A method for simultaneous identification of embryonic chromosomal structural abnormalities and disease-causing gene carrier status
A technology for chromosomal abnormalities and disease-causing genes, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, genomics, microbial measurement/testing, etc. The effects of eliminating potential reproductive barriers, improving health levels, and avoiding technical barriers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0139] Example 1: Blastocyst culture, biopsy and whole genome amplification method
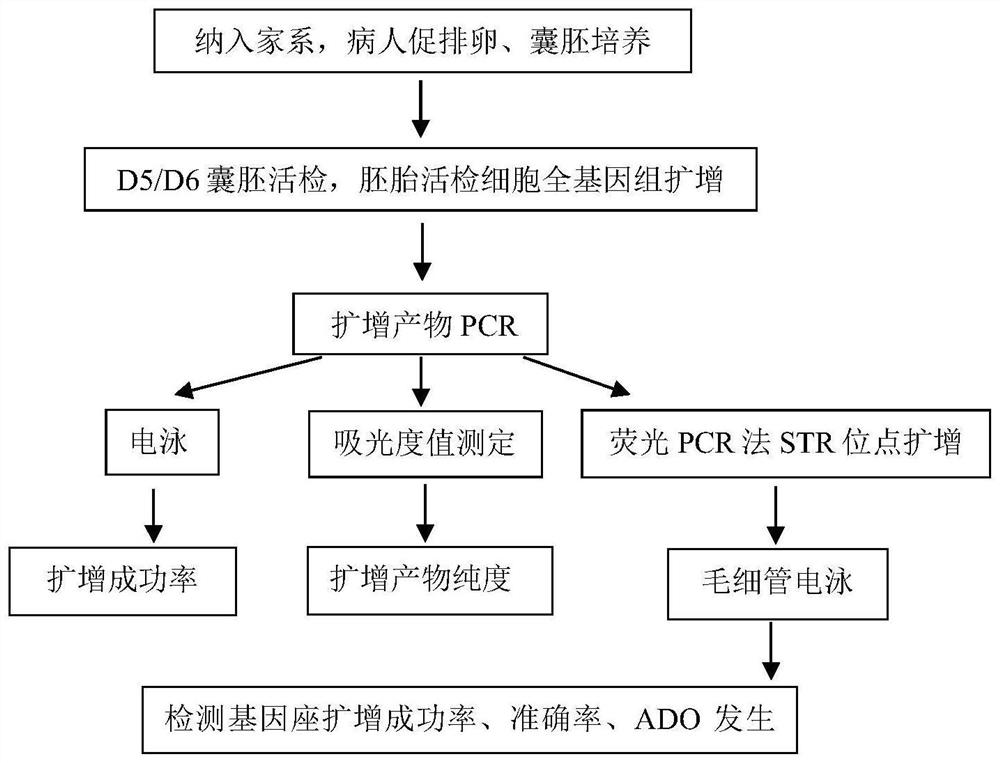
[0140] After the patient undergoes ovulation induction, intracytoplasmic sperm injection, and blastocyst biopsy, the biopsy cells are placed in a PCR tube containing alkaline denaturing buffer (KOH) for cell lysis, and then the whole genome is amplified, and the blastocyst Culture and biopsy were carried out by clinical routine methods. Genomic DNA from the pg level was amplified to at least the ng level for subsequent experiments. Use fluorescent PCR and capillary electrophoresis to test the DNA amplification efficiency. For details, see figure 1 .
[0141] (1) Single-cell whole-genome amplification by MDA method
[0142] 1. Prepare two 0.2mL imported EP tubes, add 2.5μL and 4μL water respectively, and use them as volume control tubes for later use.
[0143] 2. Centrifuge the sample for 1 min, check the liquid volume, compare it with the control tube, take a photo and save it, and record ...
Embodiment 2
[0211] Example 2: Building a detection analysis model
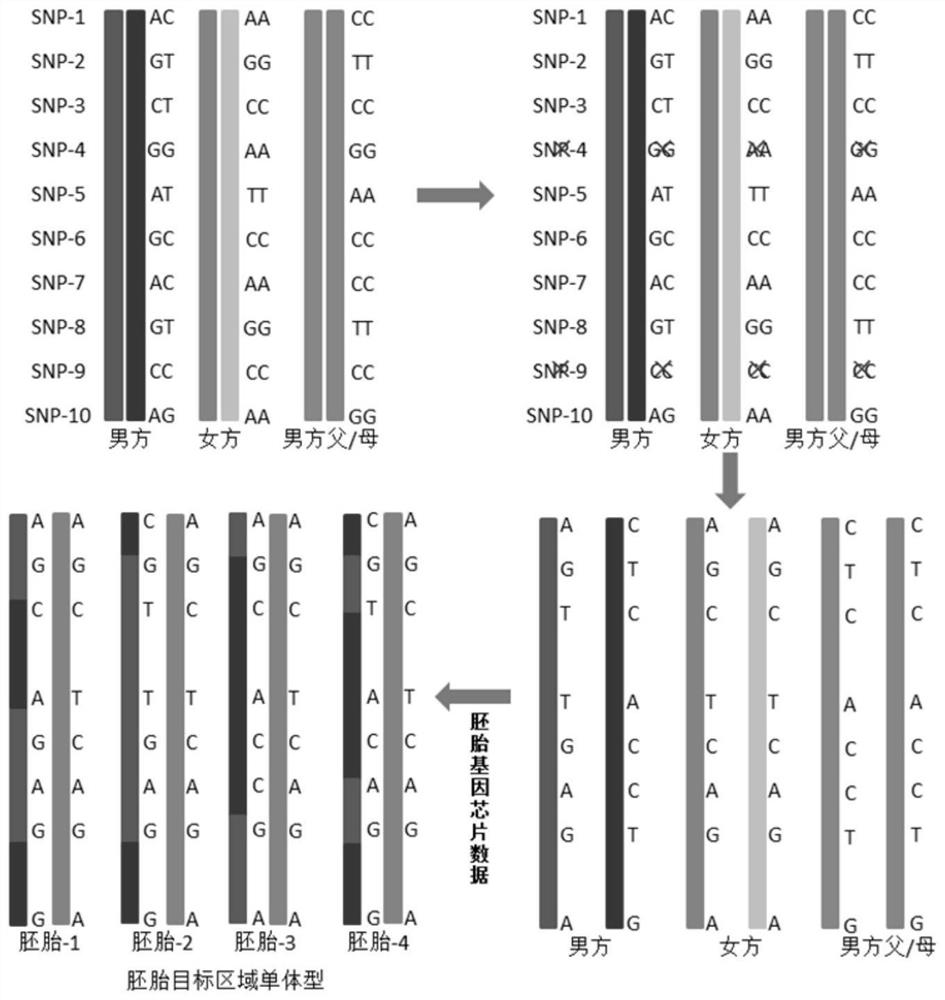
[0212] Perform genome-wide SNP typing on family samples, define information SNP selection criteria, perform haplotype linkage analysis on information SNP genetic markers, and distinguish different haplotypes of disease-causing gene alleles and homologous chromosomes in patients through haplotype analysis , through linkage analysis to clarify the haplotypes of carrying disease-causing genes and non-carrying disease-causing genes, clarifying the haplotypes of structurally abnormal chromosomes and structurally normal chromosomes, and constructing an embryo detection and analysis model.
[0213] Substitute the SNP data of the whole genome of the embryo to be tested into the detection and analysis model, analyze the embryo chromosome aneuploidy through the SNP allele frequency (BAllele Frequency), determine the haplotype of the embryo through the detection and analysis model, and analyze whether the embryo carries the pathogeni...
Embodiment 3
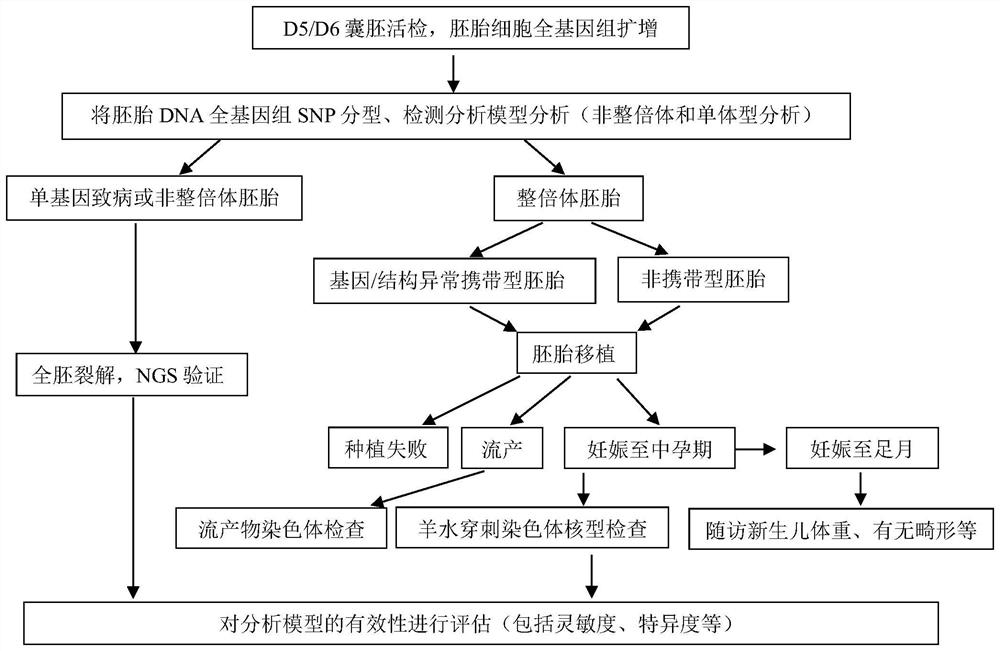
[0229] Example 3: Embryo detection and pregnancy outcome follow-up
[0230] After the analysis of the detection analysis model, the embryo is diagnosed:
[0231] (1) For embryos that only carry the haplotype of the disease-causing gene of one of the couple, the embryo is diagnosed as carrying the disease-causing gene;
[0232] (2) For the embryos carrying the haplotype of the disease-causing gene of both spouses at the same time, it is diagnosed as an abnormal diseased embryo;
[0233] (3) For embryos that do not carry the haplotype of the disease-causing gene of the couple, it is diagnosed as a normal embryo of the disease-causing gene;
[0234] (4) For embryos that do not carry the abnormal haplotype of the couple's chromosome structure, they are diagnosed as embryos with normal chromosome structure;
[0235] (5) For embryos carrying abnormal chromosome structure haplotypes of the couple, it is diagnosed as embryos with abnormal chromosome structure;
[0236] (6) For embr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com