Method for wall breaking treatment of papaya cell wall skeleton structure
A skeleton structure and cell wall technology, applied in the field of wall breaking treatment of papaya cell wall skeleton structure, can solve the problems of low overall utilization rate, low separation efficiency, and inability to directly eat, so as to improve bioavailability, avoid oxidative degradation, The effect of increased bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
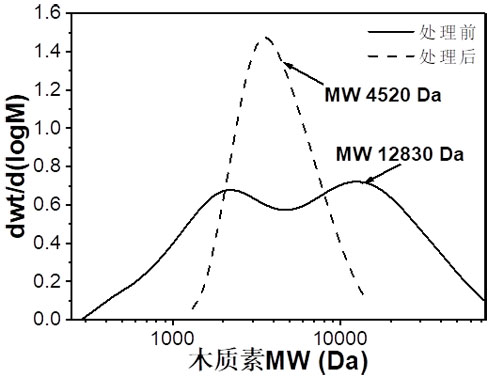
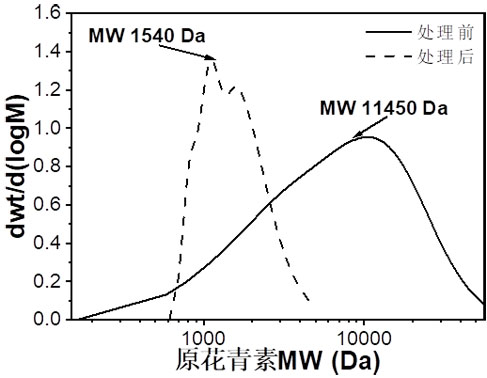
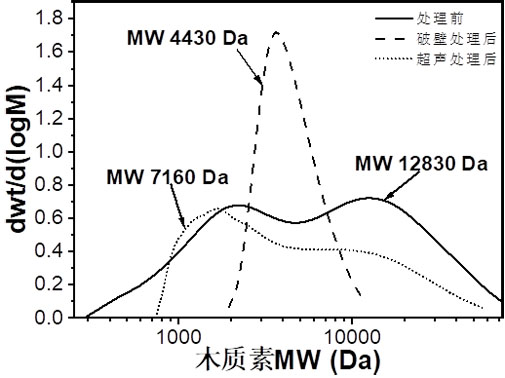
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] After the ripe papaya fruit was washed and deseeded, the fruit was cut into thin slices about 2 mm thick, and the papaya slices were soaked in color-protecting solution (0.5% ascorbic acid + 0.5% citric acid) at room temperature for 30 min; Soak the papaya slices in hot water containing 0.5% sodium D-isoascorbate at 95°C for 5 minutes to inactivate the enzymes, then quickly take them out and put them in cold water to cool. Put the cooled papaya into the seasoning liquid (5% xylitol liquid) and soak for 80 minutes; put the seasoned papaya into the food low-temperature quick-freezing machine, the temperature in the quick-freezing machine reaches below 20°C, and the freezing time is 4 hours; Put the frozen papaya into a vacuum low-temperature food conditioning device for 60 min, the processing temperature is 120°C, the pressure is controlled at -0.085 MPa, and the solvent medium is triglyceride; The pressure was controlled at 0.085 MPa, the centrifuge speed was 300 rpm / min...
Embodiment 2
[0028] After the ripe papaya fruit was washed and deseeded, the fruit was cut into thin slices about 4 mm thick, and the papaya slices were soaked in color-protecting solution (mass concentration: 0.5% ascorbic acid + 0.5% citric acid) at room temperature for 30 min; The soaked papaya slices were scalded in hot water containing 0.5% sodium D-isoascorbate at 90°C for 5 minutes to inactivate the enzyme, and then quickly taken out and placed in cold water to cool. Soak the cooled papaya in seasoning solution (5% isomalt solution) for 90 min. The first treatment method is wall-breaking treatment: put the seasoned papaya into the food low-temperature quick-freezer, the temperature inside the quick-freezer is below 20°C, and the freezing time is 4 hours; put the frozen papaya into the vacuum low-temperature food conditioning device Treat for 90 minutes, the treatment temperature is 100°C, the pressure is controlled at -0.055 MPa, and the solvent medium is triglyceride; a rotary cent...
Embodiment 3
[0031] After the ripe papaya fruit was washed and deseeded, the fruit was cut into thin slices about 3 mm thick, and the papaya slices were soaked in color-protecting solution (0.5% ascorbic acid + 0.5% citric acid) at room temperature for 30 min; The soaked papaya slices were scalded in hot water containing 0.5% sodium D-isoascorbate at 95°C for 4 minutes to inactivate the enzyme, and then quickly taken out and placed in cold water to cool. Put the cooled papaya into the seasoning solution (5% maltodextrin solution) and soak for 70 minutes; put the seasoned papaya into the food low-temperature quick-freezer, the temperature in the quick-freezer is below 20°C, and the freezing time is 4 hours; After freezing, the papaya was put into a vacuum low-temperature food conditioning device for 120 min, the processing temperature was 95°C, the pressure was controlled at 0.050 MPa, and the solvent medium was triglyceride; At 0.090 MPa, the centrifugal speed is 300 rpm / min, and the preci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com