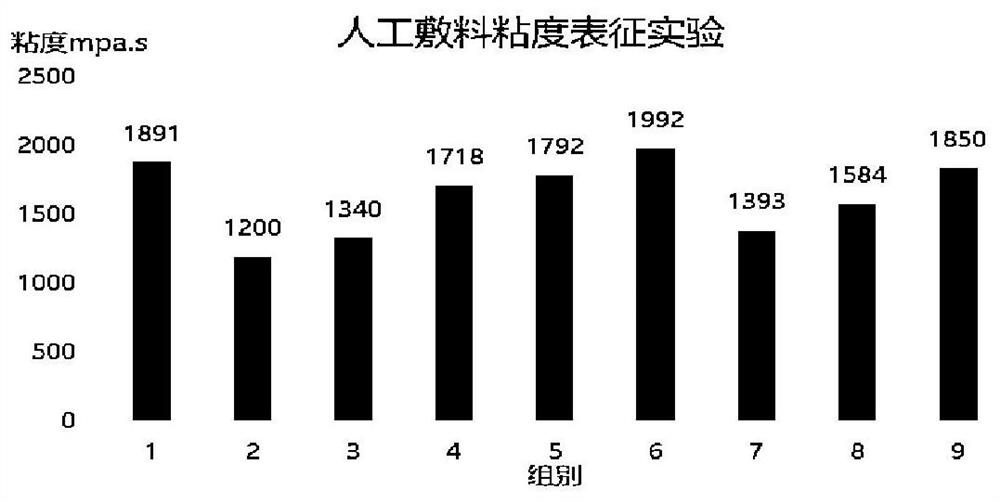
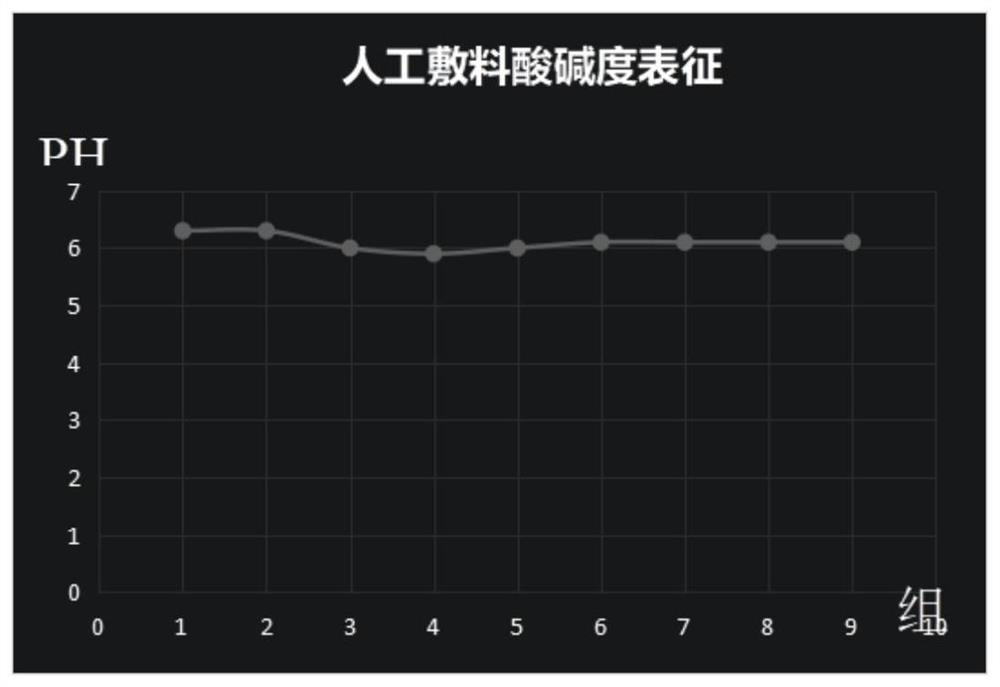
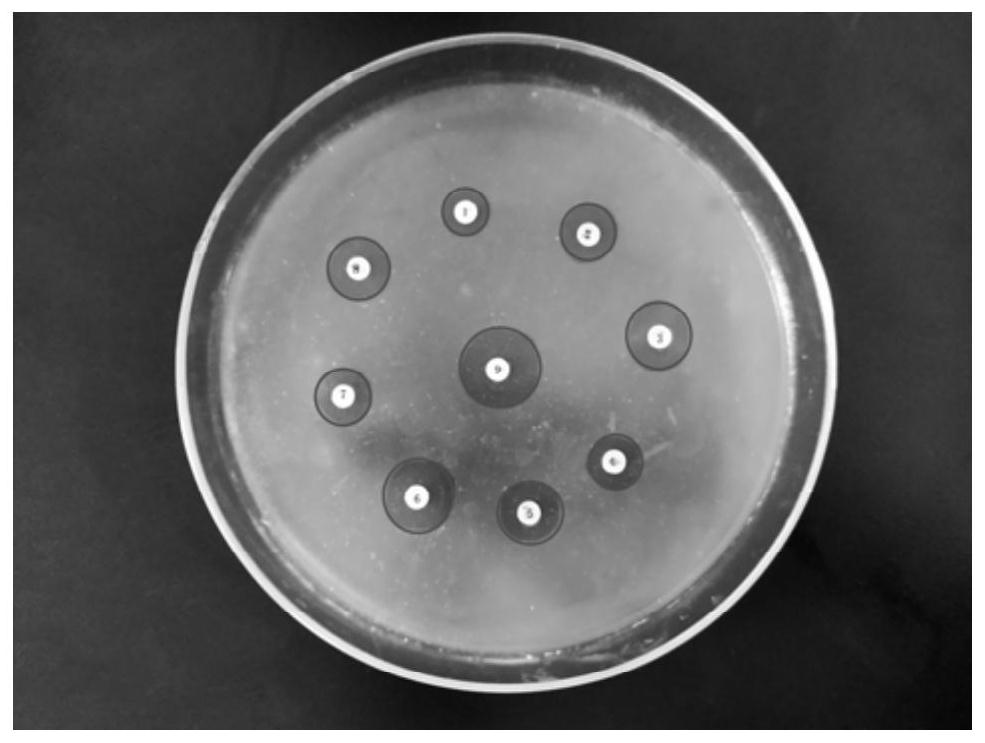
Development of polypeptide antibiotic antibacterial artificial dressing
A polypeptide antibiotic and artificial technology, applied in bandages, medical science, etc., can solve problems such as antibiotic resistance, difficulty in inhibiting bacterial infection, and failure of antibacterial artificial dressings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] 1. Preparation of chitosan matrix: Add 5g of chitosan into 80mL of 2% acetic acid solution, use a stirrer to swell evenly at a speed of 500r / min, after completely dissolving, test the pH value, use 1mol / L NaOH adjusts the pH of the solution to 4.5-5, records the amount of NaOH added to the solution, and stores it in the dark. Record it as solution A.
[0019] 2. Preparation of antimicrobial peptide solution: Dissolve 5 mg of antimicrobial peptide in 18 mL of aqueous solution and configure it into a 5 mg / 18 mL aqueous solution. In subsequent orthogonal experiments, 1 mL of 1% peptide is added accordingly. Labeled as Solution B.
[0020] 3. Vitamin C solution preparation: Boil deionized water to remove air bubbles, cover with plastic wrap, and use to prepare the solution after cooling. Take 1g of vitamin C, add boiled and cooled deionized water, and prepare a 0.1g / mL vitamin C solution. Record it as solution C.
[0021] 4. Preparation of mixed solution: Dissolve 0.3g ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] 1. Preparation of chitosan matrix: Add 5g of chitosan into 80mL of 2% acetic acid solution, use a stirrer to swell evenly at a speed of 500r / min, after completely dissolving, test the pH value, use 1mol / L NaOH adjusts the pH of the solution to 4.5-5, records the amount of NaOH added to the solution, and stores it in the dark. Record it as solution A.
[0025] 2. Preparation of antimicrobial peptide solution: Dissolve 5 mg of antimicrobial peptide in 18 mL of aqueous solution and configure it into a 5 mg / 18 mL aqueous solution. In subsequent orthogonal experiments, 1 mL of 1% peptide is added accordingly. Labeled as Solution B.
[0026] 3. Vitamin C solution preparation: Boil deionized water to remove air bubbles, cover with plastic wrap, and use to prepare the solution after cooling. Take 1g of vitamin C, add boiled and cooled deionized water, and prepare a 0.1g / mL vitamin C solution. Record it as solution C.
[0027] 4. Preparation of mixed solution: Dissolve 0.3g ...
Embodiment 3
[0030] 1. Preparation of chitosan matrix: Add 5g of chitosan into 80mL of 2% acetic acid solution, use a stirrer to swell evenly at a speed of 500r / min, after completely dissolving, test the pH value, use 1mol / L NaOH adjusts the pH of the solution to 4.5-5, records the amount of NaOH added to the solution, and stores it in the dark. Record it as solution A.
[0031] 2. Preparation of antimicrobial peptide solution: Dissolve 5 mg of antimicrobial peptide in 18 mL of aqueous solution and configure it into a 5 mg / 18 mL aqueous solution. In subsequent orthogonal experiments, 1 mL of 1% peptide is added accordingly. Labeled as Solution B.
[0032] 3. Vitamin C solution preparation: Boil deionized water to remove air bubbles, cover with plastic wrap, and use to prepare the solution after cooling. Take 1g of vitamin C, add boiled and cooled deionized water, and prepare a 0.1g / mL vitamin C solution. Record it as solution C.
[0033] 4. Preparation of mixed solution: Dissolve 0.3g ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com