Fiber chelating type monoammonium phosphate and preparation method thereof
A monoammonium phosphate, chelating technology, applied in the field of phosphate fertilizers, can solve the problem of phosphorus being easily fixed by soil and utilization, and achieve the effects of reducing fixation, solving agglomeration and improving utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
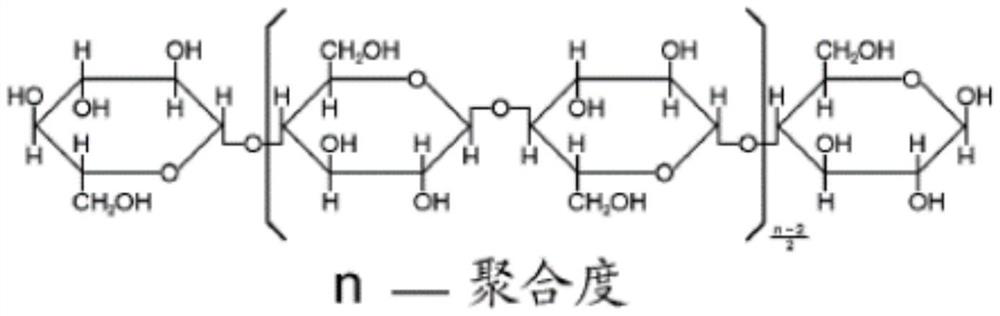
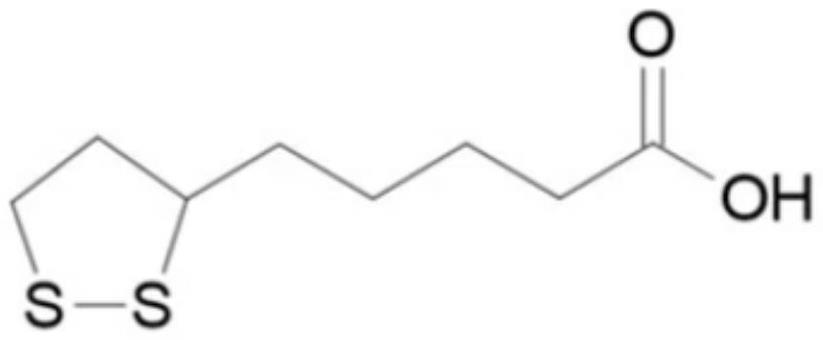
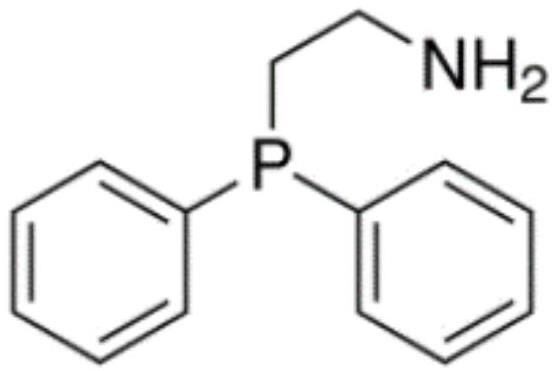
[0046] A kind of fiber chelating type monoammonium phosphate, comprises the monoammonium phosphate and chelating type cellulose fiber that mass ratio is 18:1; Wherein, chelating type cellulose fiber is after the cellulose fiber is first acidified with lipoic acid, and then It is obtained after condensation reaction with 2-(diphenylphosphino)ethylamine. The available phosphorus content of monoammonium phosphate is not less than 60%, and the total nitrogen content is not less than 12%.
[0047] Cellulose fiber is cellulose obtained by using agricultural waste materials after being treated with inorganic acids. The inorganic acids include at least one of hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid, and oxalic acid. Agricultural waste materials include rice waste after oil extraction, rice husk, At least one of corncobs and wheat husks.
[0048] The preparation method of chelating type cellulose fiber is:
[0049] S1. Weigh the cellulose fiber and mix it with a sodiu...
Embodiment 2
[0057] A kind of fiber chelating type monoammonium phosphate, comprising the monoammonium phosphate and chelating type cellulose fiber that mass ratio is 15:1; It is obtained after condensation reaction with 2-(diphenylphosphino)ethylamine. The available phosphorus content of monoammonium phosphate is not less than 60%, and the total nitrogen content is not less than 12%.
[0058] Cellulose fiber is cellulose obtained by using agricultural waste materials after being treated with inorganic acids. The inorganic acids include at least one of hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid, and oxalic acid. Agricultural waste materials include rice waste after oil extraction, rice husk, At least one of corncobs and wheat husks.
[0059] The preparation method of chelating type cellulose fiber is:
[0060] S1. Weigh the cellulose fibers and mix them with sodium hydroxide solution or potassium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 0.01mol / L. After dispersing evenly...
Embodiment 3
[0068] A kind of fiber chelating type monoammonium phosphate, comprises the monoammonium phosphate and chelating type cellulose fiber that mass ratio is 20:1; Wherein, chelating type cellulose fiber is after the cellulose fiber is first acidified with lipoic acid, and then It is obtained after condensation reaction with 2-(diphenylphosphino)ethylamine. The available phosphorus content of monoammonium phosphate is not less than 60%, and the total nitrogen content is not less than 12%.
[0069] Cellulose fiber is cellulose obtained by using agricultural waste materials after being treated with inorganic acids. The inorganic acids include at least one of hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, citric acid, and oxalic acid. Agricultural waste materials include rice waste after oil extraction, rice husk, At least one of corncobs and wheat husks.
[0070] The preparation method of chelating type cellulose fiber is:
[0071] S1. Weigh the cellulose fiber and mix it with 0.1mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com