Linear voltage regulator circuit
A linear regulator and circuit technology, applied in instruments, regulating electrical variables, control/regulating systems, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the area of the linear regulator circuit chip
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] like figure 2 As shown, the linear voltage regulator circuit includes an operational amplifier AMP, a driving PMOS transistor Pm0, a zeroth voltage dividing resistor R0, a first voltage dividing resistor R1, a switch PMOS transistor Psw, a first current source I1, and a second current source I2;
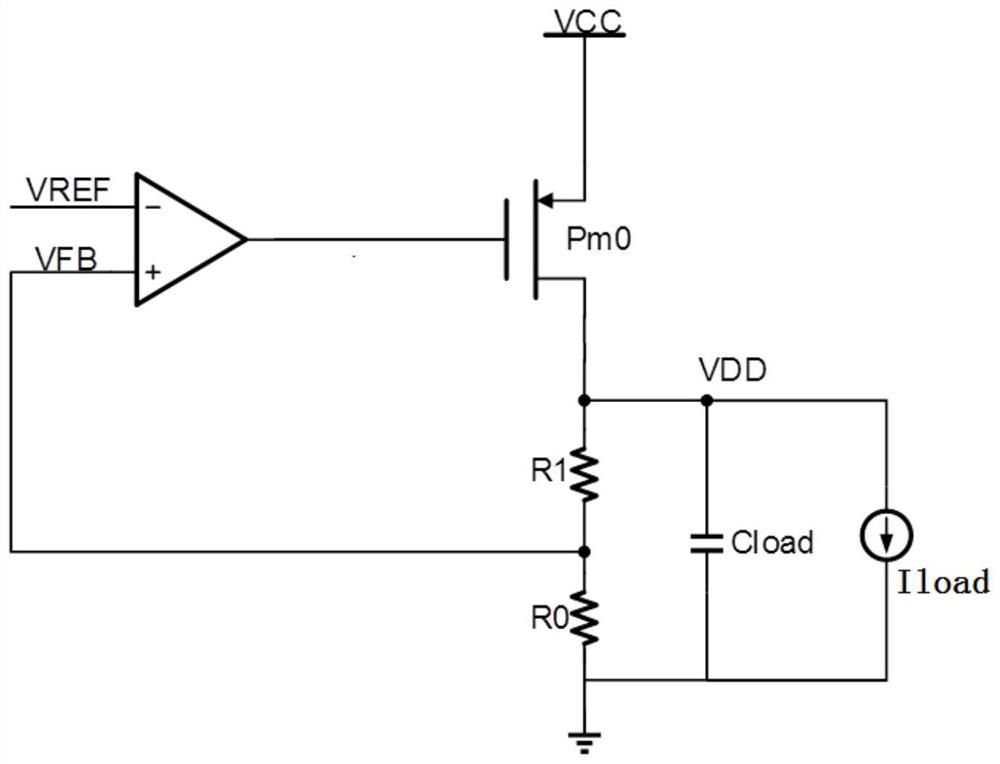
[0043] The drive PMOS transistor Pm0 has its source terminal connected to the input voltage VCC, its drain terminal connected to the ground through the zero voltage dividing resistor R0 and the first voltage dividing resistor R1 connected in series, and its drain terminal is used as the output voltage VDD of the linear voltage regulator circuit output terminal;
[0044] The source end and the drain end of the switch PMOS transistor Psw are respectively connected to the output end of the operational amplifier AMP and the gate end of the driving PMOS transistor Pm0, and the gate end is grounded;
[0045] The negative input terminal of the operational amplifier AMP is connected...
Embodiment 2
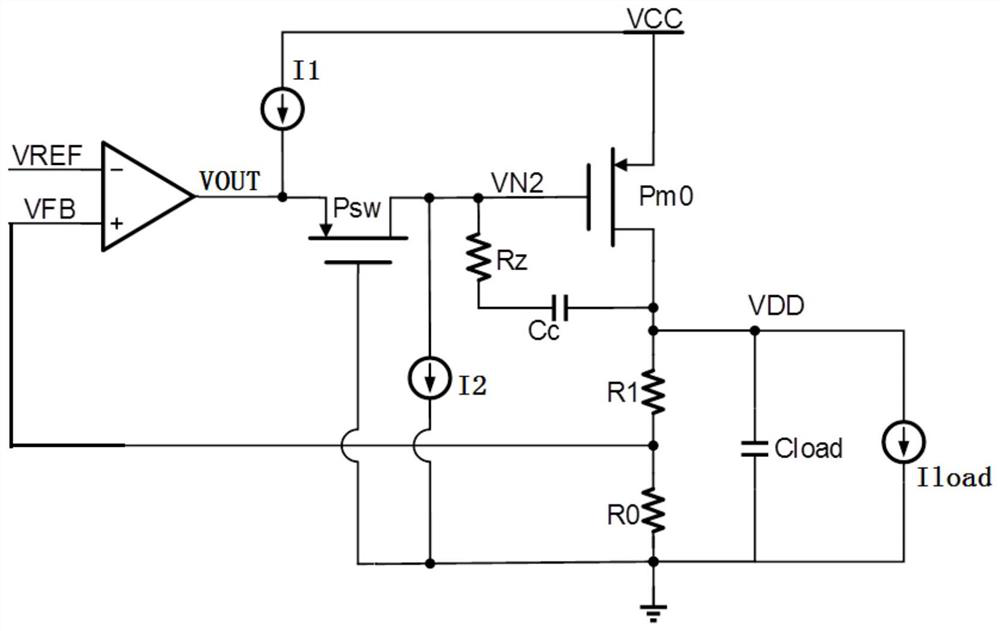
[0052] Based on implementation one, the linear voltage regulator circuit further includes a loop compensation resistor Rz and a loop compensation capacitor Cc;
[0053] The loop compensation resistor Rz and the loop compensation capacitor Cc are connected in series between the gate and drain of the driving PMOS transistor Pm0.
[0054] Preferably, the loop compensation resistor Rz is 100kΩ-200kΩ;
[0055] The loop compensation capacitor Cc is 1PF-10PF.
[0056] Preferably, the reference voltage VREF is provided by a bandgap reference (Bandgap voltage reference) circuit.
[0057] Preferably, a load capacitor Cload is connected between the drain terminal of the driving PMOS transistor Pm0 and the ground.
Embodiment 3
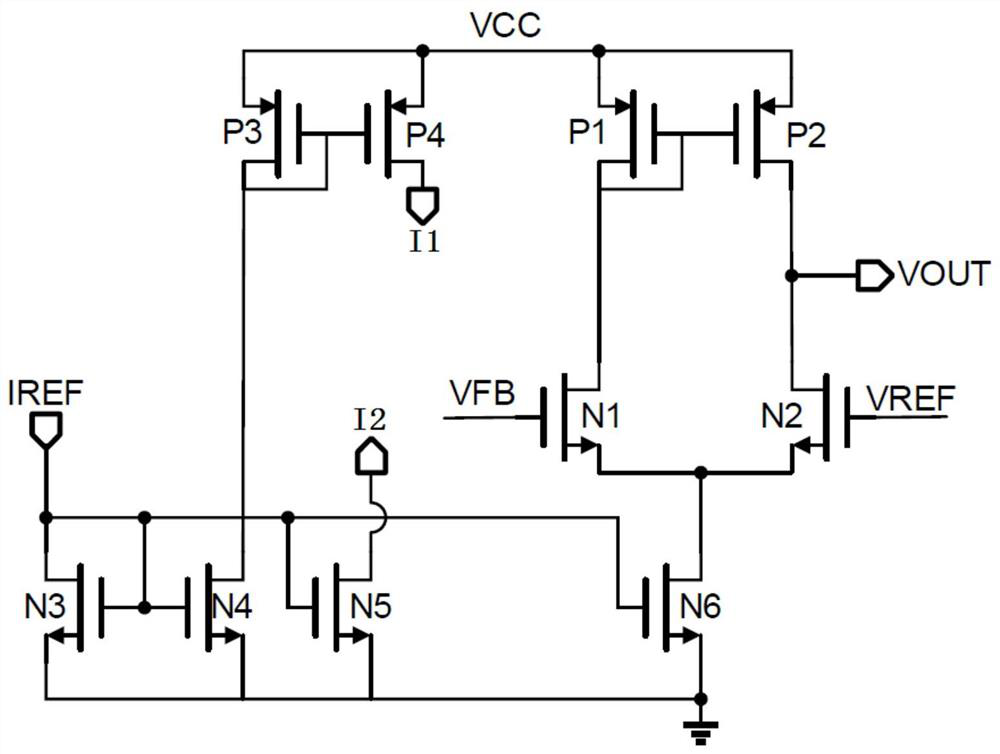
[0059] Based on the implementation of a linear regulator circuit such as image 3 As shown, the operational amplifier AMP, the first current source I1 and the second current source I2 form an operational amplifier circuit;
[0060] The operational amplifier circuit includes a first PMOS transistor P1, a second PMOS transistor P2, a third PMOS transistor P3, a fourth PMOS transistor P4, a first NMOS transistor N1, a second NMOS transistor N2, a third NMOS transistor N3, a fourth NMOS transistor N4, fifth NMOS transistor N5 and sixth NMOS transistor N6;
[0061] The gate terminal and the drain terminal of the first PMOS transistor P1 are short-circuited with the gate terminal of the second PMOS transistor P2;
[0062] The drain end of the first PMOS transistor P1 is connected to the drain end of the first NMOS transistor N1;
[0063] The drain end of the second PMOS transistor P2 is connected to the drain end of the second NMOS transistor N2, and serves as the output end of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com