Method for quantitatively analyzing microplastics in leaf vegetables
A quantitative analysis and microplastic technology, applied in the field of quantitative analysis of leafy vegetables pollutants, can solve the problems of oxidative damage, no quantitative analysis of microplastics, and damage to the structure of microplastics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Hydroponics to obtain lettuce rich in microplastics
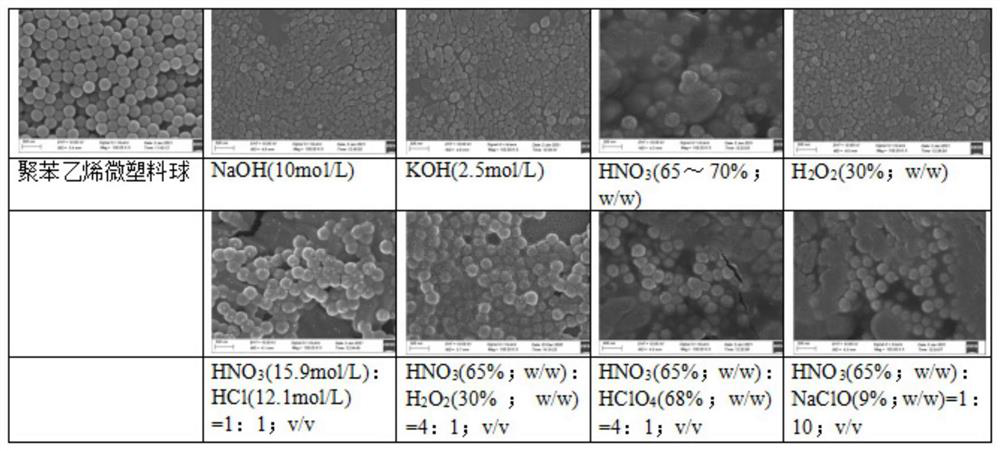
[0032] S1. Selection of microplastics: Polystyrene microplastic balls (microplastics) with a particle size of 0.2 μm purchased from Shanghai Huizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. were used as test materials. The material was wrapped with green fluorescent light at the center of the ball. The dye is not easily destroyed and quenched.
[0033] S2. Obtaining lettuce enriched with fluorescent microplastics: use 300mL Hoagland's solution as the hydroponic solution, carry out hydroponics to lettuce, and add polystyrene microplastic spheres with a concentration of 30mg / L to make Hoagland's The concentration of microplastics in the solution was 20 mg / L, and 6 parallel samples were set up; continuous culture was carried out for 10 days, the light intensity was kept at 15000 lux during the culture process, and the daytime temperature was kept at 22°C, and the nighttime temperature was kept at 16°C. Maintain the growth need...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Quantitative analysis of lettuce microplastics by different digestion agents
[0035] 1. Experimental method:
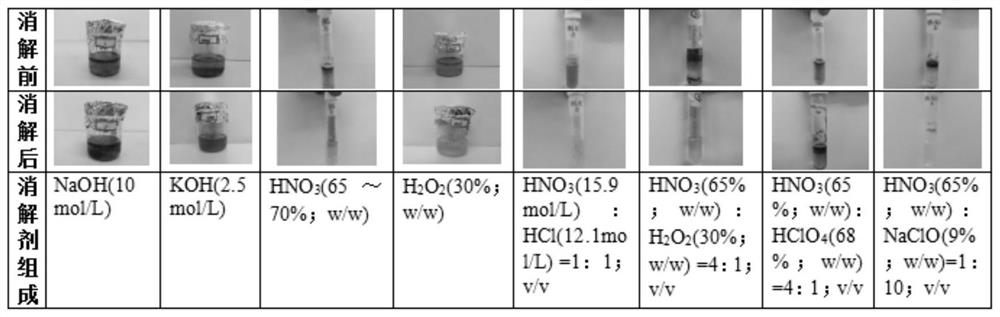
[0036] S1. Put the lettuce after ultrasound and the leaves that fell off during the hydroponics process in an oven at 45°C to dry and grind to obtain 3.2 g of lettuce powder, and then take 10 mg of lettuce powder according to the composition of the digestion agent shown in Table 1 , volume, digestion temperature and digestion time, after mixing lettuce and digestion agent for digestion, the digestion solution was obtained (photographed figure 1 );
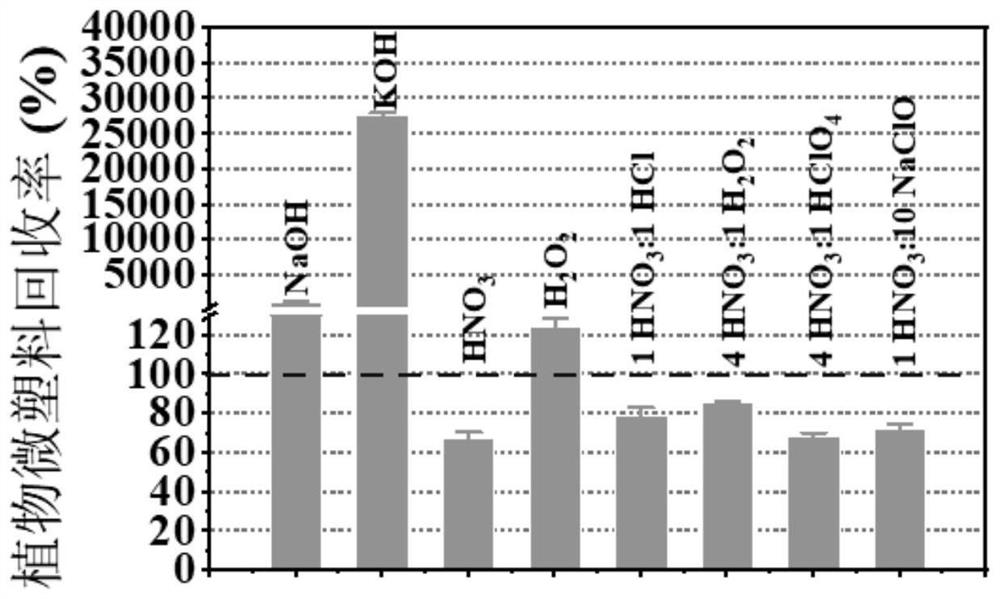
[0037] S2. Measure the fluorescence intensity of the digestion solution at a wavelength of 488nm with a NanoDrop 3300 ultra-micro-volume fluorescence spectrophotometer, and then calculate the concentration C of microplastics in the digestion solution according to the standard curve 2 , further calculation can obtain the content of microplastics in lettuce.
[0038] Table 1
[0039]
[0040] 2. Experi...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3 A method for quantitative analysis of microplastics in lettuce
[0050] 1. Experimental method
[0051] S1. Put the ultrasonicated lettuce and the leaves that fell off during the hydroponics process in an oven at 45°C to dry and pulverize to obtain 3.2g of lettuce powder, then take 10mg of lettuce powder and mix it with 4mL of digestion agent at 50°C for digestion After 4h, the digestion solution was obtained;
[0052] S2. Measure the fluorescence intensity of the digestion solution at a wavelength of 488nm with a NanoDrop 3300 ultra-trace fluorescence spectrophotometer, then calculate the concentration of microplastics in the digestion solution according to the standard curve, and further calculate the content of microplastics in lettuce;
[0053] Wherein, the digestion agent consists of H 2 o 2 Aqueous solution and HNO 3 Aqueous solution composition; The HNO 3 The concentration of the aqueous solution is 65% (w / w), H 2 o 2 The concentration of the aqu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com