Fusion imaging gene, lentivirus expression plasmid thereof, lentivirus, cell, and preparation method and application of cell
A technology for expressing plasmids and lentiviruses, applied to cells, can solve the problems of large length, difficult lentiviral particle transfection, difficulty in obtaining highly active lentiviruses, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
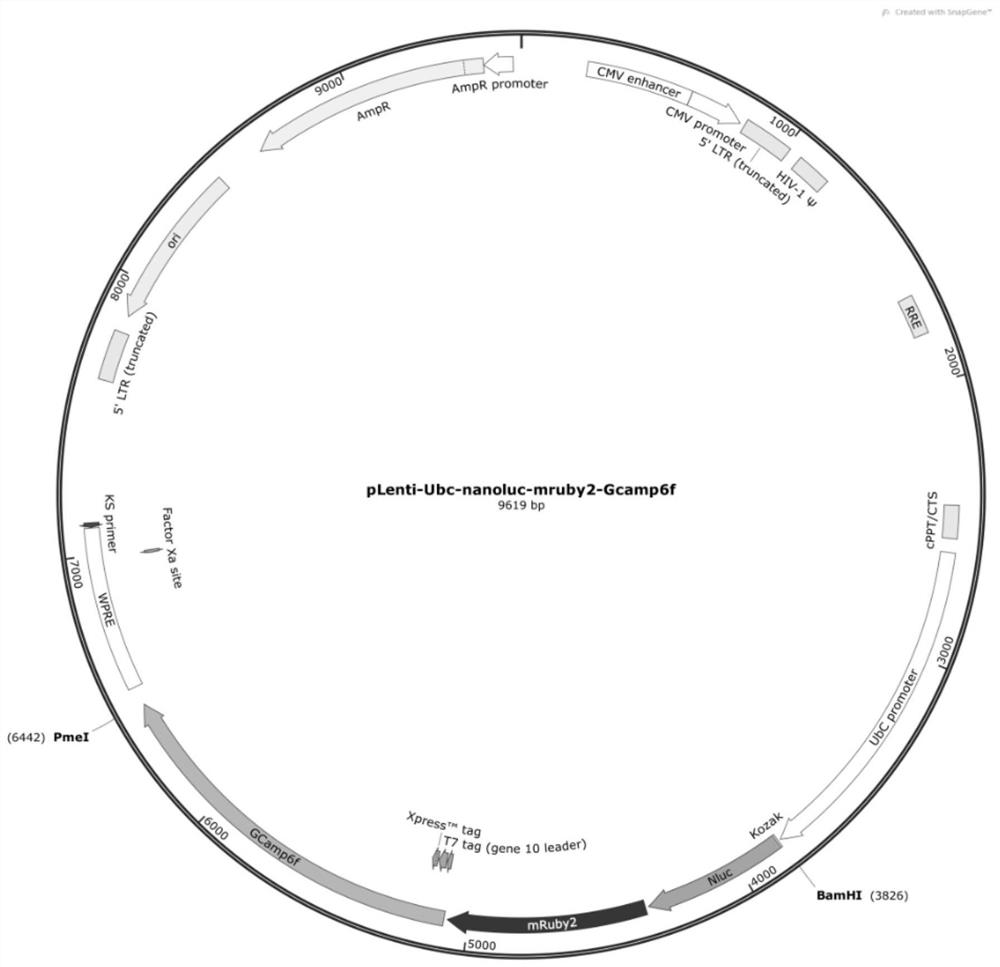
[0093] The sixth aspect of the embodiment of the present invention relates to the preparation method of the above-mentioned lentivirus. The above-mentioned pLenti-Ubc-Nanoluc-mRuby2-Gcamp6f plasmid and the lentivirus packaging plasmid are co-transfected into cells, and the obtained lentivirus carrying the fusion imaging gene is packaged. Include at least the following steps:
[0094] Co-transfect 293T cells with pLenti-Ubc-Nanoluc-mRuby2-Gcamp6f plasmid and lentiviral packaging plasmids PAX2 and pMD2G to obtain lentiviral particles carrying fusion imaging genes;
[0095] Preferably, the mass ratio of the pLenti-Ubc-Nanoluc-mRuby2-Gcamp6f plasmid, the plasmid PAX2, and the plasmid pMD2G3 is 3:2:1.
[0096] The seventh aspect of the embodiment of the present invention relates to the above-mentioned fused imaging gene-marked cells or cells infected by the above-mentioned lentivirus, preferably, the cells are selected from human embryonic stem cells and human pluripotent stem cell...
Embodiment 1
[0098] Example 1: Preparation of lentiviral particles carrying fusion multimodal imaging genes
[0099] (1) Design and construction of fused multimodal imaging genes
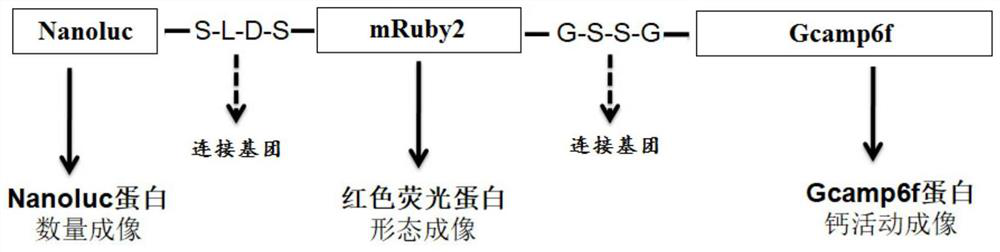
[0100] 1) In order to reduce the impact of fusion expression of multiple imaging genes on protein folding and spatial conformation, and maintain the activity of each protein, the flexible polypeptide sequences S-L-D-S (SEQ ID NO.8) and G-S-S-G (SEQ ID NO.8) and G-S-S-G (SEQ ID NO. ID NO.9) as a linking group (Linker) for connection, such as figure 1 The multi-gene fusion expression design structure diagram shown;
[0101] 2) Obtain Nanoluc gene and mRuby2 gene by gene synthesis, remove the tail stop codon, add BamHI restriction sequence (GGATCC) to the front of Nanoluc gene, and add an S amino acid gene sequence (TCG) and Xhol restriction sequence (CTCGAG) at the end ; Add a SalI restriction sequence (GTCGAC, Xhol isotail enzyme) and an S amino acid (TCG) to the front end of mRuby2 successively; add a G amino ...
Embodiment 2
[0129] Example 2: Application of fused multimodal imaging genes in human pluripotent stem cells
[0130] (1) Multimodal Imaging Gene Markers of Human Embryonic Stem Cells (hESCs)
[0131] Through the conventional lentivirus infection cell method (refer to PLoS One.2013; 8(6):e66369.), use the above-mentioned lentiviral particles carrying fusion gene probes to transfect h1ESC (gifted by Professor Cao Nan of Sun Yat-Sen University, or from ATCC, USA purchased), and the positive clones were isolated and amplified by a patented method (ZL201911133148.1). Experimental results such as Figure 8 shown by Figure 8 It can be seen that the lentiviral particles carrying the fused multimodal imaging gene prepared by the present invention successfully transfect hESC, the expression of mRuby2 can be observed, and the hESC cell line fused with the imaging gene marker is successfully obtained. It is suggested that the lentiviral particles carrying multimodal imaging genes prepared by the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com