Microelectronic packaging structure based on TSV technology
A technology of microelectronic packaging and technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, electrical solid devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor reliability, reduced yield of packaged products, warping of adapter boards, etc., to reduce volume and size. reduced effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
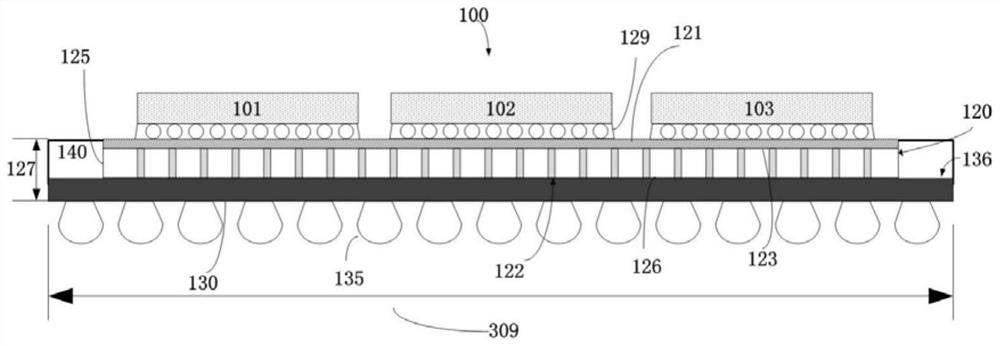
[0074] figure 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a microelectronic package 100 arranged in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. Microelectronic package 100 includes IC (Integrated Circuit) chips 101 , 102 and 103 , interposer 120 , package substrate 130 and molded stiffener 140 . The microelectronic package 100 electrically and mechanically connects the components therein, including the IC chips 101, 102 and 103 and any other logic or memory IC chips mounted on the interposer board 120, and the PCB (printed circuit board) or other substrates (not shown) external to the microelectronic package 100 . In addition, microelectronic package 100 protects IC chips 101, 102, and 103 from environmental moisture and other contamination, and minimizes mechanical shock and stress thereon. For clarity, figure 2 Some components of the IC system 100 are omitted, such as some overmolding materials used to package the IC chips 101, 102 and 103, heat sinks, and the l...
Embodiment 2
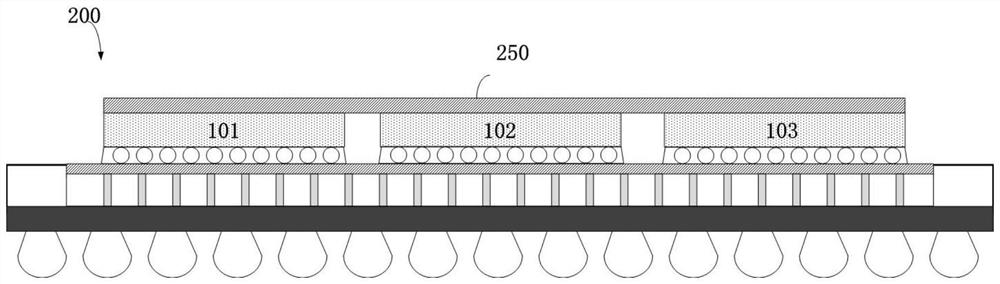
[0083] figure 2 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a microelectronic package 200 arranged in accordance with one embodiment of the invention. Microelectronic package 200 also includes heat sink 250, and microelectronic package 200 is structurally and operationally identical to figure 1 The microelectronic package 100 in is substantially similar. The heat sink 250 of the microelectronic package 200 is thermally coupled to the IC chips 101 , 102 and 103 to reduce heat generated by signal transmission between the IC chips 101 , 102 and 103 . In some embodiments, heat spreader 250 is formed from a single piece of metal with relatively high thermal conductivity, such as a stamped copper or aluminum plate. Suitable materials for making heat sink 250 include copper, aluminum, or some other metal with a thermal conductivity at least equal to that of aluminum, ie, at least about 230 Wm-1K-1.
Embodiment 3
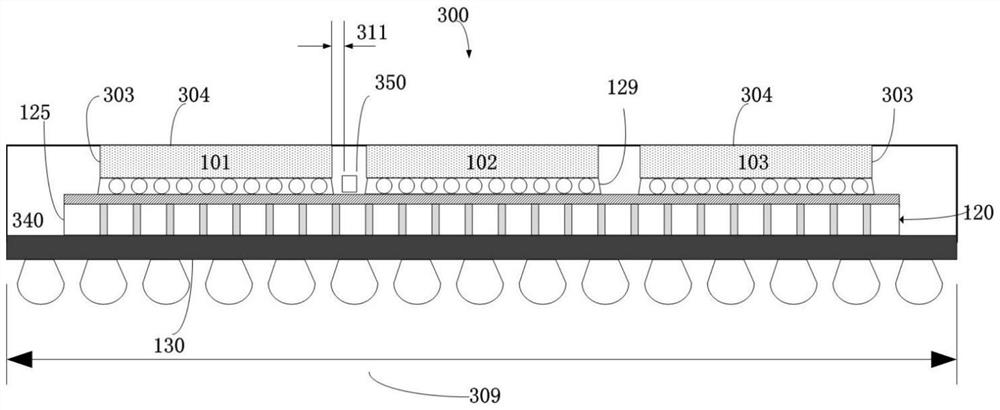
[0085] image 3 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a microelectronic package 300 arranged in accordance with one embodiment of the invention. In the microelectronic package 300, the molded stiffener 340 is configured to contact the edge surface 125 of the interposer 120, one or more surfaces of the IC chips 101, 102 and 103, and in addition the microelectronic package 300 is structurally composed and operationally with figure 1 The microelectronic package 100 in is substantially similar. In such an embodiment, a molded reinforcement plate 340 replaces the underfill material 129 . For reference, the location of underfill material 129 is at image 3 shown in . In addition, the molded stiffener 340 may also contact the edge surfaces 303 of the IC chips 101 , 102 . exist image 3 In the illustrated embodiment, molded stiffener 340 is in contact with all surfaces 303 except upper surfaces 304 of IC chips 101 , 102 and 103 .
[0086]Using molded stiffener 340 in place of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com