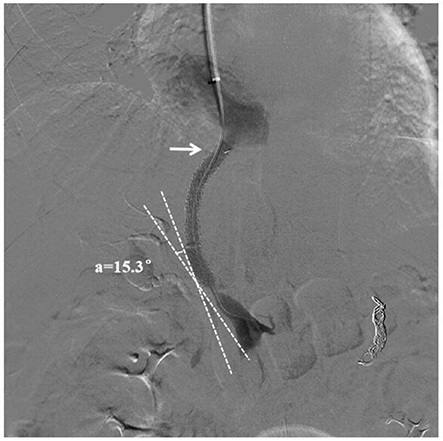
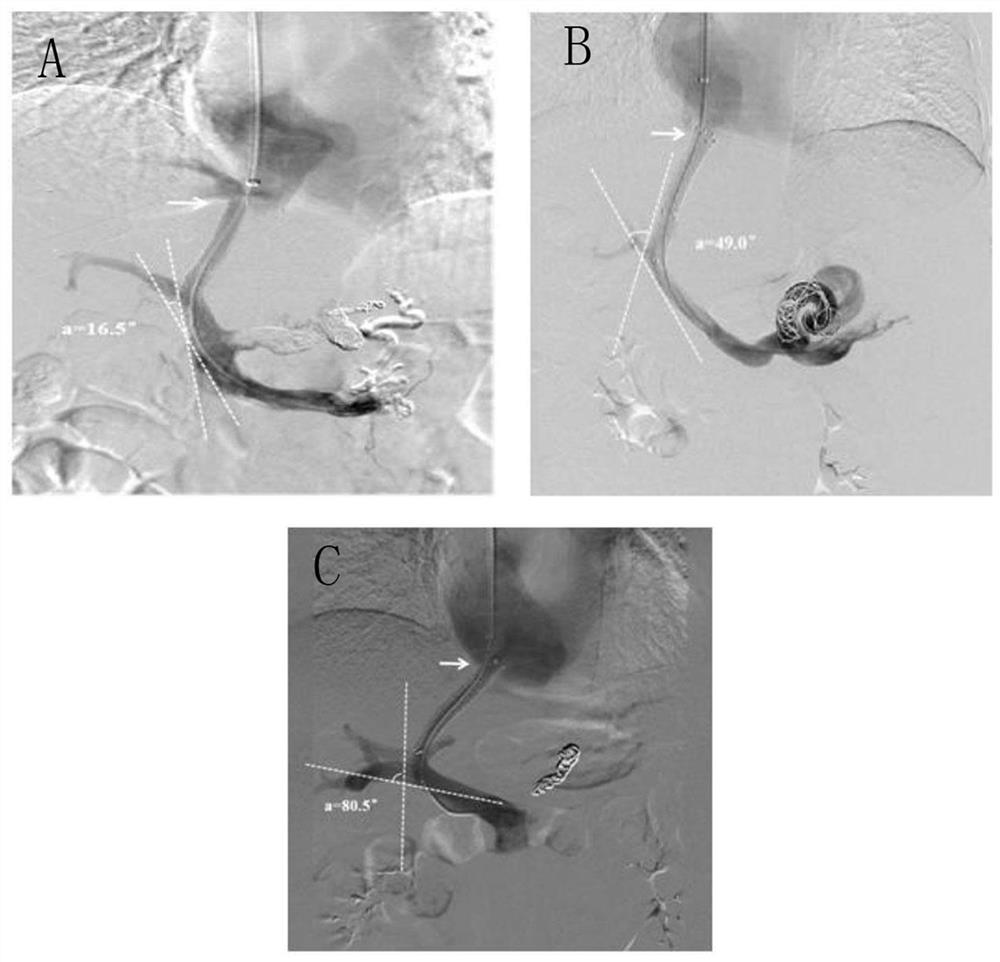
A kit for predicting stent restenosis after tips in patients with liver cirrhosis
A stent restenosis and kit technology, applied in the field of medicine and biology, can solve problems such as stenosis, and achieve the effects of high consistency, good calibration and high consistency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Example 1: Sample collection and sample processing
[0069] (1) A total of 355 patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis who received TIPS treatment in the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University from January 2012 to January 2020 were included. Inclusion criteria: 1) patients with clinically definite diagnosis of hepatitis B cirrhosis; 2) combined with portal hypertension; 3) received TIPS surgery; 4) TIPS stents were a single Viatorr stent or bare stent combined with Fluency stent. Exclusion criteria: 1) liver cirrhosis caused by other viral hepatitis, autoimmunity, alcohol and other causes; 2) patients with malignant tumors in the liver and other parts; 3) with cavernous degeneration of portal vein; 4) with other severe systemic diseases Diseases (organ failure, serious infection, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, etc.); 5) Those with less than 1 year follow-up or incomplete disease data.
[0070] (2) Collect the demographic data (sex, age, diabetes me...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2: Screening of independent factors associated with stent restenosis after TIPS in patients with liver cirrhosis
[0075] (1) Univariate Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the independent factors that may be associated with stent restenosis after TIPS in patients with liver cirrhosis:
[0076] In the modeling group, SPSS 21.0 statistical software was used to conduct univariate Logistic regression analysis on clinical factors that may be associated with stent restenosis after TIPS in patients with liver cirrhosis. predicted value.
[0077] Univariate Logistic regression analysis showed that the risk factors associated with stent restenosis after TIPS were: age, diabetes, portal vein thrombosis, history of splenectomy, platelet count, INR, portal vein puncture location and stent location (p 0.05) (see Table 1 for the results of univariate Logistic regression analysis).
[0078] Table 1 Univariate Logistic regression analysis of stent restenosis afte...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Example 3: Establishment of a prediction model for stent restenosis after TIPS in patients with liver cirrhosis
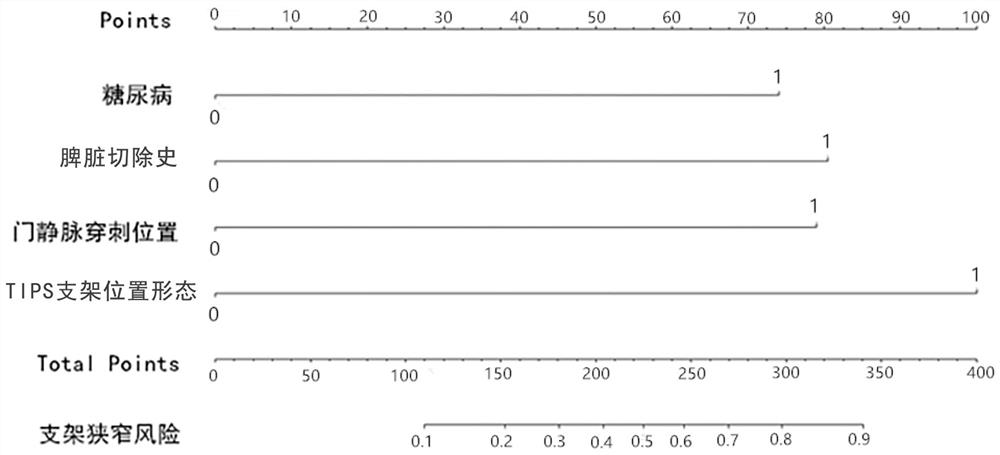
[0086] The independent factors associated with stent restenosis after TIPS in patients with liver cirrhosis obtained by multivariate Logistic regression analysis were assigned, and the assignments are shown in Table 3.
[0087] Table 3 Assignment of independent prognostic factors associated with stent restenosis after TIPS in patients with cirrhosis
[0088] variable assign TIPS stent position and shape Good = 0, Bad = 1 Portal vein puncture site Left branch = 0, right branch = 1 history of splenectomy no = 0, yes = 1 diabetes no = 0, yes = 1
[0089] According to the results of multivariate Logistic regression analysis, the risk function expression of each factor was established based on the β value of the four screened independent factors related to stent restenosis after TIPS in patients with liver cirrhosis. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com