Esophageal cancer detection reagent and application thereof in esophageal cancer detection
A detection reagent and technology for esophageal cancer, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as low repeatability, high sensitivity, and complicated equipment operation, and achieve high specificity, accuracy, simple operation, and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
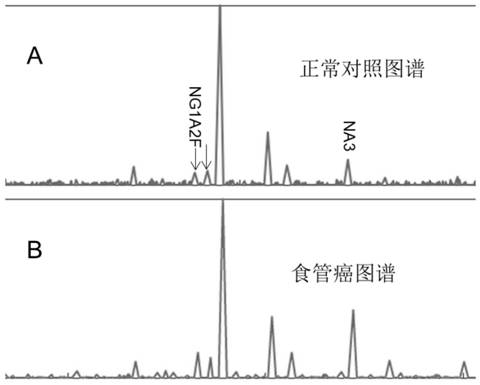
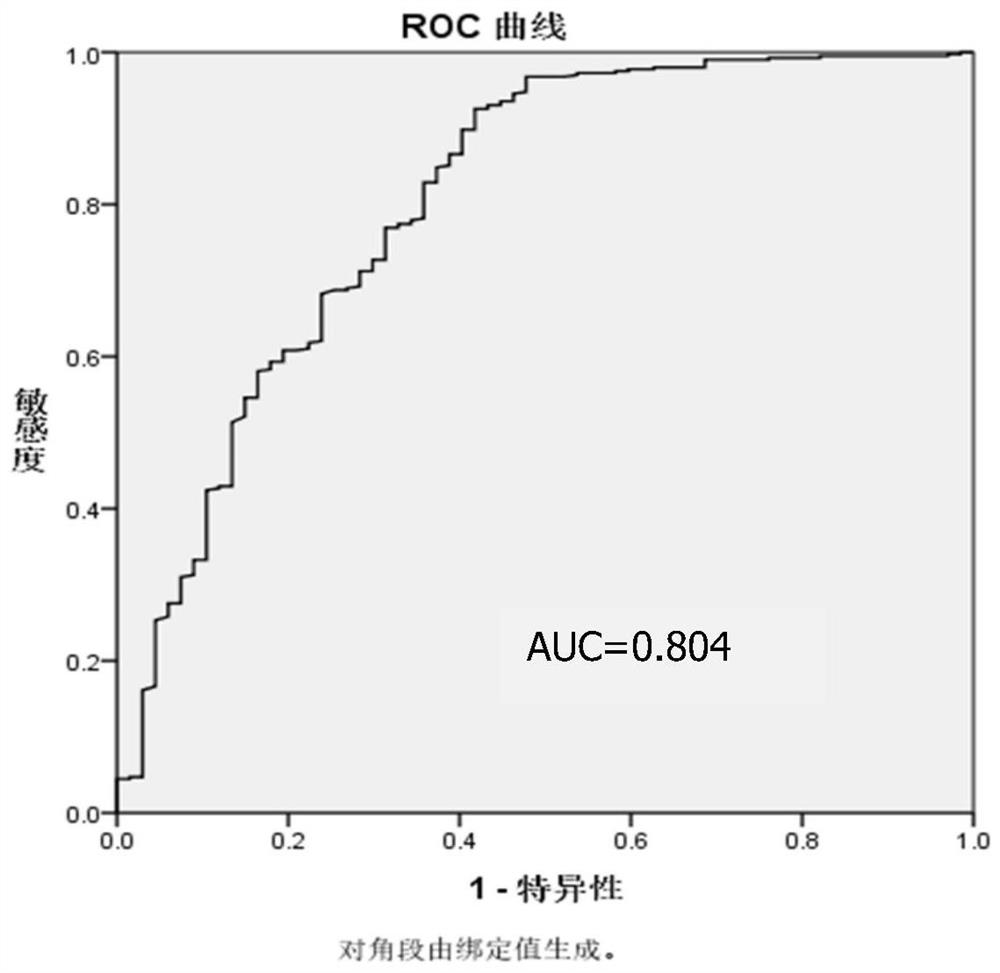
[0049] Example 1 Detection of Esophageal Cancer
[0050] Statistical analysis was carried out by measuring the G-Test specific fingerprint of serum glycoprotein oligosaccharide chains, and the materials and methods used:
[0051] 1. Test samples: Sera from patients with esophageal cancer and normal controls were collected.
[0052] 2. Experimental equipment: sugar group analyzer, PCR, centrifuge.
[0053] 3. Reagent preparation:
[0054] Reagent A: prepared by adding SDS with a mass concentration of 0.5 to 5% in ammonium bicarbonate solution with a concentration of 10 mM;
[0055] Reagent B: It is prepared by mixing 0.01~10U / 10μL glucosamidase and 0.01~10U / 10μL sialidase, and the pH value of the mixed solution is 4~9;
[0056] Reagent C: Prepared by dissolving 8-aminopyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid in DMSO, the concentration is 0.01mM~1M;
[0057] Reagent D: stop solution.
[0058] 4. Glycosequencing detection steps:
[0059] Step 1 Preparation of oligosaccharide chains
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com