Bio-based 3D printing resin and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing, bio-based technology, applied in the direction of additive processing, can solve the problems of increasing energy consumption and threatening human health, and achieve the effect of overcoming low curing depth, conducive to sustainable development, and excellent thermal and mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
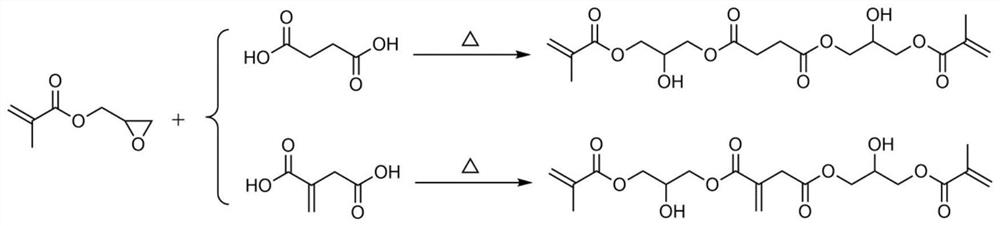
[0046] 1) Preparation of bis(2-hydroxyl-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl) succinate
[0047] 47.2g of succinic acid, 113.7g of glycidyl methacrylate, 1.6g of triphenylphosphine and 0.32g of 4-methoxyphenol were added into the flask, and then the reaction mixture was heated slowly and stirred at 100°C for 5h. Finally, a light yellow liquid was obtained, which was bis(2-hydroxy-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl)succinate. The viscosity at 50°C is 0.42Pa·s.
[0048] 2) Preparation of 3D printing resin
[0049] Bis(2-hydroxy-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl)succinate (100g), phenylbis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide (1g), Stir at 70°C for 20 minutes to mix evenly to obtain a clear liquid, and put the obtained liquid into a 405nm digital light processing (DLP) 3D printer for 3D printing and molding. Put the printed 3D printed structure into a UV curing box to cure for 5 minutes.
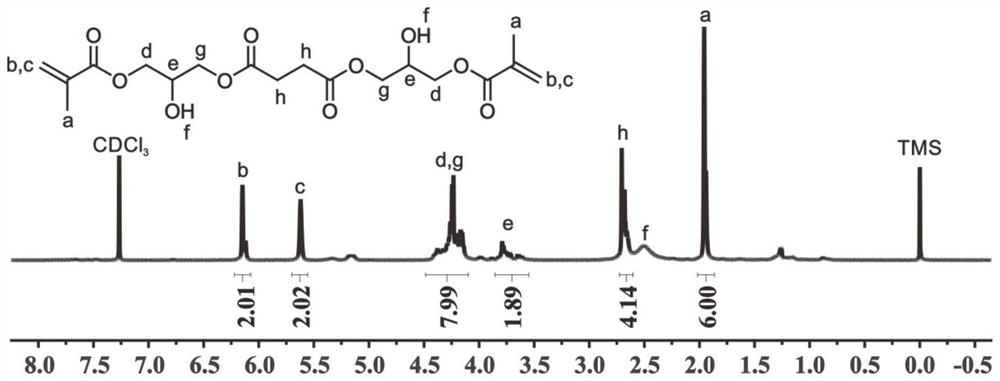
[0050] In this example, the synthetic reaction formula, H NMR spectrum and high-resolution mass spectrum of bis(2...
Embodiment 2
[0057] 1) Preparation of bis(2-hydroxyl-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl) 2-methylene succinate
[0058] 52.0 g of itaconic acid, 113.7 g of glycidyl methacrylate, 1.66 g of triphenylphosphine and 0.33 g of 4-methoxyphenol were added to the flask, and then the reaction mixture was heated slowly and stirred at 100° C. for 5 h. Finally, a pale yellow liquid was obtained, which was bis(2-hydroxy-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl) 2-methylene succinate. The viscosity at 50°C is 0.69Pa·s.
[0059] 2) Preparation of 3D printing resin
[0060] Oxidation of bis(2-hydroxy-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl) 2-methylene succinate (100 g), phenylbis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) Phosphine (1g), stirred at 70°C for 20 minutes and mixed evenly to obtain a clear liquid, which was put into a 405nm digital light processing (DLP) 3D printer for 3D printing. Put the printed 3D printed structure into a UV curing box and cure for 5 minutes.
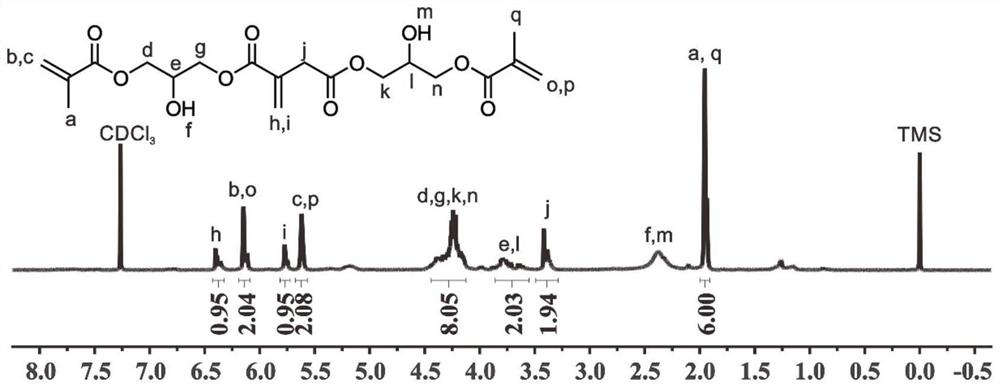
[0061] In this example, the synthetic reaction formula, H NMR spectrum and high-...
Embodiment 3
[0071] 1) Preparation of bis(2-hydroxyl-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl) succinate
[0072] 47.2g of succinic acid, 113.7g of glycidyl methacrylate, 0.8g of triphenylphosphine and 0.16g of 4-methoxyphenol were added into the flask, and then the reaction mixture was heated slowly and stirred at 120°C for 6h. Finally, a light yellow liquid was obtained, which was bis(2-hydroxy-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl)succinate. The viscosity at 50°C is 0.43Pa·s.
[0073] 2) Preparation of 3D printing resin
[0074] Bis(2-hydroxy-3-(methacryloyloxy)propyl)succinate (100g), phenylbis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide (5g), Stir at 50°C for 20 minutes to mix evenly to obtain a clear liquid, and put the obtained liquid into a 405nm digital light processing (DLP) 3D printer for 3D printing. Put the printed 3D printed structure into a UV curing box and cure for 5 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| penetration depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com