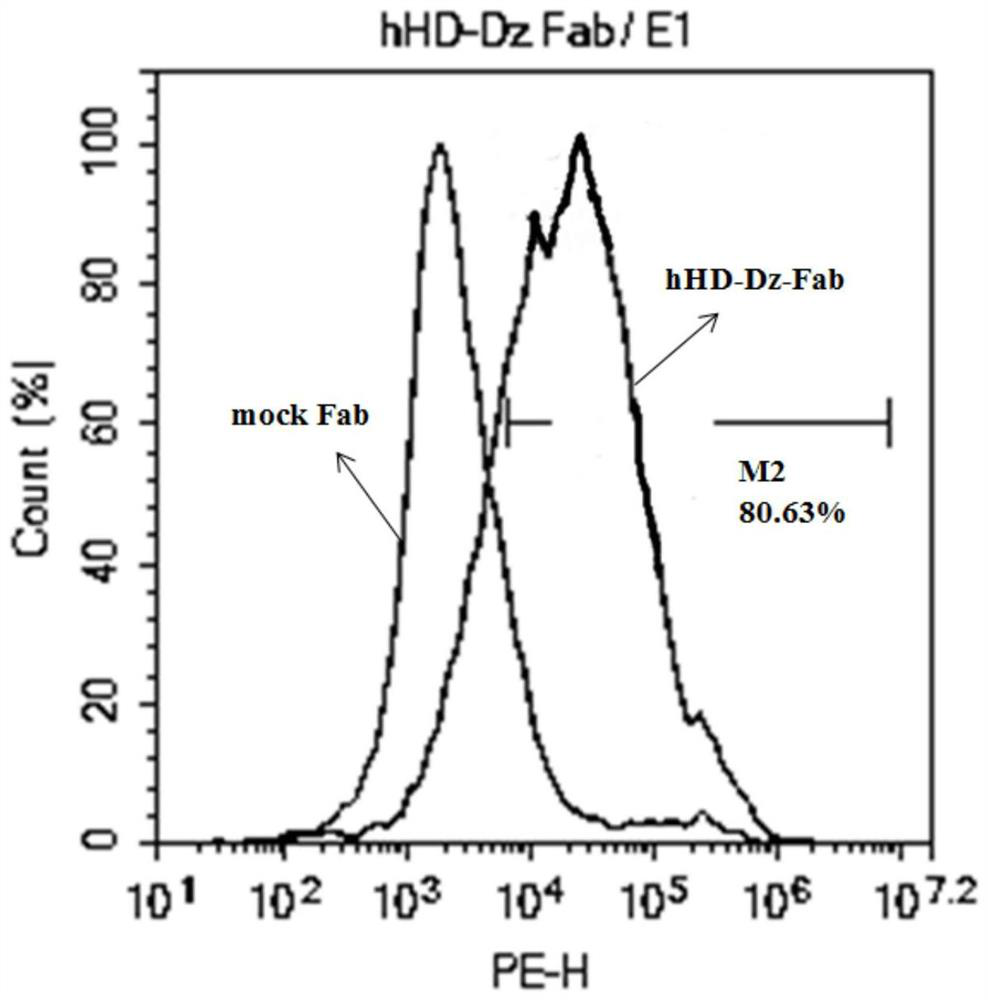
[0063] Example 3 Viral transfection of T lymphocytes and detection of target gene expression
[0064] (1) The new second-generation CAR gene (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge)-(RD-1TM+Cytoplasmic)-(CD3ζ) with chimeric antigen receptor gene (schematic diagram as shown in figure 1 ), traditional second-generation CAR gene (anti-HER2 scFV)-(CD8αhinge+TM)-(4-1BB)-(CD3ζ) (schematic diagram as figure 1 ) into the lentiviral vector PCLK, and co-transfected T cells with two helper vectors psPAX2 and pMD2.G, respectively packaged to obtain virus particles, and obtained high-concentration lentiviral vectors after centrifugation and concentration.
[0065] (2) Lymphocytes were separated by density gradient centrifugation, and lymphocytes were stimulated with CD3 antibody (1ug / ml) and IL-2 (100IU / ml). One day later, the lymphocytes were collected for virus transfection, the lymphocytes were cultured for 48 hours, and the transfected lymphocytes were collected.
[0066] (3) The collected lymph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com