Co-library-building method capable of distinguishing DNA and RNA sources
A source and library technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of inability to distinguish whether the sequencing results come from DNA or RNA, the inability to distinguish the specific source of sequencing information, and increasing the number of unknown pathogens The difficulty of detection and other issues, to achieve the effect of reducing gene fusion and gene mutation events, improving connection efficiency, and reducing self-connection rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1: Establishment of DDRC-seq process
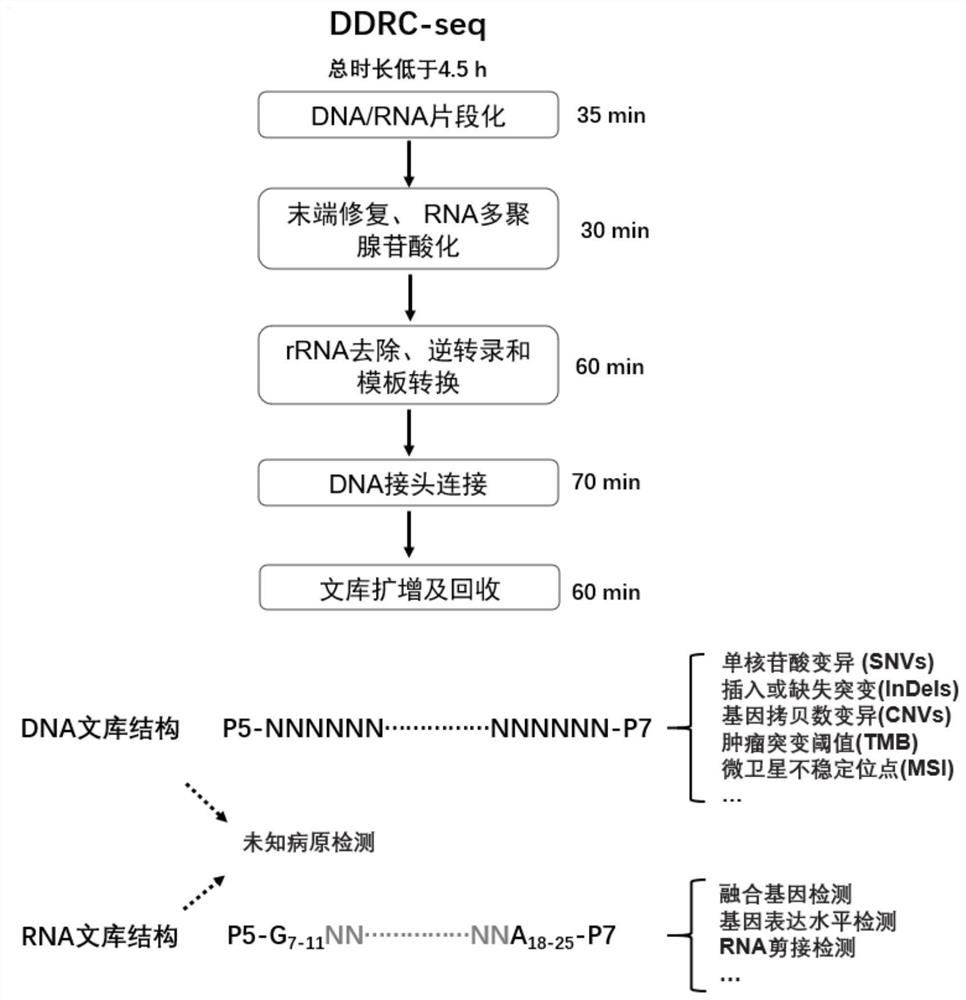
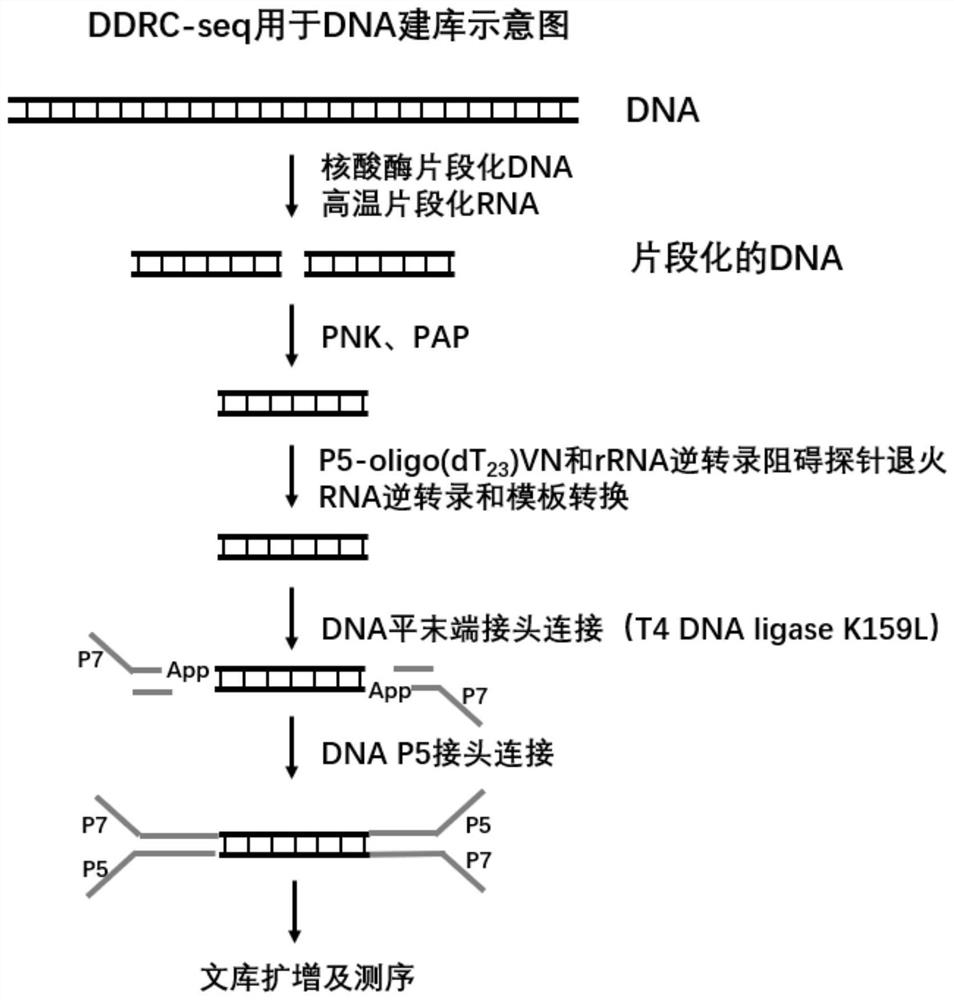
[0066] In this example, we set up the process of DDRC-seq, the flow chart is shown in figure 1 and figure 2 . The specific method is as follows:
[0067] 1) DNA and RNA fragmentation:
[0068] Table 2
[0069] components Dosage DNA & RNA 100ng fragmentation buffer 4μL DSN (Evrogen) 2μL Total 17μL
[0070] Fragmentation buffer: 200mM Tris-HCl, 300mM KCl, 20mM MgCl 2 , pH 8.3.
[0071] React at 37°C for 20 minutes, react at 85°C for 15 minutes, and store at 4°C.
[0072] 2) RNA end repair, polyadenylation
[0073] table 3
[0074] components Dosage The above reaction system 17μL T4 PNK (Yeasen, 12902) 1μL E.coli Poly(A) Polymerase(NEB,M0276S) 2μL Total 20 μL
[0075] React at 37°C for 30 minutes.
[0076] 3) rRNA removal, reverse transcription and template switching
[0077] Table 4
[0078] components Dosage ...
Embodiment 2
[0104] Example 2: Effect of DDRC-seq on library construction with different DNA inputs
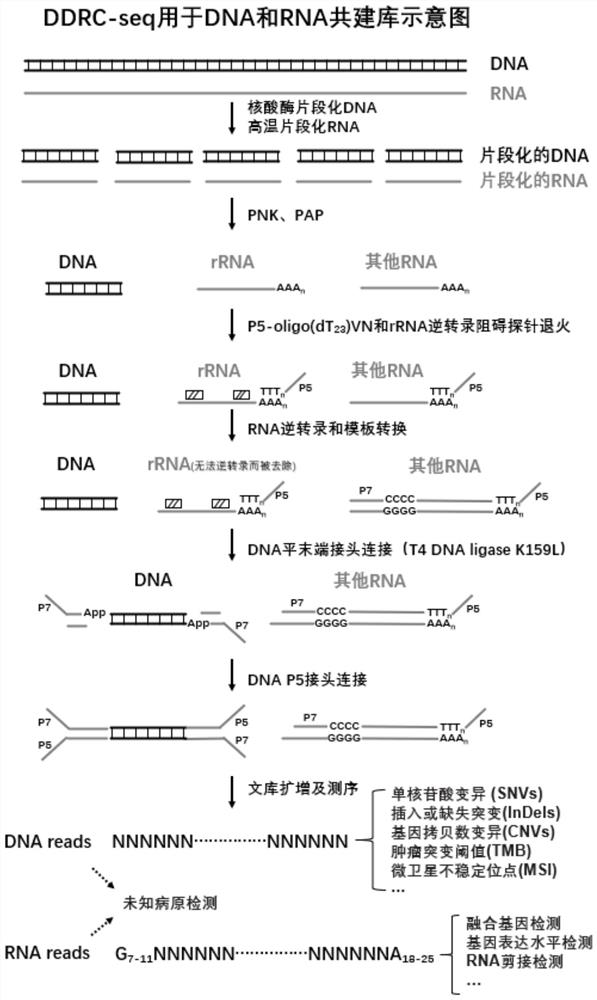
[0105] In this example, we verified the library construction effect of DDRC-seq under the condition of calf thymus 0.1ng-100ng gDNA input. The experimental procedure is shown in Example 1. The schematic diagram is shown in image 3 , see Table 9 for the number of PCR cycles and library yield, and see Table 9 for the distribution of library sizes. Figure 4 , for the analysis of sequencing results, see Figure 5-7 .
[0106] Table 9
[0107]
[0108] The results are shown in Table 9 and Figure 4-5 As shown, DDRC-seq has good library yield and library size for 0.01-100ng calf gDNA input. like Image 6 and Figure 7 , in the DNA sequencing data, the calf genome alignment rate of the library sequencing data of 100ng DNA input amount reaches 99.64%, among which there is a co-constructed library RNA structure (G 7-11 NN…NNA 18-25 ) data accounted for only 0.007%; the comparison rate ...
Embodiment 3
[0109] Example 3: Effect of DDRC-seq on library construction with different RNA inputs
[0110] In this example, we verified the library construction effect of DDRC-seq under the condition of HEK293F 0.1ng-1000ng RNA input. The experimental procedure is the same as that in Example 1. The schematic diagram is shown in Figure 9 , see Table 10 for the number of PCR cycles and library yield, see Table 10 for library size distribution Figure 10 , for the analysis of sequencing results, see Figure 11-16 .
[0111] Table 10
[0112]
[0113] The results are shown in Table 10 and Figure 10-11 As shown, DDRC-seq has good library yield and library size for 0.1-1000ng human RNA input. like Figure 11-Figure 15 , in the DNA sequencing data, the human transcriptome alignment rate of the library sequencing data of 1000ng RNA input amount reaches 99.34%, among which there is a co-constructed library RNA structure (G 7-11 NN…NNA 18-25 ) data accounted for 99.32%, compared to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com