Tissue specific promoter and application thereof
A tissue-specific, promoter technology, applied in applications, tissue culture, specific peptides, etc., can solve the problems of low transfection efficiency of F8 virus vector, production of antibodies and inhibitor reactions, low protein secretion and function, etc., to reduce immunity. Risk of rejection, efficacy of protection, effect of low antibody response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] In this embodiment, a lentiviral vector is constructed, which carries the specific promoter of the present invention and the F8 gene, and specifically includes the following steps:
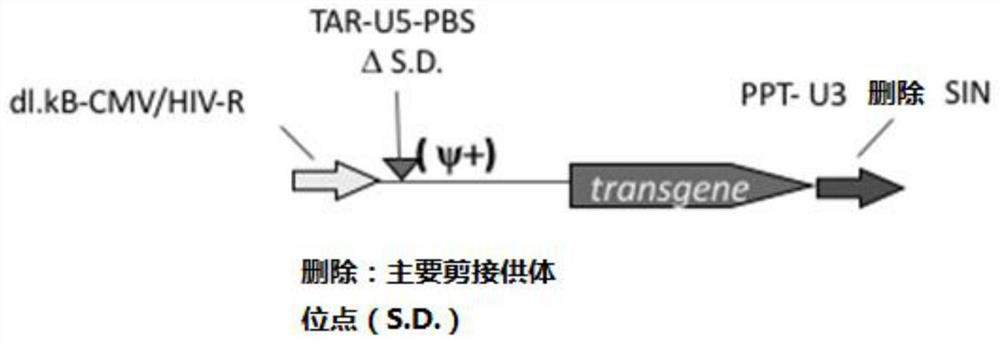
[0063] (1) Schematic diagram of the structure of the lentiviral vector pEGWI as shown in figure 1 As shown, the wild-type 5' splice donor site was mutated, the enhancer in U3 was deleted, and the silencer (CH4 silencer) was added in U3. For the specific transformation method, please refer to "Contributions of Viral Splice Sites and cis-Regulatory Elements toLentivirus Vector Function, Cui et al. Journal of Virology, July 1999, p.6171–6176”;
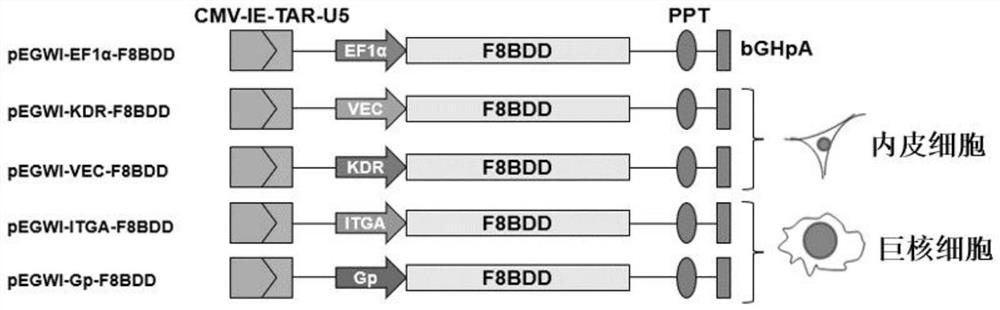
[0064] (2) Insertion of different tissue-specific promoters and the F8-BDD gene:
[0065] Whole-gene synthesis of Wasabi gene sequence (expressing fluorescent protein), F8 gene (F8-BDD) sequence (SEQ ID NO:5) with B domain deletion, and tissue-specific promoters EF1α (SEQ ID NO:6), VEC (SEQ ID NO:1), KDR (SEQ ID NO:2), ITGA (SEQ ID NO:3) and the nucl...
Embodiment 2
[0069] In this example, the lentiviral vector constructed in Example 1 was further packaged, purified, and concentrated to obtain a recombinant lentivirus. For the experimental method, refer to ([1] Chang L J, Urlacher V, Iwakuma T, et al. Efficacy and safety analyzes of a recombinant human immunodeficiency virus type 1derived vectorsystem[J].Gene Therapy,1999,6(5):715-728.[2]Chang L J,Zaiss A K.Chang,LJ and Zaiss,AK.Lentiviral vectors.Preparation and use.Methods Mol Med 69:303-318[J].Methods in molecular medicine,2002,69:303-318.)
[0070] For specific steps, please refer to the above documents, and a brief description is as follows:
[0071] (1) The lentiviral vector constructed in Example 1 and the packaging helper plasmid pNHP and pHEF-VSV-G were co-transfected into mammalian cells HEK293T and cultured for 48 hours, and the supernatant viral vector was collected;
[0072] (2) Purify and concentrate the lentivirus obtained from the cultivation to obtain the recombinant len...
Embodiment 3
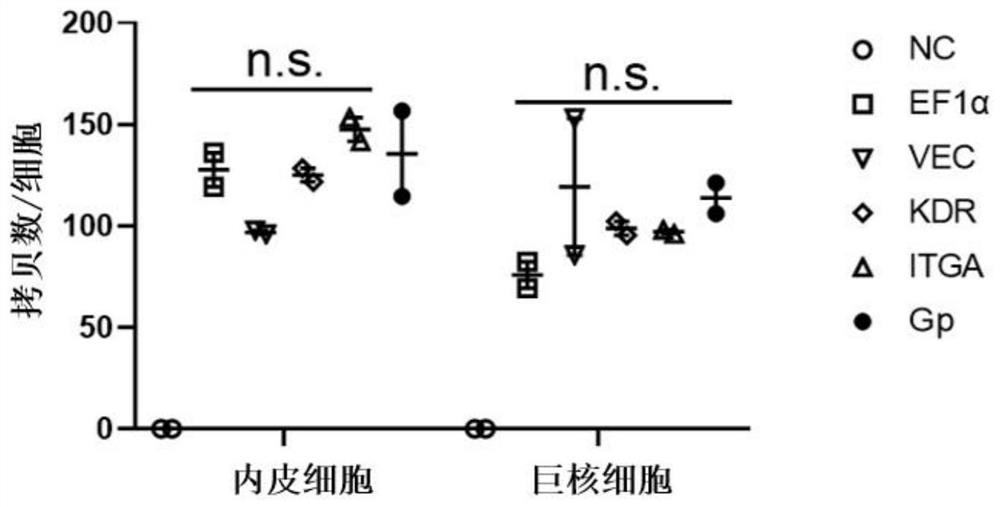
[0075] In this example, the recombinant lentivirus containing different promoters and Wasabi gene prepared in Example 2 was used for in vitro testing, and the specificity of the promoter in different cells was detected by detecting the amount of fluorescent protein expressed by the Wasabi gene.
[0076] The five lentiviruses (LV-EF1α-Wasabi, LV-VEC-Wasabi, LV-KDR-Wasabi, LV-ITGA-Wasabi and LV-Gp-Wasabi) prepared in Example 2 carrying the normal Wasabi gene were respectively transfected into the endothelium Cell (EC), megakaryocyte (Megakaryocyte) two cell lines, lentiviral transfection method is:
[0077] DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin solution was added to a six-well plate (Corning, USA), and 3 × 10 4 endothelial cells, or 1×10 5 megakaryocytes at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured under conditions for 18 h, transfected with lentivirus at MOI=200, and supplemented polybrene (Polybrene, 8 μg / mL, Sigma-Aldrich) to a final medium volume of 600...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com