Tin plating bath and a method for depositing tin or tin alloy onto a surface of a substrate
A technology for electroplating baths and tin alloys, applied in circuits, electrical components, electrical solid devices, etc., can solve problems such as difficult control of electroplating results, and achieve the effect of high electroplating rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0106] Unless specified differently below, the products were used as described (concentrations, parameters, other derivatives) in the corresponding technical data sheets (as available on the filing date). Practical applications usually require a plating rate of at least 2 μm / h.
[0107] Determining the thickness of metal or metal alloy deposits : The deposit thickness was measured at 10 positions on each substrate and used to determine the layer thickness by XRF using the XRF instrument Fischerscope XDV-SDD (Helmut Fischer GmbH, Germany). Layer thicknesses can be calculated from such XRF data by assuming a layered structure of the deposit. Alternatively, the thickness of the deposit was measured with a quartz crystal microbalance (SRS QCM200, Stanford Research Systems, Inc.) according to the frequency variation in the quartz crystal.
[0108] Measurement of Plating Rate : The plating rate is obtained by dividing the thickness of the tin deposit by the time required to obt...
example 1
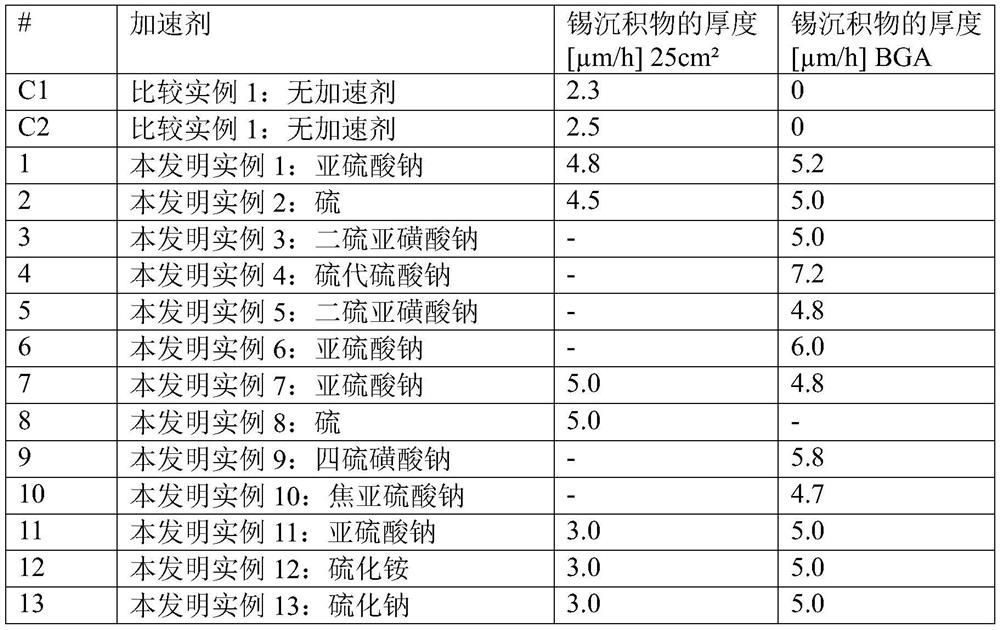
[0110] Invention example 1: Sodium sulfite as accelerator in electroless tin plating bath
[0111] In a beaker, 660.66 g of potassium pyrophosphate was dissolved in deionized water and 220 g of titanium(III) chloride was added to the solution and dissolved while stirring the solution. The volume of the resulting solution was adjusted to 1000 mL with deionized water.
[0112] The resulting solution was stirred at 60 °C for two to three hours until a dark blue solution with precipitate formed. The solution was filtered (10 μm) and the titanium concentration was determined via titration. The titanium concentration should generally be in the range of 190 to 215 mM. The resulting solution has a pH of about 7.8 to 8.3.
[0113] The solution described above is used to prepare the tin electroplating bath of the present invention, which comprises the following components:
[0114] c(Sn 2+ )=60mmol / L
[0115] c(Ti 3+ )=60mmol / L
[0116] c (pyrophosphate) = 700mmol / L
[0117] ...
example 2
[0124] Inventive Example 2: Sulfur as Accelerator in Electroless Tin Plating Baths
[0125] The method described for Inventive Example 1 was repeated, but sodium sulfite was replaced with 1 ppm sulfur nanoparticles and the aerodynamic diameter measured by an aerodynamic particle size analyzer (APS) was below 100. The results are summarized in Table I.
[0126] The tin electroplating bath was stable and exhibited no precipitation or precipitation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com